UP Board Solutions for Class 11 Sociology Introducing Sociology Chapter 1 Sociology and Society (समाजशास्त्र एवं समाज)
These Solutions are part of UP Board Solutions for Class 11 Sociology. Here we have given UP Board Solutions for Class 11 Sociology Introducing Sociology Chapter 1 Sociology and Society (समाजशास्त्र एवं समाज).
पाठ्य-पुस्तक के प्रश्नोत्तर
प्रश्न 1.
समाजशास्त्र के उदगम और विकास का अध्ययन क्यों महत्त्वपूर्ण है?
उत्तर
समाजशास्त्र का उद्गम एवं विकास पश्चिमी यूरोप की सामाजिक परिस्थितियों की देन है। औद्योगिक क्रांति, फ्रांस की क्रांति तथा ज्ञानोदय की इसके विकास में महत्त्वपूर्ण भूमिका रही है। इनके परिणामस्वरूप न केवल पश्चिमी समाजों में एक नवीन आर्थिक क्रियाकलाप की पद्धति (जिसे पूँजीवाद कहा जाता है) विकसित हुई अपितु इनसे इन देशों की सामाजिक संरचना पर भी गहरा प्रभाव पड़ा। गाँव से शहरों की ओर प्रवर्जन, सामाजिक गतिशीलता, शिक्षा एवं रोजगार में वृद्धि, लौकिक दृष्टिकोण के विकास के साथ-साथ अनेक सामाजिक समस्याएँ भी विकसित होने लगीं। औद्योगिक मजदूरों एवं खेतिहर मजदूरों की संख्या में वृद्धि हुई तथा उत्पादन कार्यों में इनका शोषण होने लगा। पूँजीवाद की सेवा हेतु सत्रहवीं एवं उन्नीसवीं शताब्दी में बड़ी संख्या में अफ्रीकियों को दास बनाया गया। यद्यपि उन्नीसवीं शताब्दी के प्रारंभ में दास प्रथा कम होने लगी, तथापि अनेक उपनिवेशवादी देशों में यह बँधुआ मजदूरों के रूप में आज भी प्रचलित है।।
समाजशास्त्र के उद्गम और विकास के अध्ययन का महत्त्व
समाजशास्त्र के उद्गम और विकास के अध्ययन के महत्त्व को निम्नलिखित शीर्षकों के अंतर्गत स्पष्ट किया जा सकता है-
1. पारिभाषिक महत्त्व-समाजशास्त्र के अध्ययन से समाजशास्त्र के पारिभाषिक शब्दों, अध्ययन विषयों और धारणाओं का ठीक-ठीक परिचय प्राप्त हो जाता है। इन शब्दों का वैज्ञानिक अध्ययन समाज के स्वरूप को समझने में सहायक होता है। समाजशास्त्र में अनेक पारिभाषिक शब्द होते हैं, जिनको हम नित्यप्रति बोलचाल की भाषा में प्रयोग करते हैं। लेकिन समाजशास्त्र के अंतर्गत उन शब्दों का विशेष स्थान होता है, जिनको समझ लेने के पश्चात् अनेक प्रमों का निवारण हो जाता है। रीति-रिवाज, जाति, संस्था, समाज, संस्कृति, प्रजाति तथा समूह ऐसे ही अनेक शब्द हैं, परंतु समाजशास्त्र में इनका सामान्य अर्थ न होकर विशेष अर्थ होता है। समाजशास्त्र के अध्ययन से इन शब्दों का सही-सही ज्ञान प्राप्त होता है तथा इनमें हो रहे परिवर्तनों का भी ज्ञान हो जाता है।।

2. समाज का वैज्ञानिक ज्ञान–समाजशास्त्र के अध्ययन द्वारा समाज के विषय में वैज्ञानिक ज्ञान
प्राप्त होता है। समाजशास्त्र के अंतर्गत समाज संबंधी सभी बातों का अध्ययन किया जाता है। समाज क्या है? समाज का स्वरूप क्या है? समाज का विकास किस प्रकार हुआ है? सामाजिक परिवर्तन के क्या कारण हैं? आदि प्रश्नों का उत्तर समाजशास्त्र वैज्ञानिक ढंग से देता है। समाज के विषय में वैज्ञानिक ज्ञान होना समाज के लिए तथा इसे एक निश्चित दिशा प्रदान करने के लिए अनिवार्य है।
3. सामाजिक जीवन की समस्याओं का ज्ञान–समाजशास्त्र हमें सामाजिक जीवन की सामान्य समस्याओं की जानकारी प्रदान करता है। समाज की विभिन्न समस्याओं; जैसे-अपराध, किशोर अपराध, श्वेतवसन अपराध, जनसंख्या की समस्या, निर्धनता और बेकारी आदि का ज्ञान तथा इनके प्रचलन के कारणों का पता हमें समाजशास्त्र के अध्ययन द्वारा ही होता है। समाजशास्त्र के उद्गम और विकास ने सामाजिक समस्याओं को समझने तथा उनका समाधान खोजने में राजनीतिज्ञों, समाज-सुधारकों तथा नीति-निर्धारकों को सहायता प्रदान की है।
4. सांस्कृतिक लाभ-सांस्कृतिक विकास, सामाजिक विकास में विशेष सहायक होता है। सांस्कृतिक विकास के बिना समाज का विकास असम्भव है; अतः सामाजिक विकास के लिए यह आवश्यक है कि इसके अर्थों, स्वरूपों तथा क्रियाओं के नियमों को भली प्रकार समझा जाए। समाजशास्त्र संस्कृति के पूर्ण स्वरूप पर प्रकाश डालने का कार्य करता है। उसके अध्ययन से संस्कृति के महत्त्वपूर्ण तत्त्वों को सरलता से समझा जा सकता है। समाजशास्त्र के अध्ययन से ही हम समझते हैं कि संस्कृति क्या है, विभिन्न संस्कृतियाँ किस प्रकार समानता रखती हैं और उनमें क्या-क्या भिन्नताएँ हैं।।
5. पारिवारिक जीवन को सफल बनाने में सहायक–व्यक्ति और परिवार का अटूट संबंध है। व्यक्ति परिवार में जन्म लेता है और उसका लालन-पालन भी परिवार में ही होता है। इस प्रकार वह परिवार के अन्य सदस्यों से अनेक प्रकार से संबंधित होता है। प्रत्येक व्यक्ति का परिवार में अपना-अपना स्थान होता है और साथ-ही-साथ उसके अधिकार और कर्तव्य होते हैं। इन अधिकारों और कर्तव्यों के उचित संतुलन पर ही परिवार का सुख-दु:ख निर्भर करता है। समाजशास्त्र के अध्ययन द्वारा विभिन्न परिवारिक समस्याओं का ज्ञान होता है तथा संतुलन स्थापित करने में सहायता मिलती है।
6. सामाजिक परिस्थितियों से अनुकूलन में सहायक-समाजशास्त्र हमें समाज के स्वरूप की । विस्तृत जानकारी कराता है। इसके अध्ययन से हम सामाजिक वातावरण तथा विभिन्न सामाजिक परिस्थितियों को सरलता से समझ जाते हैं। समाजशास्त्र का अध्ययन व्यक्ति के दृष्टिकोण को अधिक व्यापक बना देता है। वर्तमान युग औद्योगिक युग है। औद्योगीकरण और यंत्रीकरण के कारण सामाजिक जीवन अत्यधिक जटिल हो गया है और प्रतिदिन नवीन परिवर्तन दृष्टिगोचर हो रहे हैं। समाजशास्त्र द्वारा इन जटिलताओं और परिवर्तनों का ज्ञान होता है, जिससे सामाजिक परिस्थितियों से अनुकूलन करने में बड़ी सहायता मिलती है।
7. अंतर्राष्ट्रीय जीवन को सुखद बनाने में सहायक-समाजशास्त्र के अध्ययन से केवल अपने समाज का ही ज्ञान नहीं होता वरन् विश्व समाज को भी ज्ञान प्राप्त होता है। समाजशास्त्र विश्व के विभिन्न भागों में निवास करने वाले व्यक्तियों की जीवन-शैली और रहन-सहन के ढंगों को भी ज्ञान प्रदान करता है। आज यातायात के साधनों तथा संचार साधनों की अपूर्व प्रगति ने हमारे जीवन को अंतर्राष्ट्रीय बना दिया है। ऐसी दशा में समाजशास्त्र का अध्ययन अत्यंत रोचक एवं लाभकारी सिद्ध होता है। समाजशास्त्र के अध्ययन से जब हम दूसरे समाजों के विभिन्न पक्षों का अध्ययन करते हैं तो विश्व के अन्य निवासियों के रीति-रिवाजों, परम्पराओं और प्रवृत्तियों में होने वाले संघर्ष के कारण हमें ज्ञात हो जाते हैं। इन्हें समझकर संघर्ष के स्थान पर सहानुभूति, सहिष्णुता और उदारता की भावनाओं का प्रसार हो सकता है। इस प्रकार अंतर्राष्ट्रीय जीवन को
सुखद बनाने तथा अंतर्राष्ट्रीय संघर्ष को समझने में समाजशास्त्र विशेष रूप से सहायक होता है।

प्रश्न 2.
‘समाज’ शब्द के विभिन्न पक्षों की चर्चा कीजिए। यह आपके सामान्य बौद्धिक ज्ञान की समझ से किस प्रकार अलग है?
उत्तर
सामान्य रूप से ‘समाज’ शब्द से प्रत्येक व्यक्ति परिचित है। ऐसा कहा जाता है कि जहाँ जीवन है वहीं समाज भी है। ‘समाज’ एक अत्यधिक प्रचलित शब्द है जिसको साधारण बोलचाल की भाषा में व्यक्तियों के समूह के लिए प्रयुक्त किया जाता है। उदाहरण के लिए–‘आर्य समाज’, ब्रह्म समाज’, ‘धर्म समाज’, ‘विद्यार्थी समाज’ तथा ‘बाल समाज’, आदि शब्दों का प्रयोग व्यक्ति इसी अर्थ में करते हैं। कुछ लोग ‘समाज’ शब्द का प्रयोग व्यक्तियों के समूह के रूप में अथवा एक समिति या संस्था के रूप में भी करते हैं। इसी कारण समाज के अर्थ के संबंध में काफी अनिश्चितता पायी जाती है। समाजशास्त्र में समाज’ शब्द का प्रयोग जनसाधारण द्वारा लगाए गए इन अर्थों में नहीं होता, वरन् यह एक विशिष्ट अर्थ को प्रतिपादित करता है। समाजशास्त्र एक विज्ञान है तथा विज्ञान होने के नाते इसकी अपनी एक शब्दावली है। वैज्ञानिक शब्दावली में प्रत्येक शब्द को विशिष्ट अर्थ में प्रयोग किया जाता है। ‘समाज’ भी इसी प्रकार का एक शब्द (संकल्पना या अवधारणा) है, जिसका संबंध समाजशास्त्र की शब्दावली से है। इस नाते न केवल इसका स्पष्ट अर्थ है, अपितु इसके विभिन्न पक्षों के बारे में भी किसी प्रकार का संदेह नहीं है।
मैकाइवर एवं पेज (Maclver and Page) के अनुसार-“समाज रीतियों एवं कार्य-प्रणालियों, प्रभुत्व एवं पारस्परिक सहयोग, अनेक समूहों और उनके विभाजनों, मानव-व्यवहार के नियंत्रणों एवं स्वाधीनताओं की एक व्यवस्था है। इस निरंतर परिवर्तनशील जटिल व्यवस्था को हम समाज कहते हैं। यह सामाजिक संबंधों का जाल (Web of social relationships) है और यह सदैव परिवर्तित होता रहता है। समाज की यह परिभाषा समाज के विभिन्न पक्षों को पूर्णतः स्पष्ट करने वाली मानी जाती है। समाज मूर्त न होकर अमूर्त होता है। यह कोई अखंडित व्यवस्था नहीं है अपितु इसमें अनेक समूह एवं उप-समूह पाए जाते हैं। व्यक्तियों के व्यवहार हेतु निश्चित रीतियाँ एवं कार्य-प्रणालियाँ होती हैं जिन्हें संस्थाएँ कहा जा सकता है। संस्थाएँ व्यक्ति को समाज की मान्यताओं के अनुरूप व्यवहार करने हेतु प्रेरित करती हैं। व्यक्ति को स्वतंत्रता तो होती है परंतु वह अन्य व्यक्तियों से व्यवहार हेतु समाज द्वारा मान्य रीतियों में से ही किसी एक का चयन कर सकता है। विभिन्न व्यक्तियों में जो संबंध पाए जाते हैं उन्हीं को समाज कहते हैं। संबंध स्थिर नहीं रहते अपितु निरंतर परिवर्तित होते रहते हैं। इस प्रकार, समाज के विभिन्न पक्ष मिलकर एक जटिल व्यवस्था का निर्माण करते हैं।
समाज के क्रमबद्ध ज्ञान एवं सामान्य बौद्धिक ज्ञान में अंतर
समाजशास्त्र में समाज का क्रमबद्ध (विधिवत्) अध्ययन किया जाता है। यह अध्ययन एक विशिष्ट दृष्टिकोण या चिंतन द्वारा किया जाता है, जिसे समाजशास्त्रीय चिंतन कहते हैं। यह चिंतन सामान्य बौद्धिक ज्ञान से भिन्न होता है। सामान्य बौद्धिक ज्ञाने में दार्शनिक एवं धार्मिक अनुचिंतन सम्मिलित किया जाता है। उदाहरणार्थ-हम अपने दैनिक जीवन में बहुत-सी बातों एवं घटनाओं को देखते हैं परंतु उनके बारे में वैज्ञानिक चिंतन नहीं करते अर्थात् उनका क्रमबद्ध वर्णन करने का प्रयास नहीं करते। यदि हम किसी भिखारी को किसी चौराहे या सार्वजनिक स्थल पर भीख माँगते हुए देखते हैं तो सामान्य बौद्धिक ज्ञान से यह सोच लेते हैं कि वह शायद गरीब है इसलिए भीख माँग रहा है। यदि इसी को हम समाजशास्त्रीय दृष्टिकोण से देखें तो हमारा चिंतन पूर्णतया अलग होगा। हमारी सोच के प्रमुख बिंदु इस प्रकार होंगे—क्या सभी गरीब भिक्षा माँगने पर विवश होते हैं? यदि नहीं तो, केवल कुछ व्यक्ति ही भिक्षावृत्ति क्यों करते हैं? भिक्षावृत्ति एक राष्ट्रीय समस्या क्यों है? गरीबी के अतिरिक्त भिक्षावृत्ति के क्या कारण हैं? क्या इस समस्या के कारणों का पता लगाकर इसका निराकरण करना संभव है? भिक्षावृत्ति जनहित का मुद्दा क्यों हैं? सरकार भिक्षावृत्ति के निवारण के लिए क्या प्रयास कर रही है?
समाज का क्रमबद्ध चिंतन व्यक्तियों में जिस दृष्टिकोण को विकसित करता है उसी को समाजशास्त्रीय दृष्टिकोण या चिंतन कहते हैं। यह चिंतन हमें भिक्षावृत्ति के इतिहास, भिखारियों की जीवन दशाओं, उनके सामाजिक-आर्थिक कारणों तथा इस समस्या के समाधान की खोज करने की उत्सुकता से भर देता है। समाज का क्रमबद्ध अध्ययन रोजमर्रा के सामान्य प्रेक्षण से भी भिन्न है। रोजमर्रा की घटनाएँ व्यक्तियों में समाजशास्त्रीय सोच विकसित नहीं करतीं। हम बहुत-सी घटनाओं को देखकर भी अनदेखा कर देते हैं। उदाहरणार्थ-अपने पड़ोस में एक कामकाजी महिला को अपने पति, सास-ससुर या अन्य सदस्य से झगड़ते हुए देखकर हम सोच लेते हैं कि अमुक महिला ही ऐसी है। यदि इसी को हम समाजशास्त्रीय चिंतन की दृष्टि से देखें तो हमारे सामने कामकाजी महिलाओं से संबंधित अनेक मुद्दे सामने आ जाएँगे। कामकाजी महिलाएँ ही ऐसा क्यों करती हैं? क्या बिना कामकाजी महिलाओं वाले परिवारों में भी ऐसा होता है? क्या आस-पड़ोस में कोई ऐसा परिवार भी है जिसमें कामकाजी महिला को अपने परिवार के सदस्यों से किसी प्रकार का मतभेद नहीं है तथा सभी सदस्य उसके पारिवारिक दायित्वों को पूरा करने में सहयोग देते हैं?
समाज के क्रमबद्ध ज्ञान एवं सामान्य बौद्धिक ज्ञान में अंतर को सामने रखते हुए ही टी० बी० बॉटोमोर ने इस तथ्य पर बल दिया है कि व्यक्ति हजारों वर्षों से समाज में रह रहे हैं, परंतु समाजशास्त्र एक नवीन विषय है। स्पष्ट है कि समाज में रहना तथा समाज में हो रही घटनाओं का सामान्य चिंतन या प्रेक्षण समाजशास्त्र नहीं है।

प्रश्न 3.
चर्चा कीजिए कि आजकल अलग-अलग विषयों में परस्पर लेन-देन कितना ज्यादा है।
उत्तर
मानव द्वारा अर्जित ज्ञान को मुख्य रूप से दो प्रमुख भागों में विभाजित किया जा सकता है—प्राकृतिक विज्ञान तथा सामाजिक विज्ञान। प्राकृतिक विज्ञानों के अंतर्गत भौतिकशास्त्र, रसायनशास्त्र, जीवविज्ञान, वनस्पतिविज्ञान आदि आते हैं। सामाजिक विज्ञानों के अंतर्गत राजनीतिशास्त्र, अर्थशास्त्र, मनोविज्ञान, दर्शनशास्त्र, मानवशास्त्र तथा समाजशास्त्र आदि विषय आते हैं। समाजशास्त्र यद्यपि प्राकृतिक विज्ञानों से पर्याप्त भिन्न है परंतु उसका राजनीतिशास्त्र, इतिहास, अर्थशास्त्र आदि विभिन्न सामाजिक विज्ञानों से घनिष्ट संबंध है।
समाजशास्त्र में प्रायः उन्हीं तथ्यों और विषयों का अध्ययन किया जाता है जिनका कि सामान्यतः अन्य सामाजिक विज्ञान भी अध्ययन करते हैं; परंतु इसके दृष्टिकोण में भिन्नता पाई जाती है। अन्य सामाजिक विज्ञानों का क्षेत्र पर्याप्त सीमित है, जबकि समाजशास्त्र का क्षेत्र व्यापक और विस्तृत है क्योंकि अन्य शास्त्र जीवन के एक विशिष्ट पहलू (राजनीतिक, ऐतिहासिक या आर्थिक) का ही विवेचन करते हैं, जबकि समाजशास्त्र उन सबका समन्वय करके संपूर्ण समाज एवं जीवन का अध्ययन करता है। आजकल अलग-अलग सामाजिक विज्ञानों में अत्यधिक सहयोग पाया जाता है। मानव के सामाजिक व्यवहार को समझने हेतु यह सहयोग आवश्यक भी है। विभिन्न विषयों में पाए जाने वाले सहयोग के परिणामस्वरूप ही आज अंत:विषयक उपागम (Inter-disciplinary approach) पर अधिक बल दिया जाता है। यह उपागम सामाजिक व्यवहार को विभिन्न समाज-वैज्ञानिकों द्वारा संयुक्त रूप से समझने के परिणाम का प्रतिफल है। बार्स एवं बेकर जैसे विद्वान् समाजशास्त्र को न तो अन्य सामाजिक विज्ञानों का स्वामी मानते हैं और न ही सेवक वरन् समाजशास्त्र को अन्य सामाजिक विज्ञानों की बहन-मात्र मानते हैं। उनके शब्दों में, “समाजशास्त्र अन्य सामाजिक विज्ञानों की न मालकिन है। और न उनकी दासी, वरन् उनकी बहन है।” वे आगे और स्पष्ट करते हुए लिखते हैं, “यद्यपि सामाजिक विज्ञानों को बहन मानने में सबसे बाद में उत्पन्न होने के कारण यह सबसे छोटी बहन है, परंतु प्रभाव की दृष्टि से सबसे बड़ी-चढ़ी है। छोटी होते हुए भी ये सब बहनों को एक-दूसरे के पास लाती है और उनके सामाजिक अध्ययन के कार्य में पूरा सहयोग देती है।”
विज्ञापन जैसे विषय का अध्ययन अर्थशास्त्र तथा समाजशास्त्र दोनों विषयों में किया जाता है। अर्थशास्त्री विज्ञापनों द्वारा किसी कंपनी की आय में होने वाली वृद्धि पर ध्यान केंद्रित करते हैं तो समाजशास्त्री इन विज्ञापनों का समाज के विभिन्न वर्गों पर पड़ने वाले प्रभाव की बात करते हैं। इसी भाँति, चुनावों एवं मतदान को समझने हेतु राजनीतिशास्त्र एवं समाजशास्त्र एक-दूसरे को सहयोग प्रदान करते हैं। इतिहासकारों द्वारा अतीत के बारे में जो ठोस विवरण प्रस्तुत किए जाते हैं उनके सार से समाजशास्त्री वर्गीकरण एवं सामान्यीकरण करने का प्रयास करता है। इसी भॉति, अन्य सामाजिक विज्ञानों में भी परस्पर संबंध एवं सहयोग पाया जाता है।
प्रश्न 4.
अपनी या अपने दोस्त अथवा रिश्तेदार की किसी व्यक्तिगत समस्या को चिह्नित कीजिए इसे समाजशास्त्रीय समझ द्वारा जानने की कोशिश कीजिए।”
उत्तर
मान लीजिए कि आप, आपका कोई दोस्त अथवा रिश्तेदार उच्च शिक्षा प्राप्त करने के बावजूद बेरोजगार है। उसकी यह स्थिति “शिक्षित बेरोजगारी’ कहलाती है। वह इस बेरोजगारी के कारण निराश रहता है तथा परिवार एवं अन्य समूहों से उसका व्यवहार सामान्य नहीं होता। इस समस्या को जब कोई सामान्य बौद्धिक ज्ञान से देखने का प्रयास करता है तो वह यह सोच सकता है कि आपके दोस्त अथवा रिश्तेदार का भाग्य ही ऐसा है। भगवान ने उसका पढ़ना-लिखना तो सुनिश्चित किया था, परंतु रोजगार नहीं। यह भी हो सकता है कि वह दोस्त अथवा रिश्तेदार स्वयं आलसी हो तथा रोजगार करना ही न चाहता हो। यह भी संभव है कि परिवारवाद की भावना में जकड़े होने के कारण दूरदराज के क्षेत्र में रोजगार मिलने पर वह जाना ही नहीं चाहता है। आपका दोस्त अथवा रिश्तेदार ऐसे क्षेत्र में भी निवास करने वाला हो सकता है जिसमें रोजगार के अवसर ही उपलब्ध नहीं हैं। समाजशास्त्रीय समझ पहले तो बेरोजगारी को क्रमबद्ध रूप में परिभाषित करने तथा इसे समझने को प्राथमिकता देती है। यह समझ इस शिक्षित बेरोजगारी को जनहित मुद्दे के रूप में देखने तथा इसके कारणों की खोज करने पर बल देती है। लाखों-करोड़ों लोग उच्च शिक्षा प्राप्त करने के उपरांत भी बेरोजगार क्यों रहते हैं? जब समाजशास्त्रीय समुझ द्वारा इसे देखने का प्रयास किया जाएगा तो हो सकता है कि हमारा ध्यान शिक्षा-प्रणाली के दोषपूर्ण होने, उच्च शिक्षा में अत्यधिक छात्र संख्या होने, व्यावसायिक शिक्षा का अभाव होने अथवा देश में मॉग एवं पूर्ति में असंतुलन होने जैसे कारणों पर केंद्रित हो।
शिक्षित बेरोजगारी की भाँति निर्धनता, मद्यपान, मादक द्रव्य व्यसन जैसी व्यक्तिगत समस्या को यदि समाजशास्त्रीय समझ से देखने का प्रयास किया जाएगा तो हमारा नजरिया सामान्य बौद्धिक ज्ञान से देखने वाले नजरिये से पूर्णतः भिन्न होगा। इन व्यक्तिगत समस्याओं को भी हम जनहित के मुद्दों के रूप में देखेंगे तथा इनके कारणों का पता लगाने का प्रयास करेंगे। यदि सम्भव हो तो इनका समाधान भी बताएँगे।
क्रियाकलाप आधारित प्रश्नोत्तर
प्रश्न 1.
एक गरीब और गृहविहीन दंपती को समाजशास्त्रीय कल्पना द्वारा कैसे समझा जा सकता है? (क्रियाकलाप 1)
उत्तर
एक गरीब एवं गृहविहीन दंपती की समाजशास्त्रीय कल्पना इसे एक जनहित मुद्दे के रूप में देखने तथा इसके कारणों की खोज करने पर बल देती है। समाज की संरचना में ऐसी कौन-सी विसंगतियाँ हैं जो कुछ दंपतियों को गरीब एवं गृहविहीन बनाती हैं, जबकि अन्य को अमीर एवं ओलीशान मकानों में रहने का अवसर प्रदान करती है। समाजशास्त्रीय कल्पना हमें एक गरीब एवं गृहविहीन दंपती की स्थिति को भगवान की देन मानने से रोकती है तथा हमारा ध्यान समाज की विसंगतियों की ओर दिलाने का प्रयास करती है।

प्रश्न 2.
गृहविहीनता के कारणों का संक्षेप में वर्णन कीजिए। (क्रियाकलाप 1)
उत्तर
समाजशास्त्रीय कल्पना हमें मृहविहीनता के कारणों को सामाजिक संरचना में निहित विसंगतियों में खोजने हेतु प्रेरित करती है। गृहविहीनता का कारण निर्धनता या बेरोजगारी हो सकती है। अथवा किसी व्यक्ति का गाँव से शहर की ओर नौकरी की तलाश में किया गया प्रवसन हो सकता है। निर्धनता एवं नौकरी में मिलने की स्थिति का परिणाम गृहविहीनता हो सकता है। गृहविहीनता का कारण वर्ग समाज में असमानता की संरचना भी है और वे लोग इस स्थिति में जीवन-यापन हेतु विवश हो जाते हैं जिनकी कार्य की अनियमितता दीर्घकालिक होती है, जबकि उन्हें मजदूरी कम मिलती है। चूंकि गृहविहीनता सामाजिक संरचना में पाई जाने वाली विसुंगतियों का परिणाम है, इसलिए सरकार इसे जनहित का मुद्दा मानते हुए गरीब एवं गृहविज्ञान लोगों के लिए मुफ्त आवास उपलब्ध कराने का। प्रयास करती है।
प्रश्न 3.
भारत में सामाजिक असमानता के प्रमुख क्षेत्रों का वर्णन कीजिए। (क्रियाकलाप 2)
उत्तर
भारत में शिक्षा, स्वास्थ्य, रोजगार, जीवन के अवसर, जाति, वर्ग इत्यादि सामाजिक असमानता के प्रमुख क्षेत्र हैं। सर्वाधिक असमानता जातिगत है तथा परंपरागत रूप से उच्च जातियाँ आर्थिक एवं राजनीतिक दृष्टि से भी ऊँची रही है। इसके विपरीत, निम्न जातियों की स्थिति न केवल संस्कारात्मक दृष्टि से निम्न रही है अपितु वे आर्थिक दृष्टि से भी पिछड़ी हुई थी तथा राजनीति में भी उनकी किसी प्रकार की पकड़ नहीं थी। इसी के कारण निम्न जातियों में शिक्षा की दर निम्न है, निम्न आर्थिक स्थिति के कारण पोषक भोजन न मिलने से स्वास्थ्य की समस्या बनी रहती है तथा रोजगार मिलने में भी कठिनाई होती है।
प्रश्न 4.
गरीबी की प्रकृतिवादी एवं समाजशास्त्रीय व्याख्या किस प्रकार से की जा सकती है? (क्रियाकलाप 3)
उत्तर
गरीबी की प्रकृतिवादी एवं समाजशास्त्रीय व्याख्या में स्पष्ट अंतर पाया जाता है। प्रकृतिवादी व्याख्या के अनुसार लोग गरीब इसलिए हैं क्योंकि वे काम से जी चुराते हैं, समस्यामूलक परिवारों से आते हैं, पारिवारिक बजट बनाने में अयोग्य हैं, उनमें बुद्धिमता की कमी है तथा कार्य के लिए स्थानांतरण से डरते हैं। यदि वे स्थानांतरण कर लेते तो हो सकता है उन्हें उचित रोजगार मिल जाता जो । उनकी निर्धनता के निराकरण में सहायक सिद्ध होता। समाजशास्त्रीय व्याख्या के अनुसार गरीबी का कारण समाज में असमानता की संरचना है और वे लोग इससे ज्यादा प्रभावित होते हैं जिनकी कार्य की अनियमितता दीर्घकालिक है, जबकि उन्हें मिलने वाली मजदूरी कम होती है।

प्रश्न 5.
भारत में ग्रामीण समाज से शहरी समाज में परिवर्तन होने की प्रक्रिया को समझाइए। (क्रियाकलाप 4)
उत्तर
भारत में ग्रामीण समाज से शहरी समाज में परिवर्तन होने की गति ब्रिटेन जैसे देश की तुलना में धीमी रही है। इसका प्रमुख कारण औद्योगीकरण का उस तीव्र गति से विकास न होना है जिस गति से ब्रिटेन एवं अन्य पश्चिमी देशों में हुआ है। साथ ही, कृषिप्रधान समाज होने के नाते व्यक्ति अपने व्यवसाय एवं परिवारवाद की भावना से इस प्रकार से बँधा हुआ था कि वह अवसर मिलने पर भी औद्योगिक क्षेत्रों में जाने से हिचकिचाता था। अब भी बहुत-से ग्रामवासी शहरों एवं औद्योगिक केंद्रों में नौकरी के बाद पुन: अपने गाँव लौट जाते हैं। अंग्रेजी शासनकाल के दौरान शहरी केंद्रों में तो वृद्धि हुई परंतु ब्रिटिश निर्मित वस्तुओं के प्रयोग के साथ अधिकांश लोग कृषि क्षेत्र की तरफ भी उन्मुख हुए क्योंकि उच्च तकनीकी से कृषि उत्पादन में वृद्धि की भी संभावना थी।
प्रश्न 6.
किसी परंपरागत गाँव एवं कारखाने (या कॉल सेंटर) में कार्य किस प्रकार नियोजित किया जाता है? (क्रियाकलाप 5)
उत्तर
किसी परंपरागत गाँव में कार्यों को समयबद्ध रूप से नियोजित नहीं किया जाता है। यह निर्धारित तो होता है कि परिवार के किस सदस्य को क्या कार्य करना है परंतु समय पड़ने पर एक सदस्य का कार्य दूसरी सदस्य कर सकता है। इस दृष्टि से परंपरागत गाँव में कार्यों के निष्पादन में कठोर नियंत्रण नहीं पाया जाता है। व्यावसायिक विशेषीकरणका भी अभाव पाया जाता है तथा समय पड़ने पर एक ही व्यक्ति मालिक, श्रमिक, बढ़ई, लोहार आदि बन सकती है। कार्य के बदले निश्चित पारिश्रमिक अथवा मेहनताने का प्रावधान भी नहीं होता है। इसके विपरीत, कारखाने को एक आर्थिक कठोर नियंत्रण के रूप में देखा जाता है तथा माक्र्स जैसे विद्वान तो इसे दमनकारी मानते हैं। कारखानों में काम करने वालों के लिए निश्चित कार्य, समय की पाबंदी, कार्य करने के निश्चित घंटे, हफ्ते के दिन इत्यादि निर्धारित हो जाते हैं। साथ ही, कार्य के बदले निश्चित पारिश्रमिक का भी प्रावधान होता है। नियोक्ता एवं कर्मचारी दोनों के लिए समय अब धन है, यह व्यतीत नहीं होता बल्कि खर्च हो। जाता है।
प्रश्न 7.
औद्योगिक पूँजीवाद ने गाँव और शहरों में भारतीय जनजीवन को किस प्रकार बदल डाला? (क्रियाकलाप 6)
उत्तर
औद्योगिक पूँजीवाद ने गाँव एवं शहरों में भारतीय जनजीवन को काफी सीमा तक प्रभावित किया है। भारत जैसे देश में इससे न केवल जाति पर आधारित व्यावसायिक संरचना परिवर्तित हुई है, अपितु जातीय दूरी एवं जाति के आधार पर खान-पान के प्रतिबंध भी लगभग समाप्त हुए हैं। लोगों के ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों से शहरी क्षेत्रों की ओर स्थानांतरण से संयुक्त परिवार का विघटन प्रारंभ हुआ है तथा एकाकी परिवारों को प्रोत्साहन मिला है। पारिवारिक संबंध भी प्रभावित हुए हैं तथा उनमें औपचारिकता के अंश का समावेश हो गया है। सामाजिक नियंत्रण के परंपरागत साधन शिथिल हुए हैं तथा व्यापारिक मनोरंजन का महत्त्व बढ़ गया है। शिक्षा का प्रचलन हुआ है तथा व्यावसायिक गतिशीलता के अवसरों में वृद्धि हुई है। परंपरागत मूल्यों एवं प्रतिमानों के साथ-साथ जीवन-पद्धति में भी काफी परिवर्तन हुए हैं। इस प्रकार, औद्योगिक पूँजीवाद ने गाँव और शहरों में भारतीय जनजीवन को पूरी तरह से परिवर्तित कर दिया है।
प्रश्न 8.
क्या आप सोचते हैं कि विज्ञापन वास्तव में लोगों के उपभोग के तरीकों को प्रभावित करते| (क्रियाकलाप 7)
उत्तर
विज्ञापनों का उद्देश्य विज्ञापित वस्तुओं के विक्रय को बढ़ाना है। कोई भी कंपनी विज्ञापन पर इसलिए धन व्यय करती है ताकि उसके उत्पादों का प्रचार-प्रसार हो तथा जनता तथा उसके उत्पादों के बारे में सचेत होकर खरीदने के लिए विवश हो जाए। इस उद्देश्य की पूर्ति के अतिरिक्त विज्ञापन निश्चित रूप से लोगों के उपभोग के तरीकों को भी प्रभावित करते हैं। विज्ञापनों से न केवल उत्पादों की बिक्री ही बढ़ती है, अपितु इससे लोगों की जीवन-पद्धति भी प्रभावित होती है। बहुत-से लोग नए-नए विज्ञापित उत्पादों को खरीदते हैं, उनका उपयोग करते हैं तथा इससे उनकी जीवन-शैली प्रभावित होती है। विज्ञापनों से समाज की मूल्य व्यवस्था भी प्रभावित हो सकती है। बहुत-से विज्ञापनों में दर्शकों को आकर्षित करने हेतु स्त्रियों को अनावश्यक रूप से दर्शाया जाता है। इससे विज्ञापनों में भी स्त्रियों को शोषण होने लगता है। इस प्रकार, विज्ञापन से अर्थशास्त्र एवं समाजशास्त्र के संबंधों का पता चलता है।
प्रश्न 9.
क्या आप सोचते हैं कि ‘अच्छे जीवन की जो परिभाषा है वह केवल आर्थिक रूप से ही परिभाषित है? (क्रियाकलाप 7)
उत्तर
अच्छे जीवन की परिभाषा केवल आर्थिक रूप से ही नहीं दी जा सकती। यह जीवन की गुणवत्ता तथा मानव के सामाजिक-सांस्कृतिक पक्ष को अनदेखा करती है। प्रति व्यक्ति आय एवं राष्ट्रीय आय में वृद्धि सदैव जीवन की गुणवत्ता से जुड़ी हुई नहीं होती। आज विकास को जीवन की, गुणवत्ता की दृष्टि से देखा जाने लगा है। किसी भी देश के नागरिकों का स्वास्थ्य, उपलब्ध पोषक भोजन की मात्रा, शिक्षा एवं रोजगार की सुविधाएँ इत्यादि से जीवन की गुणवत्ता की परख करने का प्रयास किया जाता है। हो सकता है अधिक आय के बावजूद व्यक्ति अपने स्वास्थ्य, भोजन इत्यादि के प्रति सचेत न हो। इसलिए आर्थिक रूप से अच्छे जीवन की परिभाषा अधूरी मानी जाती है।
प्रश्न 10.
क्या शाप सोचते हैं कि ‘खर्च और ‘बचत की आदतें सांस्कृतिक रूप से बनती हैं? (क्रियाकलाप 7)
उत्तर
‘खर्च’ और ‘बचत’ की आदतें अधिकांशतया सांस्कृतिक रूप से ही निर्मित होती है। इसलिए जीवन को सुगम एवं आरामदायक बनाने हेतु पश्चिमी संस्कृति में खर्च को महत्त्व दिया जाता है, न कि बचत को। चूँकि पश्चिमी समाजों में उपभोक्तावाद एवं भौतिकवादी विचारधाराओं की प्रमुखता पाई जाती है इसलिए व्यक्ति अपनी सुख-सुविधाओं हेतु अपने धन का व्यय करता है। विलासितापूर्ण जीवन व्यतीत करने की लालसा उनका ध्यान बचत पर केंद्रित नहीं होने देती। भारत जैसे देश में भौतिकवादी विचारधारा का अभाव रहा है तथा आध्यात्मिक विचारधारा प्रमुख रही है। अंग्रेजी शासनकाल से पूर्व एवं अंग्रेजी शासनकाल के दौरान भी भारत में प्राकृतिक प्रकोप एवं महामारियाँ अधिक होती थीं। इसलिए व्यक्ति अपनी आय का काफी अंश इन विपत्तियों के समय के लिए बचाकर रखता था। पारिवारिक एवं नातेदारी संबंधी दायित्व भारतीयों को व्यर्थ के खर्चे से रोकते हैं तथा उनके । विलासितापूर्ण जीवन-शैली पर काफी सीमा तक अंकुश लगाते हैं।

प्रश्न 11.
चुनावों के अध्ययन में राजनीति विज्ञान और समाजशास्त्र किस प्रकार आपस में अंतःक्रिया करते तथा परस्पर प्रभाव डालते हैं? ” (क्रियाकलाप 8)
उत्तर
चुनावों का अध्ययन एक ऐसा विषय है जो राजनीति विज्ञान और समाजशास्त्र को परस्पर नजदीक लाता है। चूंकि राजनीति विज्ञान की मुख्य रुचि राजनीति में है तथा चुनाव राजनीति से ही संबंधित हैं, इसलिए उनका चुनावों के अध्ययन में ध्यान केन्द्रित होना स्वाभाविक है। समाजशास्त्र में भी चुनावों के अध्ययन में इसलिए दिलचस्पी ली जाती है क्योंकि बहुत-से सामाजिक-सांस्कृतिक कारक चुनावों एवं मतदान व्यवहार को प्रभावित करते हैं। ऐसे सामान्य विषयों को समझने में दोनों ही विज्ञान एक-दूसरे को सहयोग प्रदान करते हैं। यह भी सत्य है कि समाजशास्त्रीय पद्धतिशास्त्र तथा समाजशास्त्र एवं राजनीति विज्ञान के संयुक्त चिंतन को अपनाकर ही इस प्रकार के अध्ययन सफलतापूर्वक किए जा सकते हैं।
प्रश्न 12.
इतिहासकारों ने कला, क्रिकेट, कपड़े, फैशन, वास्तुकला एवं भवन विन्यास के इतिहास को किस प्रकार से लिखा है? (क्रियाकलाप 9)
उत्तर
इतिहासकारों ने कला, क्रिकेट, कपड़े, फैशन, वास्तुकला एवं भवन विन्यास जैसे विषयों के इतिहास को अतीत के ठोस विवरणों, जो कि मुख्यतः राजाओं से संबंधित रहे हैं, के संदर्भ में लिखा है। इतिहास मुख्य रूप से अतीत का अध्ययन ही माना जाता है। परंपरागत इतिहास तो राजाओं और युद्धों के अध्ययन, शासकों के कार्यों, राजनीतिक व्यवस्थाओं के प्रकारों इत्यादि से ही भरा हुआ है। इसमें अपेक्षाकृत कम चकाचौंध एवं कम रोमांचक घटनाओं का अध्ययन अल्प मात्रा में ही हुआ है। इसी का परिणाम है कि इतिहास में कला, वास्तुकली एवं भवन विन्यास जैसे विषयों को भी राजसी परंपरा में ही देखा गया है।
प्रश्न 13.
असम के चाय बागानों में काम करने वाले संथाल जाति के श्रमिकों के पूर्वज भारत में कसँ से आए थे? (क्रियाकलाप 10)
उत्तर
असम में चाय बागानों में काम करने वाले लोगों में संथालों की संख्या अत्यधिक है। असम के चाय बागानों में कार्य करने हेतु संथाल पश्चिम बंगाल अथवा बिहार से श्रमिकों के रूप में जाते हैं। संथाल; भारत में पाई जाने वाली सबसे बड़ी जनजातियों में से एक है। संथाल लोगों को प्रोटो-आस्ट्रेलॉयड प्रजाति का माना जाता है क्योंकि उनमें अधिकांश लक्षण इसी प्रजाति के पाए जाते है। ये लोग अत्यधिक परिश्रमी एवं उद्यमी हैं। संथाले जनजाति के श्रमिकों के पूर्वज भारत में अफ्रीका से आए हुए माने जाते हैं। अनेक मानवशास्त्रियों का मानना है कि संथाल 65,000 से 55,000 वर्ष पहले अफ्रीका से एशिया के देशों में आए। कुछ लोग संथालों को नेपाल के थकाली लोगों से मिलते-जुलते हुए मानते हैं तथा उन्हें भारत में नेपाल से आए हुए भी मानते हैं।
प्रश्न 14.
असम में चाय की खेती की शुरूआत कब हुई? (क्रियाकलाप 10)
उत्तर
असम में चाय की खेती की शुरुआत अंग्रेजी शासनकाल में हुई। ऐसा माना जाता है कि 1823-24 ई० में, असम में तत्कालीन राजधानी रंगपुर के समीप पहाड़ियों पर चीन से लाए हुए पौधों एवं बीजों से इसकी खेती प्रारंभ हुई। असम की सिंगफो जनजाति के प्रयासों से असम में चाय के उत्पादन से भारत के अन्य प्रान्तों में रहने वाले लोगों को भी इसकी जानकारी प्राप्त हुई। तत्कालीन ब्रिटिश गवर्नर जनरल लॉर्ड विलियम बैंटिंक के प्रयासों से 1834 ई० में चाय की खेती को व्यापारिक रूप देने हेतु एक समिति का गठन किया गया। ईस्ट इंडिया कंपनी के असम स्थित प्रतिनिधि सी०ए० बूस को चाय बागानों का अधीक्षक नियुक्त किया गया। तभी से असम के विभिन्न क्षेत्रों में चाय की खेती प्रारम्भ हुई तथा आज असम की चाय पूरे विश्व के बाजारों में उपलब्ध है। 19वीं शताब्दी के अंत तक दक्षिण में नीलगिरि पहाड़ियों पर भी चाय की खेती प्रारंभ हो चुकी थी। यद्यपि भारत में चाय की खेती अनेक राज्यों में होने लगी है, तथापि आज भी दार्जिलिंग की चाय विश्व में सबसे अच्छी चाय मानी जाती है।

प्रश्न 15.
क्या अंग्रेज उपनिवेशवाद से पहले चाव पीते थे? (क्रियाकलापं 10)
उत्तर
अंग्रेज उपनिवेशवाद से पहले चाय नहीं पीते थे। सबसे पहले चाय पीने का उल्लेख चीनी लोगों में मिलता है। बाद में, 17वीं शताब्दी में जापान, भारत, रूस, ईरान एवं मध्य-पूर्व में इसका प्रचलन प्रारंभ हुआ। उपनिवेशकाल में जो अंग्रेज भारत में आए उन्होंने चाय का सेवन प्रारंभ किया तथा तत्पश्चात् इंग्लैंड के बाजारों में भी चाय उपलब्ध कराई जाने लगी। तब ईस्ट इंडिया कंपनी को ही चाय को बाजारों में उपलब्ध कराए जाने का एकाधिकार था।
परीक्षोपयोगी प्रश्नोत्तर
बहुविकल्पीय प्रश्नोत्तर
प्रश्न 1.
किसने कहा है कि समाज संघर्ष से कटा हुआ (विच्छिन्न) सहयोग हैं ?
(क) इमाइल दुखम
(ख) मैकाइवर एवं पेज
(ग) फर्डिनेड दानीज
(घ) रॉबर्ट बीरस्टीड
उत्तर
(ख) मैकाइवर एवं पेज
प्रश्न 2.
“समाज सामाजिक संबंधों का जाल है।” यह निम्न में से किसका कथन है?
(क) ग्रीन
(ख) सोरोकिन
(ग) मैकाइवरं एवं पेज
(घ) जिस्बर्ट
उत्तर
(ग) मैकाइवर एवं पेज

प्रश्न 3.
‘ह्यूमन सोसायटी’ पुस्तक के लेखक कौन हैं?
(क) इमाइल दुर्चीम
(ख) आगस्त कॉम्टे
(ग) मैकाइवर एण्ड पेज
(घ) किंग्स्ले डेविस
उत्तर
(घ) किंग्स्ले डेविस
प्रश्न 4.
‘सोशल ऑर्डर’ पुस्तक के लेखक कौन हैं ?
(क) के० डेविस
(ख) गिलिन एवं गिलिन
(ग) ऑगबर्न एवं निमकॉफ
(घ) रॉबर्ट बीरस्टीड
उत्तर
(घ) रॉबर्ट बीरस्टीड
प्रश्न 5.
‘एशियन ड्रामा’ पुस्तक के लेखक कौन हैं ?
(क) मैकाइवर
(ख) गुन्नार मिर्डल
(ग) अल्वा मिर्डल
(घ) सी० एच० पेज
उत्तर
(ख) गुन्नार मिर्डल

प्रश्न 6.
‘ए हैण्ड बुक ऑफ सोशियोलॉजी पुस्तक के लेखक कौन हैं ?
(क) मैकाइवर तथा पेज
(ख) ऑगबर्न तथा निमकॉफ
(ग) इंकलिस
(घ) गिलिन तथा गिलिन
उत्तर
(ख) ऑगबर्न तथा निमकॉफ
प्रश्न 7.
‘समाजशास्त्र (Sociology) शब्द की उत्पत्ति किस भाषा से हुई ?
(क) लैटिन
(ख) फ्रांसीसी
(ग) लैटिन एवं ग्रीक
(घ) जर्मन
उत्तर
(ग) लैटिन एवं ग्रीक
प्रश्न 8.
समाजशास्त्र के जनक हैं।
(क) आगस्त कॉम्टे
(ख) पेज
(ग) सोरोकिन
(घ) वेब्लन
उत्तर
(क) आगस्त कॉम्टे
प्रश्न 9.
“समाजशास्त्र सामाजिक सम्बन्धों के स्वरूपों का अध्ययन करता है।” यह कथन किसका है?
(क) मैक्स वेबर का
(ख) वीरकांत का
(ग) जॉर्ज सिमेल का
(घ) मैकाइवर का
उत्तर
(ग) जॉर्ज सिमेल का
प्रश्न 10.
आगस्त कॉम्टे ने प्रारम्भ में समाजशास्त्र को नाम दिया-
(क) सामाजिक स्थितिशास्त्र
(ख) सामाजिक गतिशास्त्र
(ग) सामाजिक भौतिकी
(घ) सामाजिक मानवशास्त्र
उत्तर
(ग) सामाजिक भौतिकी

प्रश्न 11.
समाजशास्त्र की प्रकृति है-
(क) मानवीय
(ख) वैज्ञानिक
(ग) कलात्मक
(घ) सामान्य
उत्तर
(ख) वैज्ञानिक
प्रश्न 12.
समाजशास्त्र है-
(क) सामान्य विज्ञान
(ख) विशेष विज्ञान
(ग) व्यावहारिक विज्ञान
(घ) आदर्शात्मक विज्ञान
उत्तर
(क) सामान्य विज्ञान
प्रश्न 13.
समाजशास्त्र समाज का विज्ञान है।’ यह कथन किसका है ?
(क) गिस्बर्ट
(ख) दुर्वीम
(ग) वार्ड
(घ) कॉम्टे
उत्तर
(ग) वार्ड
प्रश्न 14.
समाजशास्त्र व अर्थशास्त्र में सामान्य रूप से अध्ययन किया जाता है
(क) खानाबदोश समूह का
(ख) जनजातीय समूह का
(ग) बलहीन समूह का
(घ) ग्रामीण समूह को
उत्तर
(घ) ग्रामीण समूह का
प्रश्न 15.
विज्ञानों के वर्गीकरण में कॉम्टे ने सबसे प्राचीन विज्ञान किसे कहा?
(क) भौतिकी
(ख) रसायनशास्त्र
(ग) जीव विज्ञान
(घ) गणित
उत्तर
(क) भौतिकी
प्रश्न 16.
नवीनतम सामाजिक विज्ञान कौन-सा है ?
(क) मानवशास्त्र,
(ख) समाजशास्त्र
(ग) मनोविज्ञान
(घ) अर्थशास्त्र
उत्तर
(ग) मनोविज्ञान
प्रश्न 17.
मानवशास्त्र को समाजशास्त्र से मिलाने वाली शाखा का नाम है-
(क) मानवीय समाजशास्त्र
(ख) भौतिक मानवशास्त्र
(ग) सामाजिक मानवशास्त्र
(घ) मानवशास्त्रीय समाजशास्त्र
उत्तर
(ग) सामाजिक मानवशास्त्र
प्रश्न 18.
“समाजशास्त्र विशेष रूप से मनोविज्ञान को सहायता देता है, जिस प्रकार मनोविज्ञान समाजशास्त्र को विशेष सहायता देता है।” यह कथन किसकन है ?
(क) मैकाइवर एवं पेज का.
(ख) कार्ल पियर्सन का
(ग) ई०ए० हावेल का
(घ) आर०एन० मुखर्जी का
उत्तर
(क) मैकाइवर एवं पेज का

प्रश्न 19.
आगस्त कॉम्टे के अनुसार सबसे बाद का विज्ञान है
(क) गणित
(ख) भौतिकी
(ग) जीव विज्ञान
(घ) समाजशास्त्र
उत्तर
(घ) समाजशास्त्र
निश्चित उत्तरीय प्रश्नोत्तर
प्रश्न 1.
किस विद्वान का यह कथन है “समाज एक जीवन रचना के समान है?
उत्तर
यह कथन हरबर्ट स्पेन्सर का है।
प्रश्न 2.
“समाज एक प्रकार की चेतना है।” यह कथन किस विद्वान का है?
उत्तर
यह कथन गिडिंग्स का है।
प्रश्न 3.
“समाज संघर्ष से कटा हुआ सहयोग है।” यह कथन किस विद्वान का है?
उत्तर
यह कथन मैकाइवर तथा पेज का है।
प्रश्न 4.
“समाज सामाजिक संबंधों का जाल है।” यह कथन किस विद्वान का है?
उत्तर
यह कथन मैकाइवर तथा पेज का है।

प्रश्न 5.
‘समाज (‘सोसायटी’) पुस्तक के लेखक कौन हैं?
उत्तर
‘समाज’ (‘सोसायटी’) पुस्तक के लेखक मैकाइवर तथा पेज हैं।
प्रश्न 6.
सामाजिक संबंधों के जाल को हम क्या कहते हैं?
उत्तर
सामाजिक संबंधों के जाल को हम समाज कहते हैं।
प्रश्न 7.
समाज की प्रकृति कैसी होती है?
उत्तर
समाज की प्रकृति अमूर्त होती है।
प्रश्न 8.
‘एक समाज की प्रकृति कैसी होती है?
उत्तर
‘एक समाज’ की प्रकृति मूर्त होती है।
प्रश्न 9.
किस विद्वान ने ‘वर्गविहीन समाज की कल्पना की है?
उत्तर
‘वर्गविहीन समाज’ की कल्पना कार्ल मार्क्स ने की है।
प्रश्न 10.
यह किसका कथन है कि “मनुष्य एक सामाजिक प्राणी है?
उसर
यह कथन अरस्तू का है।
प्रश्न 11.
‘दि ग्रुप माइंड’ पुस्तक के लेखक कौन हैं?
उत्तर
‘दि ग्रुप माइंड’ पुस्तक के लेखक मैक्डूगल हैं।

प्रश्न 12.
समाजशास्त्र के जनक कौन है?
उत्तर
समाजशास्त्र के जनक ऑगस्त कॉम्टे है।
प्रश्न 13.
सर्वप्रथम ‘समाजशास्त्र शब्द का प्रयोग किस सन में किया गया था?
उत्तर
‘समाजशास्त्र’ शब्द का सर्वप्रथम प्रयोग 1838 ई० में किया गया।
प्रश्न 14.
समाजशास्त्र को सर्वप्रथम किस नाम से संबोधित किया गया था?
उत्तर
समाजशास्त्र को सर्वप्रथम ‘सामाजिक भौतिकी’ के नाम से संबोधित किया गया।
प्रश्न 15.
‘सोशियोलॉजी पुस्तक के लेखक का नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर
‘सोशियोलॉजी’ पुस्तक के लेखक का नाम ए० डब्ल्यू ग्रीन है।
प्रश्न 16.
‘ह्वाट इज सोशियोलॉजी’ पुस्तक के लेखक का नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर
‘ह्वाट इज सोशियोलॉजी’ पुस्तक के लेखक का नाम एलेक्स इंकलिस है।
प्रश्न 17.
‘कल्चरल सोशियोलॉजी’ पुस्तक के लेखक का नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर
‘कल्चरल सोशियोलॉजी’ पुस्तक के लेखक का नाम गिलिन तथा गिलिन है।
प्रश्न 18.
‘सोशियोलॉजी : ए गाइड टू प्राब्लम एण्ड लिटरेचर’ पुस्तक के लेखक का नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर
‘सोशियोलॉजी : ए गाइड टू प्राब्लम एण्ड लिटरेचर’ पुस्तक के लेखक का नाम टी० बी० बॉटोमोर है।
प्रश्न 19.
‘ए हैंडबुक ऑफ सोशियोलॉजी पुस्तक के लेखक का नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर
‘ए हैंडबुक ऑफ सोशियोलॉजी’ पुस्तक के लेखक का नाम ऑगबर्न एवं निमकॉफ है।

प्रश्न 20.
वह कौन-सा देश है, जहाँ समाजशास्त्र विषय को अध्ययन सर्वप्रथम प्रारंभ हुआ था?
उत्तर
समाजशास्त्र विषय का अध्ययन सर्वप्रथम फ्रांस में प्रांरभ हुआ। ऑगस्त कॉम्टे फ्रांसीसी ही थे।
प्रश्न 21.
भारत में किस विश्वविद्यालय में सर्वप्रथम समाजशास्त्र को एक स्वतंत्र विषय के रूप में प्रांरभ किया गया?
उत्तर
भारत में समाजशास्त्र का स्वतंत्र विषय के रूप में अध्ययन बंबई विश्वविद्यालय में प्रारंभ हुआ।
प्रश्न 22.
भारत में एक संस्थागत विषय के रूप में समाजशास्त्र का प्रचलन कब हुआ?
उत्तर
भारत में एक संस्थागत विषय के रूप में समाजशास्त्र का प्रचलन 1819 ई० में हुआ।
प्रश्न 23.
एक अग्रणी भारतीय समाजशास्त्री का नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर
योगेंद्र सिंह एक अग्रणी भारतीय समाजशास्त्री हैं।
प्रश्न 24.
‘दि सोशल आर्डर’ पुस्तक के लेखक का नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर
‘दि सोशल आर्डर’ पुस्तक के लेखक का नाम रॉबर्ट बीरस्टीड है।
प्रश्न 25.
समाजशास्त्र, राजनीतिशास्त्र, मनोविज्ञान तथा अर्थशास्त्र किस प्रकार के विज्ञान माने जाते हैं?
उत्तर
समाजशास्त्र, राजनीतिशास्त्र, मनोविज्ञान तथा अर्थशास्त्र सामाजिक विज्ञान हैं।
प्रश्न 26.
भौतिकशास्त्र एवं रसायनशास्त्र किस प्रकार के विज्ञान हैं?
उत्तर
भौतिकशास्त्र एवं रसायनशास्त्र प्राकृतिक एवं भौतिक विज्ञान हैं।
प्रश्न 27.
‘एशियन ड्रामा’ पुस्तक के लेखक का नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर
‘एशियन ड्रामा’ पुस्तक के लेखक का नाम गुन्नार मिर्डल है।
प्रश्न 28.
‘होमो हाइरारकस’ पुस्तक के लेखक का नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर
होमो हाइरारकस’ पुस्तक के लेखक का नाम लुइस ड्यूमो है।
प्रश्न 29.
पीटर एल० बर्जर की पुस्तक का क्या नाम है?
उत्तर
पीटर एल० बर्जर की पुस्तक का नाम ‘इन्वीटेशन टू सोशियोलॉजी : ए ह्यूमनिस्टिक पर्सपेक्टिव है।

प्रश्न 30.
“समाजशास्त्र और मानवशास्त्र जुड़वाँ बहनें हैं।” यह किसका कथन है?
उत्तर
यह कथन ए०एल० क्रोबर का है।
प्रश्न 31.
“समाजशास्त्र अन्य सामाजिक विज्ञानों की न तो दासी है और न ही मालकिन है, बल्कि यह उनकी बहन है।” यह कथन किस विद्वान का है?
उत्तर
यह कथन बांर्स एवं बेकर का है।
अतिलघु उत्तरीय प्रश्नोत्तर
प्रश्न 1.
व्यक्ति सामाजिक संबंधों का निर्माण कब करते हैं ?
उत्तर
जब दो या दो से अधिक व्यक्ति अपनी विभिन्न आवश्यकताओं की पूर्ति हेतु एक-दूसरे के सम्पर्क में आते हैं, परस्पर अन्त:क्रिया करते हैं, एक-दूसरे को अर्थपूर्ण रूप से प्रभावित करते हैं एवं एक-दूसरे से प्रभावित होते हैं तो वे सामाजिक संबंधों का निर्माण करते हैं।
प्रश्न 2.
सामाजिक संबंधों को अमूर्त क्यों कहा जाता है ?
उत्तर
सामाजिक संबंधों का कोई भौतिक आकार नहीं होता है। सामाजिक संबंध मानसिक तथ्य हैं; अतः इन्हें महसूस किया जाता है, वस्तुओं की भाँति इन्हें नापा-तौला नहीं जा सकता। इसी कारण सामाजिक संबंधों को अमूर्त कहा जाता है।
प्रश्न 3.
एक समाज से क्या तात्पर्य है ? एक उदाहरण भी दीजिए।
उत्तर
एक समाज व्यक्तियों का वह समूह या संग्रह है जो कुछ संबंधों या व्यवहार के कुछ ढंगों द्वारा संगठित है, जो उन्हें उन अन्यों से पृथक करते हैं जो इन संबंधों में सम्मिलित नहीं हैं या जो व्यवहार में उनसे भिन्न हैं। आर्य समाज ‘एक समाज’ का उत्तम उदाहरण है।
प्रश्न 4.
सामाजिक विज्ञानों की अध्ययन सामग्री क्या है तथा उनमें पारस्परिक संबंध क्यों है ?
उत्तर
सामाजिक विज्ञानों में मानवीय क्रियाओं, समाज और सामाजिक घटनाओं का अध्ययन किया जाता है। विभिन्न सामाजिक विज्ञानों में से प्रत्येक के द्वारा सामाजिक जीवन के किसी-न-किसी पहलू का अध्ययन किये जाने के कारण उन सभी में पारस्परिक सम्बन्धों का होना स्वाभाविक है।

प्रश्न 5.
लगभग सभी सामाजिक विज्ञान क्यों अपनी सीमाएँ पार कर दूसरों के क्षेत्र में प्रवेश कर जाते हैं ?
उत्तर
सामाजिक विज्ञानों के बीच कोई स्पष्ट सीमा-रेखा नही खींची जा सकती तथा इनमें अध्ययन किये जाने वाले कई विषय समान प्रकार के होते हैं। इसी कारण लगभग सभी सामाजिक विज्ञान अपनी सीमाएँ पार कर दूसरों के क्षेत्र में प्रवेश कर जाते हैं।
प्रश्न 6.
समष्टिता किसे कहते हैं?
उत्तर
समष्टिता से अभिप्राय विभिन्न इकाइयों द्वारा निर्मित समग्र से है। समष्टिता का निर्माण अनेक व्यक्तियों द्वारा होता है।
प्रश्न 7.
मनोविज्ञान किस प्रकार का विज्ञान है?
उत्तर
मनोविज्ञान एक सामाजिक विज्ञान है जिसे प्रायः व्यवहार के विज्ञान के रूप में परिभाषित किया जाता है। यह मुख्यतः व्यक्ति से संबंधित है।
लघु उत्तरीय प्रश्नोत्तर
प्रश्न 1.
“समाज चलनों तथा कार्य-प्रणालियों, अधिकार व पारस्परिक सहायता, अनेक समूहों तथा उनके विभाजनों, मानव-व्यवहार पर नियंत्रणों एवं स्वतंत्रताओं की व्यवस्था है। सदैव परिवर्तित होने वाली इस जटिल व्यवस्था को ही हम समाज कहते हैं। यह सामाजिक संबंधों का जाल है, जो सदैव परिवर्तित होता रहता है।” इस कथन की व्याख्या कीजिए।
उत्तर
समाज सामाजिक संबंधों की अमूर्त व्यवस्था को कहते हैं। वह सामाजिक संबंधों का ताना-बाना अथवा जाल हैं। मैकाइवर एवं पेज ने भी समाज को इसी रूप में परिभाषित किया है। इनके शब्दों में, “समाज चलनों तथा कार्य-प्रणालियों, अधिकार व पारस्परिक सहायता, अनेक समूहों तथा उनके विभाजनों, मानव-व्यवहार पर नियंत्रणों एवं स्वतंत्रताओं की व्यवस्था है। इस सदैव परिवर्तित होने वाली जटिल व्यवस्था को ही इन्होंने समाज कहा हैं। समाज सामाजिक संबंधों का जाल है, जो सदैव परिवर्तित होता रहता है। मैकाइवर एवं पेज द्वारा प्रतिपादित समाज की इस परिभाषा से समाज के निम्नलिखित लक्षण स्पष्ट होते हैं-
- चलन अथवा रीतियाँ-रीतियाँ या चलन (Usages) समाज द्वारा स्वीकृत वे पद्धतियाँ है जो व्यक्तियों को सामाजिक विरासत के रूप में अपने पूर्वजों से प्राप्त होती हैं। ये वे स्वीकृत पद्धतियाँ हैं जिन्हें समाज व्यवहार के क्षेत्र में ग्रहण करने योग्य समझता है। रीतियाँ उपयोगी मानी जाती हैं तथा इनमें समाज की शक्ति निहित होती है। इसी कारण प्रत्येक व्यक्ति इनका पालन निष्ठा से करता है।
- कार्यविधियाँ अथवा कार्य-प्रणालियाँ–प्रत्येक समाज में सामाजिक व्यवस्था को उचित रूप से संचालित रखने के लिए कुछ तरीके तथा प्रणालियों होती हैं। ये प्रणालियाँ व्यक्तियों के कार्यकलापों को नियंत्रित करती है। मैकाइवर तथा पेज ने इन्हें संस्थाओं की संज्ञा दी है। संस्थाएँ वे नियम अथवा कार्य-प्रणालियाँ हैं, जो विभिन्न आवश्यकताओं की पूर्ति के लिए समाज द्वारा मान्य हैं।
- प्रभुत्व या सत्ता–समाज का संगठन प्रभुत्व पर आधारित रहता है। यह प्रभुत्व समाज के कुछ सदस्यों के हाथ में रहती है। इनके प्रति समाज के सदस्यों में प्रेम, श्रद्धा और भक्ति की भावना रहती है। इन प्रभुतासंपन्न व्यक्तियों के अभाव में समाज में अराजकता फैलने की आशंका रहती है। प्रभुत्व के कारण ही व्यक्ति समाज की मान्यताओं को अनुकरण करते हैं।
- पारस्परिक सहयोग-समाज एक व्यवस्था है, परंतु कोई भी व्यवस्था तब तक सुसंगठित नहीं हो सकती जब तक कि पारस्परिक सहयोग न हो। सामाजिक संबंधों के जाल की रचना में पारस्परिक सहयोग का विशेष हाथ रहता है; अतः समाज के लिए उसके सदस्यों में पारस्परिक सहयोग का होना परम आवश्यक है। समाज में पाया जाने वाला संघर्ष भी सहयोग के अंतर्गत ही होता है।
- समूह और श्रेणियाँ–समाज एक अखंड व्यवस्था के रूप में विद्यमान नहीं है, अपितु इसके अन्दर अनेक समूहों एवं श्रेणियों का समावेश रहता है। वास्तव में, इन्हीं समूहों एवं श्रेणियों द्वारा समाज का निर्माण होता है।
- मानव व्यवहार का नियंत्रण-प्रत्येक समाज में व्यक्ति तथा समूह पर नियंत्रण रखने वाले तत्त्व (जैसे जनरीति, रूढ़ि, धर्म और कानून आदि) होते हैं। ये व्यक्ति को मनचाहा आचरण करने से रोकते हैं। इनकी अवेहलना करने वाले व्यक्ति की समाज द्वारा उपेक्षा की जाती हैं या वह दंडित किया जाता है।
- स्वतंत्रता-समाज में व्यक्ति को कुछ स्वतंत्रता अवश्य होनी चाहिए। स्वतंत्रता के अभाव में व्यक्ति का पूर्ण विकास नहीं हो सकता; अतः नियंत्रण के साथ-साथ समाज में स्वतंत्रता का होना भी आवश्यक है। आज अधिकांश विचारक यह मानते हैं कि नियंत्रण और स्वतंत्रता एक-दूसरे के विरोधी न होकर पूरक हैं। पूर्वोक्त विवेचन से यह स्पष्ट हो जाता है कि मैकाइवर तथा पेज की समाज की परिभाषा समाज के प्रमुख लक्षणों अथवा आधारों को स्पष्ट करने में पूर्णतः सफल रही है।

प्रश्न 2.
समाज में पायी जाने वाली समानता एवं असमानता को स्पष्ट कीजिए।
उत्तर
समाज में पायी जाने वाली समानता एवं असमानता समाज में समानता एवं असमानता या भिन्नता दोनों पायी जाती हैं। कोई भी समाज ऐसा नहीं हैं जिसमें पूर्णतया समानता अथवा पूर्णतया असमानता पायी जाती हो। प्रत्येक समाज में दोनों ही बातें अनिवार्य रूप से पायी जाती है, परंतु समाज के संगठन के लिए असमानता का समानता के अंतर्गत पाया जाना अनिवार्य हैं। बाह्य दृष्टिकोण से दोनों परस्पर विरोधी प्रतीत होती है, पर वास्तविकता में ये परस्पर पूरक हैं। समानता व्यक्तियों में पाए जाने वाले सहयोग एवं संबंधों को प्रोत्साहन देती है। सामाजिक संबंधों की स्थापना के लिए यह अनिवार्य है कि व्यक्तियों में शारीरिक एवं मानसिक दोनों प्रकार की समानताएँ हों; क्योंकि इन समानताओं के परिणामस्वरूप ही उनकी आवश्यकताएँ भी समान होती हैं, इने । आवश्यकताओं की पूर्ति के लिए सामाजिक संबंधों की स्थापना होती है। गिडिंग्स ने समानता को ‘सजातीयता की भावना’ कहा है। मैकाइवर एवं पेज के अनुसार, “समाज का अस्तित्व उन्हीं लोगों में होता है जो एक-दूसरे से शरीर या मस्तिष्क के किसी अंश में समान हैं और इस तथ्य को जानने के लिए पर्याप्त निकट या बुद्धिमान है।”
समाज में यद्यपि समानता पायी जाती है, तथापि असमानता की उपेक्षा नहीं की जा सकती। प्रत्येक व्यक्ति एक-दूसरे से भिन्नता रखता है। यह भिन्नता, आयु तथा शारीरिक क्षमता अदि.के भेदों के द्वारा उत्पन्न होती है तथा इसी के आधार पर समाज के समस्त व्यक्ति भिन्न-भिन्न कार्यों में लगे रहते हैं। यदि सभी व्यक्ति एक समान कार्य करने लगे तो समाज में संघर्ष की स्थिति उत्पन्न हो जाएगी और सामाजिक व्यवस्था की निरंतरता खतरे में पड़ जाएगी। श्रम-विभाजन में पाई जाने वाली भिन्नता; असमानता की सूचक है। असमानता के कारण ही स्त्री-पुरुष आकर्षित होते हैं और परिवार की आधारशिला रखते हैं। विचारों, आदर्शो, दृष्टिकोणों आदि की भिन्नता से ही समाज की संस्कृति का विकास होता है। असमानता परस्पर सहयोग को बढ़ावा देकर समाज के संगठन को दृढ़ बनाती है। इस प्रकार, हम देखते हैं कि समाज के लिए समानता और असमानता दोनों ही अनिवार्य हैं। समानता व्यक्तियों में अपनत्व तथा चेतना उत्पन्न करती हैं, और असमानता के आधार पर परस्पर संबंधों की स्थापना होती है; परंतु समाज में समानता प्रधान है, असमानता का स्थान गौण है।
प्रश्न 3.
भारत में समाजशास्त्र का क्या महत्त्व है?
उत्तर
भारत जैसे देशों में समाजशास्त्र को अत्यंत महत्त्वपूर्ण विषय माना जाता है। ग्रामों की प्रधानता होने के नाते भारत में ग्रामोत्थान कार्यक्रमों की सफलता हेतु ग्रामीण समाज का ज्ञान होना आवश्यक है। यह ज्ञान समाजशास्त्र ही उपलब्ध कराता है। भारत में समाजशास्त्रं प्रजातांत्रिक दृष्टिकोण के विकास, औद्योगिक समस्याओं के हल, सामाजिक असमता को समझने, असामान्य एवं अपराधी व्यवहार को समझने, राष्ट्रीय एकता को बनाए रखने, अनुसूचित जातियों एवं जनजातियों सहित समाज के कमजोर वर्गों की समस्याओं के निदान तथा सामाजिक संतुलन स्थापित करने में सहायक रहा है।
प्रश्न 4.
समाजशास्त्र समाज का वैज्ञानिक अध्ययन है। तर्क दीजिए।
उत्तर
‘समाजशास्त्र’ शब्द का शाब्दिक अर्थ ही समाज का अध्ययन या समाज का विज्ञान है। विज्ञान अनुसंधान की पद्धति है। यह किसी भी विषय के बारे में क्रमबद्ध ज्ञान है। इसीलिए ओडम, वार्ड, जिंसबर्ग की परिभाषाएँ समाज पर ही केंद्रित हैं। उदाहरणार्थ–गिडिंग्स के शब्दों में, “समाजशास्त्र समग्र रूप से समाज का क्रमबद्ध वर्णन तथा व्याख्या है। इसी प्रकार, जिंसबर्ग के अनुसार, समाजशास्त्र को समाज के अध्ययन के रूप में पभिाषित किया जा सकता है।” यह पूर्णतः सही भी है, क्योंकि समाजशास्त्र आज निश्चित रूप से एक विज्ञान है। इस संदर्भ में निम्नांकित बातें महत्त्वपूर्ण हैं-
- समाज एवं सामाजिक जीवन के अध्ययन में भी अनुभव, परीक्षण, प्रयोग व वर्गीकरण जैसे वैज्ञानिक चरणों का प्रयोग किया जाता है।
- व्यक्ति के सामूहिक जीवन का अध्ययन वैज्ञानिक पद्धति द्वारा किया जाता है।
- समाज के विभिन्न पहलुओं को वैज्ञानिक पद्धति द्वारा समझा जा सकता है।
- समाज की संरचना एवं प्रकार्यों का अध्ययन वैज्ञानिक पद्धति द्वारा किया जा सकता है।
- समाजशास्त्रीय पद्धति स्वयं वैज्ञानिक है क्योंकि इसमें वैज्ञानिक पद्धति के सभी चरणों को अपनाया जाता है।
समाज की सबसे बड़ी इकाई मानव और उसके अन्य मानवों के साथ संबंधों का अध्ययन समाजशास्त्र में ही होता हैं। राज्य, वर्ग, जाति, समितियाँ, समुदाय, संस्थाएँ इत्यादि समाज में महत्त्वपूर्ण स्थान रखती हैं तथा इन्हीं से मिलकर समाज की संरचना का निर्माण होता है। समाजशास्त्र इन सबकी उत्पत्ति एवं विकास का अध्ययन करता है। इसमें यह ज्ञात करने का भी प्रयास किया जाता है कि सामाजिक जीवन तथा समाज कौन-से प्राकृतिक एवं भौगोलिक तथा सांस्कृति तत्त्वों से प्रभावित होता है। इसी दृष्टिकोणों से यह कहा जाता है कि समाजशास्त्र समाज का अध्ययन है। उपर्युक्त विवेचन के आधार पर यह कहा जा सकता है कि गिडिंग्स तथा वार्ड की परिभाषाएँ, जिनमें समाजशास्त्र को समाज के विज्ञान के रूप में परिभाषित किया गया है, पूर्णः सही है।

प्रश्न 5.
समाजशास्त्र को सामाजिक संबंधों का अध्ययन करने वाला विषय क्यों कहा गया है?
उत्तर
समाजशास्त्र समाज का विज्ञान है तथा समाज को सामाजिक संबंधों का ताना-बाना माना जाता है। इसलिए कुछ समाजशास्त्री समाजशास्त्र की परिभाषा समाज के अध्ययन के रूप में न देकर सामाजिक संबंधों के अध्ययन के रूप में देते हैं। उदाहरणार्थ-मैकाइवर एवं पेज के अनुसार, समाजशास्त्र सामाजिक संबंधों के विषय में हैं (तथा) इन संबंधों के जाल को हम समाज कहते हैं।” इसी प्रकार, क्यूबर के अनुसार, “समाजशास्त्र को मानव संबंधों के वैज्ञानिक ज्ञान के ढाँचे के रूप में परिभाषित किया जा सकता है।”
वस्तुतः सामाजिक संबंध ही समाजशास्त्र की मुख्य विषय-वस्तु है, इसलिए इसे सामाजिक संबंधों का अध्ययन करने वाला विषय कहा जाता है। सामाजिक संबंधों का अर्थ है कि कम-से-कम दो व्यक्ति ऐसे हैं जिन्हें एक-दूसरे का आभास है तथा जो एक-दूसरे के प्रति कुछ-न-कुछ कार्य कर रहे हैं।
प्रश्न 6.
“मनुष्य एक सामाजिक प्राणी है।” इस कथन की समीक्षा कीजिए।
उत्तर
शताब्दियों पूर्व कहा गया अरस्तू का यह वाक्य पूर्णतया सत्य है, “मनुष्य एक सामाजिक प्राणी है।” एक व्यक्ति जो समाज में अन्य व्यक्तियों के साथ तथा उनके मध्ये नहीं रहता, वह या तो देवता है। अथवा पशु।” अन्य शब्दों में, व्यक्ति के समाज से अलग रहकर जीवन व्यतीत करने की कल्पना नहीं की जा सकती। मनुष्य का जीवन, उसकी समृद्धि तथा प्रगति समाज में ही संभव हैं। परस्पर मिलकर सहयोग के साथ रहने की मनुष्य में जन्मजात प्रवृत्ति होती है। समाज में उसका जन्म, विकास और
आवश्यकताओं की पूर्ति होती है और समाज में ही वह अंततः मृत्यु को प्राप्त हो जाता है। समाज के बिना व्यक्ति का अस्तित्व संभव नहीं है, क्योंकि अपनी वश्यकताओं की पूर्ति वह स्वयं नहीं कर सकता। समाज ही समाजीकरण की प्रक्रिया द्वारा उसे एक जैविक प्राणी से सामाजिक प्राणी बनाता है। मनुष्य में प्रेम, आदेश देना, खेलना-पितृभाव, घृणा, क्रोध, मोह आदि भावनाएँ स्वाभाविक रूप से विद्यमान रहती है। इन सब भावनाओं की पूर्ति मनुष्य समाज में रहकर ही कर सकता है। मनुष्य समाज में रहकर सहयोग, सहिष्णुता, प्रेम आदि गुणों की प्राप्ति करता है। व्यक्ति के व्यक्तित्व का विकास समाज में रहकर ही संभव है। मनुष्य समाजीकरण के माध्यम से सांस्कृतिक मूल्यों को ग्रहण करता है। तथा सांस्कृतिक विरासत को आगे बढ़ाने का कार्य करता है। उसके ज्ञान में वृद्धि समाज में रहकर ही संभव है।
प्रश्न 7.
समाजशास्त्र तथा मनोविज्ञान के संबंधों की विवेचना कीजिए।
उत्तर
समाजशास्त्र तथा मनोविज्ञान दोनों परस्पर संबंधित सामाजिक विज्ञान हैं। समाजशास्त्र सामाजिक क्रियाओं से संबंधित हैं, जबकि मनोविज्ञान मानसिक दशाओं से संबंधित है। आज अधिकांश विद्वान मनोविज्ञान को भी व्यवहार के अध्ययन के रूप में परिभाषित करने लगे हैं। जे०एस० मिल का विचार है कि मस्तिष्क की विधियों के बिना सामान्य सामाजिक विज्ञान स्थापित ही नहीं हो सकता अर्थात् समाजशास्त्र को आधार प्रदान करने वाला विज्ञान मनोविज्ञान है। जिंसबर्ग तथा कुछ अन्य समाजशास्त्रियों का यह मत है कि समाजशास्त्रीय सामान्यीकरण मनोवैज्ञानिक नियमों से संबंधित किए जाने पर अधिक दृढ़ता से स्थापित किए जा सकते हैं। वास्तव में, यह मिल और दुर्णीम के मतों में मध्य स्थिति को प्रकट करने वाला दृष्टिकोण है। नैडल का भी यही विचार है कि मनोविज्ञान की सहायता से सामाजिक जाँच अच्छी तरह से की जा सकती है।

प्रश्न 8.
भारत में समाजशास्त्र के विकास के बारे में आप क्या जानते हैं?
उत्तर
भारत में समाजशास्त्र का एक संस्थागत विषय के रूप में विकास 1919 ई० में हुआ जबकि प्रो० शैट्रिक गेडिस नामक अंग्रेज समाजशास्त्री की अध्यक्षता मे बंबई विश्वविद्यालय में स्नातकोत्तर स्तर पर समाजशास्त्र का अध्यापन कार्य प्रारंभ हुआ। भारत में समाजशास्त्र का विकास उपनिवेशवाद, आधुनिक पूँजीवाद एवं औद्योगीकरण का परिणाम माना जाता है। अंग्रेज समाजशास्त्रियों ने 19वीं शताब्दी के भारत में यूरोपीय समाजों का अतीत देखा। यद्यपि भारत में औद्योगीकरण का प्रभाव उतना नहीं था जितना कि पश्चिमी समाजों पर, तथापि पश्चिमी समाजशास्त्रियों ने पूँजीवाद एवं आधुनिक समाजों पर लिखे अपने लेखों को भारत में हो रहे सामाजिक परिवर्तनों को समझने के लिए प्रांसगिक माना। उनके एवं भारतीय समाजशास्त्रियों द्वारा आदिम समूहों, ग्रामीण एवं नगरीय क्षेत्रों में अध्ययनों से भारत में समाजशास्त्र की नींव मजबूत होती गई।
प्रश्न 9.
हमें यूरोप में समाजशास्त्र के प्रारंभ और विकास को क्यों पढ़ना चाहिए?
उत्तर
यूरोप में समाजशास्त्र के प्रारंभ और विकास का अध्ययन हमारे लिए अत्यंत महत्त्वपूर्ण है। इसका प्रमुख कारण यह है कि समाजशास्त्र के अधिकांश मुद्दे उस समय की बात करते हैं जब 18वीं एवं 19वीं शताब्दी की यूरोपीय समाज में औद्योगीकरण एवं पूंजीवाद के आगमन से क्रांतिकारी परिवर्तन होने प्रारंभ हुए। शहरीकरण की प्रक्रिया, कारखानों के उत्पादन इत्यादि मुद्दे न केवल यूरोप अपितु सभी आधुनिक समाजों के लिए प्रासंगिक थे। औद्योगिक क्रांति के अतिरिक्त फ्रांसीसी क्रांति तथा । ज्ञानोदय जैसे मुद्दे भी यूरोप से ही जुड़े हुए हैं। इन सबका पूरे विश्व पर गहरा प्रभाव पड़ा है। भारतीय समाज का अतीत अंग्रेजी पूँजीवादी एवं उपनिवेशवाद के इतिहास में घनिष्ठ रूप से जुड़ा हुआ है। इसलिए भारत जैसे देश में समाजशास्त्र को समझने हेतु यूरोप में समाजशास्त्र के प्रांरभ और विकास को पढ़ना आवश्यक है।
प्रश्न 10.
समाजशास्त्र और अर्थशास्त्र के मध्य संबंध स्पष्ट कीजिए।
उत्तर
समाजशास्त्र और अर्थशास्त्र का परस्पर घनिष्ठ संबंध है। अर्थशास्त्र भी एक सामाजिक विज्ञान है, क्योंकि उसमें मनुष्य की आर्थिक क्रियाओं का अध्ययन किया जाता है। अर्थशास्त्र वस्तुओं और सेवाओं के उत्पादन एवं वितरण का अध्ययन करता है तथा इसका मुख्य विषय आर्थिक क्रियाएँ हैं। इसमें मुख्य रूप से इस बात पर विचार किया जाता है कि उत्पादन के साधनों का अर्जन किस प्रकार किया जा सकता है और उससे संबंधित विभिन्न नियम क्या-क्या हैं परंतु उत्पादन के साधनों का संबंध मनुष्य से होता है और मनुष्य समाज का क्रियाशील सदस्य है। समाजशास्त्र के माध्यम से सामाजिक संबंधों को समझने का प्रयास किया जाता है और अर्थशास्त्र द्वारा समाज और व्यक्ति की आर्थिक गतिविधियों को समझने का प्रयास किया जाता है। अन्य शब्दों में हम कह सकते हैं कि अर्थशास्त्र संबंधों का अध्ययन करता है और समाजशास्त्र सामाजिक संबंधों का, परंतु आर्थिक संबंध सामाजिक संबंध पर आश्रित होते हैं। वास्तव में आर्थिक संबंध सामाजिक संबंधों के गुच्छे की एक कड़ी-मात्र हैं। इस प्रकार, अर्थशास्त्र और समाजशास्त्र दोनों एक-दूसरे के अत्यधिक निकट हो जाते हैं, दोनों एक-दूसरे को प्रभावित करते हैं।
प्रश्न 11.
समाजशास्त्र और राजनीतिशास्त्र में संबंध बताइए। अथवा समाजशास्त्र तथा राजनीतिशास्त्र के अंतर्संबंधों की व्याख्या कीजिए।
उत्तर
समाजशास्त्र तथा राजनीतिशास्त्र ऐसे सामाजिक विज्ञान हैं जिनमें घनिष्ठ संबंध पाया जाता है। प्रमुख राजनीतिशास्त्री कैटलिन एवं अनेक अन्य विद्वानों ने इस बात पर बल दिया है कि “समाजशास्त्र व राजनीतिशास्त्र को अलग-अलग करना संभव नहीं है और वास्तव में ये दोनों एक ही चित्र के दो पहलू हैं।” समाजशास्त्र के लिए राजनीतिशास्त्र तथा राजनीतिशास्त्र के लिए समाजशास्त्र का ज्ञान होना आवश्यक है। इसी संबंध में गिडिंग्स का कथन है, “समाजशास्त्र के प्रारंभिक सिद्धांतों से अनभिज्ञ लोगों को राज्य के सिद्धांतों को पढ़ाना वैसे ही व्यर्थ है, जैसे न्यूटन द्वारा बताए गए गति-नियमों को न जानने वाले व्यक्ति को खगोलशास्त्र अथवा ऊष्मा विज्ञान पढ़ाना।” कोई भी राज्य समाज से पहले जन्म नहीं ले सकता, जबकि यह तो संभव है कि समाज हो और राज्य न हो। समाज ही राज्य को जन्म देता है और राज्य समाज के ढाँचे में कानूनों द्वारा परिवर्तन करता रहता है। समाजशास्त्र ने जिस सामाजिक विज्ञान को सर्वाधिक प्रभावित किया है वह राजनीतिशास्त्र ही है। इसी का एक परिणाम यह निकला है। कि आज राजनीतिशास्त्र में राजनीतिक व्यवस्था की बजाय राजनीतिक व्यवहार के अध्ययन पर अधिक बल दिया जा रहा है जिसके बारे में सामान्यीकरण भी किया जा सकता है।
दीर्घ उत्तरीय प्रश्नोत्तर
प्रश्न 1.
समाजशास्त्र को परिभाषित कीजिए तथा इसके विकास की संक्षिप्त विवेचना कीजिए।
उत्तर
किसी भी विज्ञान अथवा शास्त्र के विषय में पूर्ण ज्ञान प्राप्त करने से पूर्व आवश्यक होता है कि उस विज्ञान अथवा शास्त्र की एक समुचित परिभाषा निर्धारित कर ली जाए। परिभाषा के निर्धारण से शास्त्र अथवा विज्ञान की सीमाएँ निश्चित हो जाती हैं। निश्चित सीमाओं के अंतर्गत अध्ययन करना सरल होता है। साथ ही, सीमित क्षेत्र का अध्ययन अपेक्षाकृत अधिक व्यवस्थित तथा शुद्ध भी होता है। समाजशास्त्र भी इस सामान्य नियम का अपवाद नहीं है।
समाजशास्त्र के इतिहास पर दृष्टिपात करने से ज्ञात होता है कि यह एक नवविकसित सामाजिक, विज्ञान है। सर्वप्रथम इस शब्द का प्रयोग फ्रांसीसी विद्वान ऑगस्त कॉम्टे (Auguste Comte) ने 1838 ई० में किया। इसलिए कॉम्टे को समाजशास्त्र का पिता’ कहा जाता है। इन्होंने सर्वप्रथम इस विषय को ‘सामाजिक भौतिकी’ कहा। अन्य विद्वानों द्वारा इस शब्द को स्वीकार न किए जाने पर कॉम्टे ने ‘सामाजिक भौतिकी’ के स्थान पर ‘समाजशास्त्र’ शब्द का प्रयोग किया और इसी नाम से यह विषय आज भी जाना जाता है। इसका इतिहास केवल 167-68 वर्ष का है। नवविकसित विज्ञान होने के कारण समाजशास्त्र का क्षेत्र पूर्ण रूप से स्पष्ट नहीं हो सकता है। विभिन्न विद्वानों में इस विषय को लेकर मतभेद है। इसी मतभेद के कारण भिन्न-भिन्न विद्वानों ने समाजशास्त्र को अलग-अलग प्रकार से परिभाषित किया है।
समाजशास्त्र का अर्थ एवं परिभाषाएँ।
‘समाजशास्त्र’ को अंग्रेजी में ‘sociology’ कहा जाता है, जो दो शब्दों ‘सोशियो’ (Socio) तथा ‘लोजी’ (Logy) से मिलकर बना है। ‘सोशियो’ लैटिन भाषा के socius’ शब्द से बना है जिसका अर्थ ‘समाज’ है और ‘लोजी’ ग्रीक भाषा के logos’ शब्द से बना है जिसका अर्थ ‘विज्ञान’ या ‘शास्त्र’ है। इस प्रकार, शाब्दिक अर्थ में समाजशास्त्र वह विषय या विज्ञान है, जिसमें समाज का अध्ययन किया जाता है, परंतु समाजशास्त्र के अर्थ को पूर्ण रूप से समझने के लिए समाज’ और ‘विज्ञान’ का अर्थ समझना आवश्यक है।
- समाज का अर्थ–प्रायः व्यक्तियों के समूह को समाज माना जाता है, परंतु यह धारणा त्रुटिपूर्ण है। केवल व्यक्तियों के समूह को ही समाज नहीं कहा जा सकता, वरन् व्यक्तियों का वह समूह समाज है जिसके सदस्यों के मध्य पारस्परिक मानसिक या सामाजिक संबंध होते हैं और ये संबंध अमूर्त होते हैं। इस प्रकार विभिन्न व्यक्तियों के मध्य स्थापित होने वाले सामाजिक संबंधों * की अमूर्त व्यवस्था को समाज कहा जाता है।
- विज्ञान का अर्थकिसी भी विषय के व्यवस्थित और क्रमबद्ध ज्ञान को विज्ञान कहा जाता है। विज्ञान में निरीक्षण और पर्यवेक्षण के द्वारा विभिन्न समानताओं की खोज की जाती है तथा प्राप्त परिणामों के आधार पर सिद्धांतों का प्रतिपादन किया जाता है और उन्हें ज्ञान के क्षेत्र में व्यवस्थित और संगठित किया जाता है। इस प्रकार, समाज और विज्ञान के अर्थों का स्पष्टीकरण करने के पश्चात् हम इस निष्कर्ष पर पहुँचते हैं कि समाजशास्त्र वह विज्ञान है, जिसमें सामाजिक संबंधों का क्रमबद्ध, व्यवस्थित और वैज्ञानिक रूप में अध्ययन किया जाता है। अध्ययन का अर्थ है कि इसकी विषय-वस्तु को समझा और समझाया जा सकता है तथा किसी प्रकार का संदेह होने पर नवीन प्रमाण एकत्र करके उसे दूर किया जा सकता है। विभिन्न विद्वानों द्वारा दी गई परिभाषाओं से समाजशास्त्र के स्वरूप को ठीक प्रकार से समझा
जा सकता है। समाजशास्त्र की कोई एक सर्वमान्य परिभाषा नहीं है। विभिन्न विद्वानों ने इसे भिन्न-भिन्न दृष्टिकोणों से परिभाषित किया। इसी परिभाषाओं को हम अपनी सुविधा के लिए निम्नांकित श्रेणियों में विभाजित कर सकते हैं-
(अ) समाजशास्त्र समाज का अध्ययन है।
कुछ विद्वानों के अनुसार समाजशास्त्र समाज को विज्ञान है। इन विद्वानों ने समाजशास्त्र की परिभाषा समाज को प्रमुख आधार मानकर इस प्रकार दी है-
- ओडम (Odum) के अनुसार–“समाजशास्त्र वह विज्ञान है, जो समाज का अध्ययन करता है।”
- वार्ड (Ward) के अनुसार-“समाजशास्त्र समाज का विज्ञान है।”
- जिंसबर्ग (Ginsberg) के अनुसार-“समाजशास्त्र समाज के अध्ययन के रूप में परिभाषित | किया जा सकता है।
- गिडिंग्स (Giddings) के अनुसार-“समाजशास्त्र समग्र रूप से समाज का क्रमबद्ध वर्णन तथा व्याख्या है।”
उपर्युक्त परिभाषाओं में समाजशास्त्र को समाज के अध्ययन के रूप में प्रतिपादित किया गया है। समाजशास्त्र का शाब्दिक अर्थ ही समाज का अध्ययन नहीं है अपितु अनेक विद्वानों ने इसे इसी आधार पर परिभाषित भी किया है। ये परिभाषाएँ समाजशास्त्र के मूल अर्थ के निकट होते हुए भी पर्याप्त स्पष्ट एवं वैज्ञानिक नहीं है, क्योंकि इन परिभाषाओं में कहीं भी ‘समाज’ की संकल्पना को स्पष्ट नहीं किया गया है।

( ब ) समाजशास्त्र सामाजिक संबंधों का अध्ययन है
कुछ विद्वानों ने समाजशास्त्र की परिभाषा सामाजिक संबंधों के अध्ययन के रूप में की है। इन विद्वानों के अनुसार समाजशास्त्र सामाजिक संबंधों का वैज्ञानिक अध्ययन है। सामाजिक संबंधों के ताने-बाने को ही समाज कहते हैं; अत: समाज को समझने के लिए सामाजिक संबंधों को समझना आवश्यक है। ऐसी प्रमुख परिभाषाएँ निम्नलिखित हैं-
- मैकाइवर एवं पेज (Maclver and Page) के अनुसार-–“समाजशास्त्र सामाजिक संबंधों के विषय में है (तथा) इन संबंधों के जाल को हम ‘समाज कहते हैं।”
- रोज (Rose) के अनुसार–“समाजशास्त्र मानव संबंधों का विज्ञान है।”
- ग्रीन (Green) के अनुसार-“समाजशास्त्र संश्लेषणात्मक और सामान्यीकरण करने वाला वह विज्ञान है जो मनुष्यों और सामाजिक संबंधों का अध्ययन करता है।”
- क्यूबर (Cuber) के अनुसार-“समाजशास्त्र को मानव-संबंधों के वैज्ञानिक ज्ञान के ढाँचे के रूप में परिभाषित किया जा सकता है।”
- सिमेल (Simmel) के अनुसार-“समाजशास्त्र मानव-अंतर्सम्बन्धों के स्वरूपों का विज्ञान है।”
उपर्युक्त विभिन्न परिभाषाओं में समाजशास्त्र को उस सामाजिक विज्ञान के रूप में प्रतिपादित किया गया है, जिसके अंतर्गत सभी प्रकार के सामाजिक संबंधों का व्यवस्थित अध्ययन किया जाता है। सामाजिक संबंधों को आधार मानकर दी गई परिभाषाएँ समाजशास्त्र के अर्थ को पर्याप्त सीमा तक स्पष्ट करती हैं।
(स) समाजशास्त्र सामाजिक जीवन और घटनाओं का अध्ययन है।
कुछ समाजशास्त्रियों के अनुसार समाजशास्त्र सामाजिक जीवन, व्यवहारों, कार्यों तथा घटनाओं का अध्ययन है। ये विद्वान समाजशास्त्र को अग्रलिखित रूपों में परिभाषित करते हैं-
- किम्बल यंग (Kimball Young) के अनुसार-“समाजशास्त्र समूहों में मनुष्य के व्यवहार का अध्ययन करता है।
- बेनेट एवं ट्यूमिन (Beanet and Tumin) के अनुसार-“समाजशास्त्र सामाजिक जीवन के ढाँचे और कार्यों का विज्ञान है।”
- ऑगर्बन एवं निमकॉफ (Ogburn and Nimkoff) के अनुसार-“समाजशास्त्र सामाजिक जीवन का वैज्ञानिक अध्ययन है।’
उपर्युक्त परिभाषाओं में समाजशास्त्र को मुख्य रूप से सामाजिक जीवन और सामाजिक घटनाओं के वैज्ञानिक अध्ययन के रूप में प्रस्तुत किया गया है।
(द) समाजशास्त्र की अन्य परिभाषाएँ
समाज, सामाजिक संबंधों, सामाजिक जीवन तथा सामजिक घटनाओं के अतिरिक्त भी अनेक आधारों को समाजशास्त्र को. परिभाषित करने के लिए अपनाया गया है। ऐसी प्रमुख परिभाषाएँ निम्नलिखित हैं-
- वेंबर (Weber) के अनुसार-“समाजशास्त्र वह विज्ञान है जो कि सामाजिक क्रियाओं की . अर्थपूर्ण व्याख्या करते हुए उन्हें समझने का प्रयास करता है।”
- जॉनसन (Johnson) के अनुसार-समाजशास्त्र वह विज्ञान है, जो सामाजिक समूहों, उनके
आन्तरिक स्वरूपों या संगठन के स्वरूपों तथा उन प्रक्रियाओं को जो इस संगठन के स्वरूपों को बनाए रखती हैं या परिवर्तित करती है और समूहों के बीच पाए जाने वाले संबंधों का अध्ययन करता है।”
- पारसन्स (Parsons) के अनुसार-“समाजशास्त्र वह विज्ञान है, जो सामाजिक कार्यों का व्याख्यात्मक अध्ययन करने का प्रयास करता है।”
उपर्युक्त परिभाषाओं से यह स्पष्ट हो जाता है कि समाजशास्त्र समाज, सामाजिक संबंधों, सामाजिक जीवन, सामाजिक घटनाओं, सामाजिक क्रियाओं, सामाजिक समूहों तथा सामाजिक कार्यों इत्यादि का क्रमबद्ध अध्ययन करने वाला विज्ञान है।
समाजशास्त्र का उद्गम एवं विकास
व्यक्ति अपने स्वभाव के कारण एक जिज्ञासु प्राणी है और इसी जिज्ञासु प्रवृत्ति के कारण उसने प्रारंभ से ही अपने समय में प्रचलित विविध प्रकार की सामाजिक, आर्थिक और राजनीतिक समस्याओं को समझने का प्रयास किया है। भारत के प्राचीन ग्रंथों में समाज के विभिन्न पहलुओं का उल्लेख विविध प्रकार से किया गया है। उदाहरणार्थ-वैदिक साहित्य एवं हिंदू शास्त्रों (जैसे उपनिषदों, महाभारत एवं गीता आदि ग्रंथों) में वर्ण एवं जाति व्यवस्था, संयुक्त परिवार प्रणाली, आश्रम व्यवस्था, विभिन्न संस्कारों तथा ऋण व्यवस्था जैसे अनेक महत्त्वपूर्ण सामाजिक पहलुओं का विधिवत् विवरण मिलता है। जो कि आज के समाजशास्त्रीय विश्लेषणों के किसी भी मापदंड से कम नहीं है। अरस्तू की पुस्तक ‘पॉलिटिक्स’, प्लेटो की ‘रिपब्लिक’ तथा कौटिल्य का अर्थशास्त्र’ आदि ऐसे ग्रंथ हैं जिनमें समाज के विभिन्न पहलुओं की चर्चा की गई है।
यद्यपि सामाजिक पहलुओं के अध्ययन की एक लंबी परंपरा रही है, फिर भी समाजशास्त्र विषय का एक संस्थागत विषय के रूप में उद्भव एवं विकास 19वीं शताब्दी में हुआ जबकि ऑगस्त कॉम्टे ने सर्वप्रथम 1838 ई० में ‘समाजशास्त्र’ शब्द का प्रयोग किया। इनका विचार था कि कोई भी विषय ऐसा नहीं है जो कि समाज के विभिन्न पहलुओं का समग्र रूप में अध्ययन कर सकता हो। इस कमी को दूर करने के लिए इन्होंने इस नवीन विषय का निर्माण किया। उन्नीसवीं शताब्दी के समाजशास्त्र को यद्यपि निश्चयात्मक (Positive) विज्ञान माना गया है जिसका प्रभाव प्राकृतिक विज्ञानों के समान था, फिर भी यह इतिहास के दर्शन एवं जैविक सिद्धांतों के प्रभाव के कारण उविकासवादी था। साथ ही इसमें मनुष्य के संपूर्ण जीवन एवं संपूर्ण इतिहास से संबंधित अध्ययन किए जाते थे अर्थात् इसकी प्रकृति विश्वकोशीय थी। 19वीं शताब्दी में समाजशास्त्र के विकास में अनेक बौद्धिक एवं भौतिक परिस्थितियों ने सहायता प्रदान की, जिनमें से चार बौद्धिक परिस्थितियों को टी० बी० बॉटोमोर (T.B. Bottomore) ने महत्त्वपूर्ण माना है। ये परिस्थितियाँ निम्नलिखित हैं-
- राजनीति का दर्शन (Political philosophy)
- इतिहास का दर्शन (The philosophy of history)
- उविकास के जैविक सिद्धांत (Biological theories of evolution) तथा
- सामाजिक एवं राजनीतिक सुधारात्मक आंदोलन (The movements for social and political reform)
इनमें से दो, इतिहास के दर्शन तथा सामाजिक सर्वेक्षण (जो कि आंदोलनों के परिणामस्वरूप शुरू हुए), ने प्रारंभ में महत्त्वपूर्ण योगदान दिया है। एक विशिष्ट शाखा के रूप में इतिहास का दर्शन अठारहवीं शताब्दी की देन है जिसे अबे डे सेंट-पियरे (Abbe de saint-Pieare) तथा ग्यिम्बाटिसटा विको (Giambattista Vico) ने शुरू किया। प्रगति के जिस सामान्य विचार को निर्मित करने का इन्होंने प्रयत्न किया उसने मानव की इतिहास संबंधी धारणा को गंभीर रूप से प्रभावित किया। फ्रांस में मॉण्टेस्क्यू (Montesquieu) और वॉल्टेयर (Voltaire), जर्मनी में हर्डर (Herder) तथा स्कॉटिश इतिहासज्ञों एवं दार्शनिकों; जैसे फग्र्युसन (Ferguson), मिलर (Millar), रॉबर्टसन (Robertson) इत्यादि की रचनाओं में इतिहास के दर्शन का प्रभाव स्पष्ट रूप से देखा जा सकता है। 19वीं शताब्दी के प्रारंभ में हीगल (Hegel) तथा सेंट साइमन (Saint Simon) के लेखों के परिणामस्वरूप इतिहास का दर्शन एक प्रमुख बौद्धिक प्रभाव बन गया। इन्हीं दोनों विचारकों से कार्ल माक्र्स (Karl Marx) तथा ऑगस्त कॉम्प्टे (Auguste Comte) की रचनाएँ विकसित हुईं। समाज की नवीन धारणा, जो कि राज्य की धारणा से भिन्न है, दार्शनिक इतिहासकारों की ही देन है। आधुनिक समाजशास्त्र के विकास में सहायक दूसरा महत्त्वपूर्ण तत्त्व सामाजिक सर्वेक्षण कहा जा सकता है जिसके दो प्रमुख स्रोत थे—प्रथम, यह विश्वास के प्राकृतिक विज्ञान की पद्धतियों को सामाजिक घटनाओं एवं मानव क्रियाकलापों के अध्ययन में प्रयुक्त किया जा सकता है और दूसरा, यह विश्वास कि गरीबी प्रकृति या दैवीय प्रकोप नहीं है अपितु मानव प्रयास द्वारा इसे दूर किया जा सकता है। इन दोनों विश्वासों के परिणामस्वरूप समाज-सुधारक के लिए किए गए इन आंदोलनों का 18वीं तथा 19वीं शताब्दी के पश्चिमी यूरोप की सामाजिक परिस्थितियों से प्रत्यक्ष संबंध था। सामाजिक परिवर्तन में रुचि के कारण ऐतिहासिक तथा सामाजिक आंदोलनों की ओर ध्यान दिया जाने लगा। अनेक विद्धानों; जैसे बाल्डरीज (Baldridge) ने उन सामाजिक, आर्थिक तथा राजनीतिक दशाओं का भी वर्णन किया है जिन्होंने समाजशास्त्र के विकास को प्रेरित किया है। ये दशाएँ निम्नलिखित हैं-
- वैज्ञानिक क्रांति-वैज्ञानिक क्रांति के परिणामस्वरूप वैज्ञानिक पद्धति की श्रेष्ठता सिद्ध हो चुकी थी और पश्चिमी यूरोप में नित्य नए आविष्कार हो रहे थे। अध्ययन के लिए तथ्यों के अवलोकन, वर्गीकरण एवं विश्लेषण की यह पद्धत समाज एवं सामाजिक जीवन के अध्ययन के लिए भी उपयोगी एवं आवश्यक समझी जाने लगी थी।
- प्रौद्योगिकीय क्रांति-वैज्ञानिक आविष्कारों का उत्पादन के यंत्रों के क्षेत्र में प्रयोग होने लगा था। कपड़े की बुनाई के क्षेत्र में वृहत् मशीनों के प्रयोग ने एक नई क्रांति को जन्म दिया। इसी प्रकार, यंत्रों को चलाने के लिए शक्ति के नए साधन भी खोज निकाले गए थे; जैसे-भाप, डीजल आदि। इससे उत्पादन के क्षेत्र में प्रौद्योगिकीय क्रांति का सूत्रपात हुआ और पुराने तरीके बेकार सिद्ध होने लगे तथा प्रौद्योगिकीय क्रांति के प्रभावों को समझने की आवश्यकता महसूस की जाने लगी।
- औद्योगिक क्रांति-विज्ञान और तकनीकी के प्रयोग ने औद्योगिक क्रांति को जन्म दिया और बड़ी मशीनों द्वारा वृहत् स्तर पर उत्पादन प्रारंभ हुआ। परिणामतः पुरानी लघु उत्पादन व्यवस्था समाप्त होने लगी। सामाजिक व्यवस्था चरमराने लगी। औद्योगिक केंद्रों में बड़ी संख्या में श्रमिकों का संकेंद्रण बढ़ गया। कृषि के स्थान पर उद्योग धन का स्रोत बन गए। नई सामाजिक संरचना की आवश्यकता महसूस होने लगी। बढ़ती हुई बेकारी और गरीबी तथा श्रमिकों की निम्न दशा ने सामाजिक विचारकों को प्रेरित किया कि वे तत्कालीन सामाजिक व्यवस्था पर पुनर्विचार करें।
- बाजारों का विस्तार एवं साम्राज्यवाद–इंग्लैंड, फ्रांस, जर्मनी, स्पेन आदि देशों में बने माल की खपत के लिए और कच्चे माल की तलाश में, विदेशों में व्यापार के क्षेत्र खोजने की होड़ लग गई। भाप द्वारा चालित जहाजों के द्वारा विदेशी व्यापार सरल हो गया। अनेक व्यापारिक कंपनियाँ स्थापित की गई जो अमेरिका, एशिया तथा अफ्रीका के देशों में पहुँची। ये व्यापारिक कंपनियाँ अपने माल की सुरक्षा के लिए अपनी फौज भी रखती थी। धीरे-धीरे साम्राज्यवाद की प्रवृत्ति बढ़ गई। साथ ही साम्राज्य को बनाए रखने के लिए विजित देश के मूल निवासियों की भाषा, रीति-रिवाज आदि का अध्ययन भी किया गया। परिणामतः विभिन्न समाजों के संबंध में बहुमूल्य सामाजिक तथ्य एकत्र हो गए और एक पृथक् सामाजिक विज्ञान की आवश्यकता महसूस होने लगी।
- राजनीतिक क्रांति-इंग्लैंड और फ्रांस में बढ़ते हुए उद्योगवाद ने सामंतवादी व्यवस्था को चुनौती दी और वहाँ प्रजातांत्रिक क्रांतियाँ घटित हुईं। राजा और सामंतों के विरुद्ध मानव के समानता, भ्रातृत्व, स्वतंत्रता और मूल अधिकारों के लिए घटित हुई इन खूनी क्रांतियों ने पुरानी सामाजिक व्यवस्था की जड़े हिला दी। नई संरचना क्या हो?—यह प्रश्न, चिंतकों के लिए मूल प्रश्न बन गया। समाजशास्त्र का विकास इस प्रश्न से जुड़ा है।
- समाज सुधार आंदोलन–स्पष्ट है कि यूरोप और अमेरिका के देशों में, जहाँ इतनी क्रांतिकारी घटनाएँ हो रही हों, अनेक सामाजिक समस्याएँ पैदा हो गई थीं। भूखमरी और बेकारी सबसे बड़ी समस्याएँ थीं। इन समस्याओं को हल करने के लिए अनेक समाज सुधार आंदोलन हुए। ये आंदोलन नई विचारधारा एवं लक्ष्य सामने रख रहे थे। इनके नेता अपने पक्ष-पोषण में, तथ्यों के रूप में प्रमाण प्रस्तुत कर रहे थे। समाज के प्रति एक नया दृष्टिकोण विकसित हो रहा था। उपर्युक्त समसामयिक दशाओं ने फ्रांस के सेण्ट साइमन, जर्मनी के कार्ल मार्क्स जैसे विचारकों को जन्म दिया, जिन्होंने एक नए सामाजिक विज्ञान की रूपरेखा प्रस्तुत की। ऑगस्त कॉम्टे ने इस नए विज्ञान का नामकरण किया, जबकि स्पेंसर और दुर्णीम ने उसे प्रतिष्ठित किया।

बॉटोमोर (Bottomore) का कहना है कि इस प्रकार समाजशास्त्र का पूर्व इतिहास सौ वर्षों की उम्र अवधि से संबंधित है जो लगभग 1740 ई० से 1850 ई० तक की है। इन्होंने 19वीं शताब्दी में विकसित समाजशास्त्र की तीन विशेषताओं का भी उल्लेख किया है-
- यह विश्वकोशीय (Encyclopaedic) था;
- यह उविकासवादी (Evolutionary) था तथा
- यह निश्चयात्मक (Positive) था।
समाजशास्त्र के विकास में प्रारंभिक विद्वानों की समाज-सुधार में रूचि ने भी महत्त्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाई है। 1880 ई० से 1920 ई० के काल में तीव्र औद्योगीकरण के कारण सामाजिक परिवर्तन के अध्ययनों में रुचि विकसित हुई तथा 20वीं शताब्दी के प्रारंभ तक इसे विज्ञान की स्थिति प्राप्त हो गई। समाज-सुधार तथा सामाजिक अनुसंधान के घनिष्ठ संबंध के परिणामस्वरूप आनुभविक अनुसंधान को प्रोत्साहन मिला तथा नीति-निर्माण करने वालों ने समस्याओं के समाधान के लिए समाजशास्त्रियों की ओर देखना शुरू कर दिया जिससे व्यावहारिक अनुसंधान प्रारंभ हुए। हेरी एम० जॉनसन (Harry M.Johnson) के अनुसार, आज समाजशास्त्र निश्चित रूप से एक विज्ञान है यद्यपि यह अन्य विज्ञानों से थोड़ा पिछड़ा हुआ है। इसमें विज्ञान की निम्नलिखित विशेषताएँ पाई जाती हैं-
- समाजशास्त्र आनुभविक (Empirical) है, क्योंकि यह तार्किक चिंतन पर आधारित है।
- यह सैद्धांतिक (Theoretical) है, क्योंकि इसमें घटनाओं के कार्य-कारण संबंधों के आधार पर नियम बनाए जाते हैं।
- यह संचयी (Cumulative) है अर्थात् समाजशास्त्रीय सिद्धांत एक के आधार पर दूसरे बनते हैं।
- यह नैतिकता मुक्त (Nonethical) है अर्थात् समाजशास्त्री का कार्य तथ्यों की व्याख्या करना है, उन्हें अच्छा या बुरा बताना नहीं।
फ्रांस के पश्चात् अमेरिका में समाजशास्त्र का अध्ययन-कार्य सर्वप्रथम 1876 ई० में ‘येल विश्वविद्यालय से प्रारंभ हुआ और इस विषय का सर्वाधिक विकास अमेरिका में ही हुआ है। अमेरिकी समाजशास्त्रियों में समनर, रॉस, सोरोकिन, ऑगबर्न एवं निमकॉफ, मैकाइवर एवं पेज, यंग, लुंडबर्ग, जिमरमैन, पारसंस, मर्टन, किंग्स्ले डेव्रिस आदि प्रमुख हैं। आज यद्यपि फ्रांस, अमेरिका, इंग्लैंड तथा जर्मनी में समाजशास्त्र एक सर्वाधिक लोकप्रिय विषय है, फिर भी संसार में शायद ही कोई ऐसा देश हो जिसमें आज समाजशास्त्र का अध्ययन न हो रहा हो।
प्रश्न 2.
समाज किसे कहते हैं? इसकी विशेषताओं का विस्तृत वर्णन कीजिए।
अथवा
“समाज सामाजिक संबंधों का जाल है।” इस कथन की व्याख्या कीजिए।
उत्तर
समाज का सामान्य अर्थ
सामान्य बोलचाल की भाषा में समाज’ शब्द का प्रयोग व्यक्तियों के समूह के लिए किया जाता है। उदाहरण के लिए ईसाई समाज’, ‘आर्य समाज’, ‘ब्रह्म समाज’, ‘धर्म समाज’, वैश्य समाज’, ‘विद्यार्थी समाज’ तथा ‘बाल-समाज’ आदि शब्दों का प्रयोग व्यक्ति इसी अर्थ में करते हैं। इनमें से अधिकांश शब्द, जिनके साथ समाज’ शब्द जोड़ दिया गया है, समाज न होकर संप्रदाय, वर्ण, सामाजिक श्रेणी, क्षेत्रीय समूह या विशिष्ट भाषा-भाषी समूह हैं। उदाहरणार्थ यदि कोई व्यक्ति यह कहे कि वह ईसाई समाज’ का सदस्य है तो यह गलत होगा। वह ईसाई समाज’ का नहीं अपितु ‘ईसाई संप्रदाय’ का सदस्य है। इसी भाँति, ‘आर्य समाज’ या ‘ब्रह्म समाज’ समाज न होकर विशिष्ट धार्मिक ‘संप्रदाय’ है। ‘वैश्य समाज का उदाहरण न होकर एक वर्ण है। ‘विद्यार्थी मिलकर समाज का निर्माण नहीं करते, अपितु एक सामाजिक श्रेणी का निर्माण करते हैं। कुछ लोग ‘समाज’ शब्द का प्रयोग व्यक्तियों के समूह के रूप में अथवा एक समिति यो संस्था के रूप में भी करते हैं। इसी कारण समाज के अर्थ के संबंध में काफी अनिश्चिता पायी जाती है।
समाज की परिभाषाएँ
विभिन्न समाजशास्त्रियों ने ‘समाज’ शब्द की निम्नलिखित परिभाषाएँ दी हैं-
- गिडिंग्स (Giddings) के अनुसार- “समाज स्वयं एक संघ है, यह एक संगठन तथा औपचारिक संबंधों का योग है, जिसमें सहयोग देने वाले व्यक्ति एक-दूसरे से संबंधित होते हैं।”
- मैकाइवर एवं पेज के अनुसार-“समाज रीतियों एवं कार्यप्रणालियों की अधिकार एवं पारस्परिक सहायता की, अनेक समूहों तथा विभागों की, मानव व्यवहार के नियंत्रणों तथा स्वतंत्रताओं की एक व्यवस्था है। इस सदैव परिवर्तनशील, जटिल व्यवस्था को हम समाज कहते हैं। यह सामाजिक संबंधों का जाल है।”
- कूले (Cooley) के अनुसार-“समाज रीतियों या प्रक्रियाओं का एक जटिल ढाँचा है, जिसमें प्रत्येक जीवित है और दूसरों के साथ अंतक्रिया करते हुए बढ़ता है। इस प्रकार, जटिल संपूर्ण ढाँचे में एक ऐसी एकरूपता पायी जाती है कि जो एक भाग में होता है, उसका शेष भाग पर प्रभाव पड़ता है।”
- रयूटर (Reuter) के अनुसार-“(समाज) एक अमूर्त धारणा है, जो एक समूह के सदस्यों के | बीच पाए जाने वाले सामाजिक संबंधों की संपूर्णता का बोध कराती है।” 5. पारसंस के अनुसार-“(समाज) को उन मानवीय संबंधों की संपूर्ण जटिलता के रूप में परिभाषित किया जा सकता है जो साधन-साध्य संबंधों के रूप में क्रिया करने से उत्पन्न हुए हों, चाहे वे यथार्थ हों या प्रतीकात्मक।”
उपर्युक्त विभिन्न परिभाएँ ‘समाज’ शब्द का समाजशास्त्रीय अर्थ तथा इसके विभिन्न पक्षों को स्पष्ट करती है। इन परिभाषाओं के अनुसार, केवल व्यक्तियों के समूह को ही समाज नहीं कहा जा सकता। वास्तव में, व्यक्ति सामाजिक प्राणी होने के नाते जिस संगठन को जन्म देता है, वह ‘समाज’ कहलाता . है। समाज सामाजिक संबंधों की व्यवस्था को कहा जाता है। ये संबंध उन सभी व्यक्तियों के बीच पाए जाते हैं, जो मानव समाज के संदस्य होते हैं। समाज का यह संगठन अपने सदस्यों के व्यवहारों तथा संबंधों को नियंत्रित और निर्देशित भी करता है। समाज में रहने वाले व्यक्ति परस्पर व्यवहार भी करते हैं, जिनके द्वारा उनमें परस्पर सामाजिक संबंधों की स्थापना होती है। ये सामाजिक संबंध इतने अधिक व्यापक संपूर्ण व जटिल होते हैं कि इनका वर्णन नहीं किया जा सकता। वास्तव में, समाज इन्हीं सामाजिक संबंध का जाल है। ये संबंध ही प्रत्येक व्यक्ति को अन्य व्यक्तियों से संबंधित एवं अन्योन्याश्रित करते हैं। सामाजिक संबंधों में निरंतरता पायी जाती है। इसी तथ्य को ध्यान में रखते हुए ई० बी० यूटर (E.B. Reuter) ने कहा है कि जिस प्रकार जीवन एक वस्तु नहीं है बल्कि जीवित रहने की एक प्रक्रिया है, उसी प्रकार समाज एक वस्तु नहीं बल्कि संबंध स्थापित करने की एक प्रक्रिया है।’ समाज सामाजिक संबंधों का ताना-बाना होने के कारण एक अमूर्त धारणा है। इससे सदस्यों में पाए जाने वाले सामाजिक संबंधों की संपूर्णता व जटिलता का भी पता चलता है।
समाज की प्रमुख विशेषताएँ
समाज की प्रकृति को स्पष्ट रूप से समझने के लिए यह आवश्यक है कि उसकी विशेषताओं का भी उल्लेख किया जाए। समाज में निम्नलिखित प्रमुख विशेषताएँ पायी जाती हैं-
1. अमूर्त संकल्पना–समाज का रूप मूर्त न होकर अमूर्त (Abstract) है। यह अपने आप में । विभिन्न सामाजिक संबंधों की व्यवस्था है। ये ऐसे संबंध हैं जिनसे कि लोग परस्पर जुड़े रहते हैं। सामाजिक संबंधों को देखा नहीं जा सकता अर्थात् वे अमूर्त होते हैं। सामाजिक संबंधों के अमूर्त होने के कारण ही समाज भी एक अमूर्त व्यवस्था है; क्योंकि समाज मूल रूप से सामाजिक संबंधों की एक व्यवस्था है।
2. केवल व्यक्तियों का समूह-मात्र नहीं-राइट को यह कथन पूर्णतया सत्य है कि “यह . (समाज) व्यक्तियों का समूह नहीं है, वरन् यह समूह के सदस्यों के मध्य स्थापित संबंधों की व्यवस्था है। वास्तव में समाज केवल व्यक्तियों का एक समूह नहीं है, वरन् मनुष्यों में जो पारस्परिक सामाजिक संबंध होते हैं उन्हीं की एक व्यवस्था अथवा जाल है। व्यक्तियों के एक समूह को समिति तथा समुदाय के नाम से पुकारा जा सकता है, समाज के नाम से नहीं।।
3. समाज में समानता–सहयोग और पारस्परिक संबंध समाज के मुख्य आधार हैं, परंतु सहयोग और संबंध तब ही संभव हैं जबकि व्यक्तियों में समरूपता हो। सामाजिक संबंधों की स्थापना के लिए यह आवश्यक है कि व्यक्तियों में शारीरिक एवं मानसिक दोनों प्रकार की समानताएँ हों; क्योंकि समानताओं के परिणामस्वरूप ही उनकी आवश्यकताएँ भी समान ही होती हैं। इन आवश्यकताओं की पूर्ति के लिए ही सामाजिक संबंधों की स्थापना होती है। गिडिंग्स के मत में समाज को आधार ‘सजातीयता की भावना’ (Consciousness of kind) है।

4. समाज में असमानता–समाज में एकरूपता अथवा समानता के साथ ही विषमता या असमानता भी पाई जाती है। समाज के समस्त व्यक्तियों में वैयक्तिकं भिन्नता पाई जाती है। लिंग, आयु तथा शारीरिक क्षमता आदि के भेद सामाजिक संबंधों एवं जीवन में असमानता उत्पन्न करने के प्रमुख साधन हैं। इस विषमता या भेदों के कारण समाज के समस्त व्यक्ति | भिन्न-भिन्न कार्यों में लगे रहते हैं। यदि समस्त व्यक्ति एकसमान हों तो विभिन्न प्रकार के कार्य कैसे हो सकते हैं? यदि सभी व्यक्ति खेती का कार्य करने लग जाएँ तो समाज में अव्यवस्था फैल जाएगी और व्यक्तियों की विभिन्न आवश्यकताओं की पूर्ति नहीं हो सकेगी। श्रम-विभाजन के लिए भी विषमता या असमानता अनिवार्य है। इस कारण ही समाज का आर्थिक ढाँचा श्रम-विभाजन पर आधारित है, जिसमें व्यक्तियों के व्यवसाय व आर्थिक क्रियाएँ भिन्न-भिन्न होती हैं। इस प्रकार हम देखते हैं कि समाज के लिए समानता और विषमता (असमानता) दोनों ही आवश्यक हैं। समानता व्यक्तियों में अपनत्व तथा चेतना उत्पन्न करती हैं, जबकि विषमता के आधार पर परस्पर संबंधों की स्थापना होती है।
5. पारस्परिक जागरूकता—मनुष्यों में सामाजिक संबंधों की स्थापना के लिए यह आवश्यक है। | कि व्यक्तियों को एक-दूसरे के अस्तित्व को ज्ञान हो। यदि दो व्यक्ति एक-दूसरे से अनभिज्ञ एवं मुख मोड़े विपरीत दिशा में खड़े हैं तथा परस्पर अप्रभावित हैं, तो ऐसी दशा में उनमें सामाजिक संबंध स्थापित नहीं होंगे। अतः समाज की स्थापना का प्रश्न तब उत्पन्न होता है। जबकि इन व्यक्तियों को एक-दूसरे के अस्तित्व का ज्ञान होता है और वे परस्पर एक-दूसरे को प्रभावित करने लगते हैं। इस प्रकार, समाज के लिए व्यक्तियों का एक-दूसरे के अस्तित्व के प्रति जागरूक होना अनिवार्य है।
6. सहयोग एवं संघर्ष-समाज के सदस्यों में दो प्रकार के संबंध होते हैं—सहयोगपूर्ण और संघर्षमय। समाज का प्रमुख आधार सहयोग है। सहयोग के अभाव में समाज की कल्पनां भी नहीं की जा सकती। सहयोग के कारण ही श्रम-विभाजन सफल होता। सहयोग प्रत्यक्ष एवं परोक्ष (अप्रत्यक्ष) दोनों रूपों में पाया जाता है। सीमित क्षेत्र में सहयोग का प्रत्यक्ष रूप अधिक पाया जाता है तथा विस्तृत क्षेत्र में अप्रत्यक्ष सहयोग का अधिक महत्त्व होता है। सहयोग के साथ-साथ समाज में संघर्ष भी पाया जाता है। यह भी प्रत्यक्ष एवं परोक्ष (अप्रत्यक्ष) दोनों रूपों में पाया जाता है। कभी-कभी संघर्ष के द्वारा भी सहयोग की स्थापना के प्रयास किए जाते हैं। परिवार में पाए जाने वाले संबंध इसका उदाहरण हैं। परिवार में सहयोग और संघर्ष दोनों पाए जाते हैं, परंतु समाज का निरंतरता के लिए यह अनिवार्य है कि संघर्ष सहयोग के
अंतर्गत ही पाया जाए तथा कुछ सीमा से ऊपर होने पर इस पर नियंत्रण रखा जाए।
7. पारस्परिक निर्भरता—व्यक्तियों की अनेक आवश्यकताएँ होती हैं। आवश्यकताओं की पूर्ति के *लिए ही व्यक्तियों को एक-दूसरे पर निर्भर रहना पड़ता हैं। इसकी पूर्ति, बिना एक-दूसरे की सहायता के नहीं हो सकती। इस आधार पर व्यक्तियों में परस्पर निर्भरता उत्पन्न होती है तथा समाज का निर्माण होता हैं।
8. समाज और जीवन समाज और जीवन में परस्पर घनिष्ठ संबंध है। ठीक ही कहा जाता है कि जहाँ जीवन है, वहीं समाज है।” अन्य शब्दों में, समाज का संबंध केवल प्राणि-जगत से ही होता है। उसका निर्जीव जगत से कोई संबंध नहीं है। वैसे पशु और पक्षियों का भी समाज होता हैं, परंतु समाजशास्त्र का संबंध केवल मानव समाज से ही होता है। मानव समाज का स्तर पशु समाज के स्तर से अधिक ऊँचा होता है।
9. निरंतर परिवर्तनशीलता-समाज एवं उसके सदस्यों में व्याप्त संबंधों की व्यवस्था स्थिर न होकर परिवर्तनशील होती है। समाज में निरंतर परिवर्तन होते रहते हैं। मैकाइवर एवं पेज ने सामाजिक संबंधों की सदैव परिवर्तित होने वाली जटिल व्यवस्था को ही समाज कहा है। इनके शब्दों में, “यह सामाजिक संबंधों का जाल है तथा सदैव परिवर्तित होता रहता है।”
निष्कर्ष-उपर्युक्त विवेचन से स्पष्ट हो जाता है कि समाजशास्त्र में समाज’ शब्द का प्रयोग सामाजिक संबंधों के ताने-बाने के लिए किया जाता है। यह एक अमूर्त धारणा या व्यवस्था है। जनसंख्या का प्रतिपालन सदस्यों में कार्यों का विभाजन, समूह की एकता तथा सामाजिक व्यवस्था की निरंतरता समाज के प्रमुख तत्त्व हैं। प्रत्येक समाज में समानता व असमानता, पारस्परिक जागरूकता, सहयोग एवं संघर्ष, पारस्परिक निर्भरता एवं निरंतरता जैसी प्रमुख विशेषताएँ पायी जाती हैं।
प्रश्न 3.
समाजशास्त्र अन्य सामाजिक विज्ञानों से किस प्रकार संबंधित है? समाजशास्त्र का अर्थशास्त्र एवं मनोविज्ञान से संबंध स्पष्ट कीजिए।
या
समाजशास्त्र के अर्थशास्त्र और इतिहास से संबंधों की विवेचना कीजिए।
या
समाजशास्त्र का इतिहास तथा अर्थशास्त्र से संबंध स्पष्ट कीजिए।
या
समाजशास्त्र के राजनीतिशास्त्र और मनोविज्ञान से संबंध बताइए।
उत्तर
समाजशास्त्र अन्य सामाजिक विज्ञानों से घनिष्ठ रूप से संबंधित है। विभिन्न विद्वानों ने समाजशास्त्र व अन्य सामाजिक विज्ञानों के संबंध के विषय में भिन्न-भिन्न विचार प्रकट किए हैं। मुख्य विद्वानों के विचार निम्नवर्णित हैं-
गिडिंग्स के विचार-गिडिंग्स समाजशास्त्र को न तो सामाजिक विज्ञानों का समन्वय मानते हैं और न ही संयोग, वरन वे इसे स्वतंत्र विज्ञान के रूप में स्वीकार करने पर बल देते हैं। समाजशास्त्र का अपना एक भिन्न दृष्टिकोण है। इसी दृष्टिकोण के आधार पर अर्थशास्त्र, इतिहास तथा राजनीतिशास्त्र को समाजशास्त्र से अलग किया जा सकता है। वस्तुतः वह समस्त सामाजिक विज्ञानों का अध्ययन सामाजिक दृष्टिकोण के आधार पर करता है। इस स्थिति में समाजशास्त्र को अन्य सामाजिक विज्ञानों का स्वामी कहा जा सकता है।
सोरोकिन के विचार–सोरोकिन के अनुसार, समाजशास्त्र न केवल अन्य सामाजिक विज्ञानों का आधार है वरन् एक विशिष्ट विज्ञान है। सोरोकिन के शब्दों में, “समाजशास्त्र न केवल समाज के सामान्य सिद्धान्तों का अध्ययन करता है वरन यह विभिन्न सामाजिक विज्ञानों के मध्य संबंध स्थापित करता है और उन्हें पूर्ण बनाता है।” उपर्युक्त विवरण के अध्ययन से स्पष्ट हो जाता है कि समाजशास्त्र व अन्य सामाजिक विज्ञानों के पारस्परिक संबंधों के विषय में विभिन्न विद्वानों के विचारों में मतैक्य का अभाव है। प्रत्येक ने अपने दृष्टिकोण से विचारों को प्रकट किया है तथा प्रत्येक के दृष्टिकोण में कुछ-न-कुछ सत्यता है। वैसे अधिकांश विद्वान वार्ड के मत से अधिक सहमत है।
कॉम्टे के विचार–समाजशास्त्र के जन्मदाता फ्रांसीसी समाजशास्त्री ऑगस्त कॉम्टे समाजशास्त्र व अन्य सामाजिक विज्ञानों में किसी प्रकार का संबंध नहीं है। उनके मतानुसार समाजशास्त्र एक पूर्ण एवं स्वतंत्र विषय है, जिसे विभाजित नहीं किया जा सकता समाज एक पूर्णता है और उसका अध्ययन भी पूर्णता में ही होना चाहिए। इतिहास, अर्थशास्त्र व राजनीतिशास्त्र आदि सभी विषय समाज के केवल एक पहलू का ही अध्ययन करते हैं। इस कारण समाज के यथार्थ स्वरूप का अध्ययन नहीं हो पाता। इस दोष की पूर्ति केवल समाजशास्त्र द्वारा ही हो सकती है। ऐसी दशा में समाजशास्त्र के अतिरिक्त अन्य विषय व्यर्थ हैं। समाजशास्त्र एक स्वतंत्र विज्ञान है, उसे अपने अध्ययनों में किसी अन्य शास्त्र से सहायता नहीं लेनी चाहिए। वास्तव में, इनका समाजशास्त्र के विकास का उद्देश्य यही था कि इससे सभी पहलुओं को एक साथ रखकर अध्ययन किया जा सकें।
स्पेंसर के विचार–स्पेंसर के अनुसार, “समाजशास्त्र अन्य सामाजिक विज्ञानों का समन्वय मात्र है। समाजशास्त्र समस्त सामाजिक विज्ञानों में से प्रत्येक से कुछ बातें ग्रहण करती है और उनका समन्वय करता है। इस प्रकार समाजशास्त्र को स्वतंत्र विज्ञान के रूप में, जैसा कि कॉम्टे मानते हैं, स्वीकार नहीं किया जा सकता। इतिहास, भूगोल, अर्थशास्त्र तथा राजनीतिशास्त्र आदि जितने भी सामाजिक विज्ञान है, सभी पूर्ण विज्ञान हैं। ये विज्ञान समाजशास्त्र को प्रभावित कर सकते हैं, परंतु समाजशास्त्र इन्हें प्रभावित नहीं कर सकता।”
वार्ड के विचार-वार्ड स्पेंसर के मत के पक्ष में नहीं हैं। उसके अनुसार समाजशास्त्र विभिन्न सामाजिक विज्ञानों का केवल समन्वय नहीं है वरन स्वतंत्र विज्ञान है। यह सत्य है कि समाजशास्त्र में अन्य सामाजिक विज्ञानों का समन्वय होता है, परंतु यह समन्वय केवल मिश्रण नहीं है वरन् नवीन विषय की सृष्टि करने वाला संयोग होता है। विभिन्न सामाजिक विज्ञान मिलकर एक नवीन विषय को निर्माण करते हैं और अपना स्वतंत्र अस्तित्व समाप्त कर देते हैं। इस संयोग से एक नवीन विषय ‘समाजशास्त्र’ का जन्म होता है, जो पूर्णतया स्वतंत्र विज्ञान है। उदाहरण के लिए नीले और पीले रंग मिलकर हरे रंग को जन्म देते हैं जो कि पीले और नीले रंग से पूर्णतया अलग होता है। उसी प्रकार विभिन्न सामाजिक विज्ञानों से तत्त्व ग्रहण करके समाजशास्त्र सर्वथा नवीन और स्वतंत्र विज्ञान बन जाता है।
उपर्युक्त विवरण के अध्ययन से स्पष्ट हो जाता है कि समाजशास्त्र व अन्य सामाजिक विज्ञानों के पारस्परिक संबंधों के विषय में विभिन्न विद्वानों के विचारों में मतैक्य का अभाव है। प्रत्येक ने अपने दृष्टिकोण से विचारों को प्रकट किया है तथा प्रत्येक के दृष्टिकोण में कुछ-न-कुछ सत्यता है। वैसे अधिकांश विद्वान वार्ड के मत से अधिक सहमत हैं।
समाजशास्त्र का अन्य सामाजिक विज्ञानों से संबंध
समाजशास्त्र सामाजिक विज्ञानों के एक समूह का भाग है। विभिन्न सामाजिक विज्ञानों में पाया जाने वाला विभाजन सुस्पष्ट नहीं है और इसलिए सभी में कुछ सीमा तक सामान्य रुचियाँ, संकल्पनाएँ एवं अध्ययन की पद्धतियाँ हैं। इसलिए बहुत-से विद्वानों का कहना है कि सामाजिक विज्ञानों को अलग-अलग करना इनमें पाए जाने वाले अंतरों को अतिरंजित करना तथा समानताओं पर आवरण चढ़ाने जैसा होगा। अधिकांश सामाजिक विज्ञानों द्वारा अन्त:विषयक उपागम (Inter-disciplinary approach) अपनाए जाने से सामाजिक विज्ञानों में अंतर करना और भी कठिन हो गया है। फिर भी, यह कहना अतिशयोक्ति नहीं होगा कि विभिन्न सामाजिक विज्ञानों में परस्पर संबंध के बावजूद रुचियों, संकल्पनाओं एवं अध्ययन-पद्धतियों में थोड़ा-बहुत अंतर पाया जाता है। समाजशास्त्र और अन्य सामाजिक विज्ञानों में पाया जाने वाला परस्पर संबंध निम्न प्रकार हैं-
(अ) समाजशास्त्र और अर्थशास्त्र
समाजशास्त्र और अर्थशास्त्र का परस्पर घनिष्ठ संबंध हैं। अर्थशास्त्र भी एक सामाजिक विज्ञान है, क्योंकि उसमें मनुष्य की आर्थिक क्रियाओं का अध्ययन किया जाता है। समाजशास्त्र और अर्थशास्त्र के संबंधों पर विचार करने से पूर्व यह आवश्यक है कि अर्थशास्त्र के अर्थ पर प्रकाश डाला जाए। अर्थशास्त्र आर्थिक क्रियाओं का अध्ययन है। इसमें मुख्यत: उत्पादन, वितरण एवं उपभोग का अध्ययन किया जाता है। प्रमुख विद्वानों ने अर्थशास्त्र को निम्न प्रकार से परिभाषित किया है-
फेयरचाइल्ड (Fairchild) के अनुसार-“अर्थशास्त्र मनुष्य की उन क्रियाओं का अध्ययन है, जो मनुष्य की आवश्यकताओं की संतुष्टि के लिए भौतिक साधनों की प्राप्ति हेतु की जाती है।”
मार्शल (Marshall) के अनुसार–‘अर्थशास्त्र मनुष्य के धनोपार्जन के दृष्टिकोण से मनुष्य जाति का अध्ययन है।”
रॉबिन्स (Robbins) के अनुसार-“अर्थशास्त्र वह विज्ञान है जो कि मानवीय आचरणों का साध्य एवं साधनों के विभिन्न प्रयोगों के पारस्परिक संबंधों की दृष्टि से अध्ययन करता है।”
अर्थशास्त्र की परिभाषाओं से स्पष्ट है कि अर्थशास्त्र वस्तुओं और सेवाओं के उत्पादन एवं वितरण का अध्ययन करता है तथा इसका मुख्य विषय आर्थिक क्रियाएँ हैं। शास्त्रीय आर्थिक दृष्टिकोण पूर्ण रूप से आर्थिक चरों के अंतर्संबंधों (जैसे कीमत, माँग एवं पूर्ति का संबंध) का वर्णन करता है। इसमें मुख्य रूप से इस बात पर विचार किया जाता है कि उत्पादन के साधनों को अर्जन किस प्रकार किया जा सकता है और उससे संबधित विभिन्न नियम क्या-क्या हैं, परंतु उत्पादन के साधनों को संबंध मनुष्य । से होता है और मनुष्य समाज की क्रियाशील सदस्य है। समाजशास्त्र के माध्यम से सामाजिक संबंधों को समझने का प्रयास किया जाता है और अर्थशास्त्र द्वारा समाज और व्यक्ति की आर्थिक गतिविधियों को समझने का प्रयास किया जाता है। अन्य शब्दों में हम कह सकते हैं कि अर्थशास्त्र आर्थिक संबंधों का अध्ययन करता है और समाजशास्त्र सामाजिक संबंधों का, परंतु आर्थिक संबंध सामाजिक संबंधों पर आश्रित होते हैं। वास्तव में, आर्थिक संबंध सामाजिक संबंधों के गुच्छे की एक कड़ी मात्र है। इस प्रकार, अर्थशास्त्र और समाजशास्त्र दोनों एक-दूसरे के अत्यधिक निकट हो जाते हैं, दोनों एक-दूसरे को प्रभावित करते हैं। जैसे-जैसे आर्थिक प्रक्रिया समाज में विकसित होती है, वैसे-वैसे सामाजिक जीवन भी प्रभावित होता है; अर्थात् आर्थिक परिवर्तन सामाजिक परिवर्तन के प्रति भी उत्तरदायी होते हैं। इस कारण ही कुछ अर्थशास्त्रियों ने आर्थिक परिवर्तन के आधार पर सामाजिक परिवर्तनों के स्वरूप की व्याख्या की है। समाज के रीति-रिवाज, परंपराएँ, रूढ़ियाँ तथा कानून आदि परिस्थितियों द्वारा प्रभावित होते रहते हैं। अर्थशास्त्र की विभिन्न क्रियाएँ; जैसे—उत्पादन, वितरण तथा उपभोग इत्यादि; समाज में ही क्रियांवित होती हैं और सामाजिक जीवन को प्रभावित करती है। औद्योगिक विकास ने पूँजीवाद को जन्म दिया तथा पूँजीवाद ने संघर्ष को। मैकाइवर एवं पेज (Maclver and Page) ने ठीक ही लिखा है, “आर्थिक घटनाएँ सदैव सामाजिक आवश्यकताओं और क्रियाओं से प्रभावित होती है और स्वयं भी उन्हें सदा प्रभावित करती हैं।’ कार्ल मार्क्स (Karl Marx) आर्थिक कारणों को ही सामाजिक परिवर्तन का मुख्य कारण मानते हैं। इस प्रकार हम देखते हैं कि समाजशास्त्र और अर्थशास्त्र में परस्पर घनिष्ठ संबंध है। अनेक विद्वानों का तो मत यह है कि समाज की समस्त समस्याओं का समाधान केवल आर्थिक व्यवस्था के सुधार में हैं। इस कारण ही अर्थशास्त्र को समाजशास्त्र की एक शाखा भी माना जाता है। थॉमस (Thomas) के शब्दों में, “वास्तव में अर्थशास्त्र समाजशास्त्र के विस्तृत विज्ञान की एक शाखा है।”
इसी प्रकार, सिल्वरमैन (Silverman) ने लिखा है, “साधारण कार्यों के लिए अर्थशास्त्र को पितृविज्ञान समाजशास्त्र, जो सामाजिक संबंधों के सामान्य सिद्धांत का अध्ययन करता है, की एक शाखा माना जा सकता है।”
समाजशास्त्र और अर्थशास्त्र में निम्नलिखित प्रमुख अंतर पाए जाते हैं-
- समाजशास्त्र में सामाजिक संबंधों को संपूर्ण रूप से अध्ययन किया जाता है, परंतु अर्थशास्त्र में केवल आर्थिक संबंधों का ही अध्ययन किया जाता है। इस स्थिति में यह कहा जा सकता है कि अर्थशास्त्र एक सीमित विज्ञान है, जबकि समाजशास्त्र एक विस्तृत विज्ञान है।।
- समाजशास्त्र के क्षेत्र में संपूर्ण समाज सम्मिलित है, जबकि अर्थशास्त्र में केवल इसका आर्थिक पक्ष ही सम्मिलित है।
- समाजशास्त्र में समाज का अध्ययन किया जाता है, उसकी इकाई समूह है; परंतु अर्थशास्त्र की इकाई मनुष्य है तथा उसके आर्थिक पक्ष की विवेचना की जाती है।
- समाजशास्त्र एक सामान्य सामाजिक विज्ञान है, जबकि अर्थशास्त्र एक विशिष्ट सामाजिक विज्ञान है।
- समाजशास्त्र की अध्ययन पद्धतियाँ अर्थशास्त्र की अध्ययन पद्धतियों से भिन्न हैं, क्योंकि अर्थशास्त्र में केवल आगमन तथा निगमन पद्धतियों का ही मूल रूप से, प्रयोग किया जाता है। इसके विपरीत, समाजशास्त्र में सामाजिक सर्वेक्षण, समाजमिति तथा निरीक्षण आदि विभिन्न अध्ययन प्रविधियों एवं ऐतिहासिक, तुलनात्मक संरचनात्मक-प्रकार्यात्मक आदि पद्धतियों को अपनाया जाता है।
(ब) समाजशास्त्र और इतिहास
समाजशास्त्र और इतिहास सदा एक-दूसरे के निकट रहे हैं। सर्वप्रथम हमें यह समझना है कि ‘इतिहास’ का अर्थ क्या है? अंग्रेजी के शब्द ‘History’ का जन्म ग्रीक शब्द historica’ से हुआ है। जिसका अर्थ है ‘वास्तविक रूप में क्या घटित हुआ। इस अर्थ में इतिहास केवल निरंतर घटित होने वाली घटनाओं का निष्पक्ष लेखा-जोखा मात्र है। कुछ विद्वानों के विचार में इतिहास केवल युद्धों का ही विवेचन करता है, परंतु यह धारणा भ्रामक है, क्योंकि इतिहास मानव-समाज के प्रत्येक पहलू का विवेचन करता है। इतिहास की सबसे सुंदर परिभाषा रेपसन ने इन शब्दों में दी है, “इतिहास घटनाओं या विचारों की प्रगति का एक सुसंबद्ध विवरण है। इस प्रकार इतिहास एक सुसंगठित एवं क्रमबद्ध ज्ञान है, जिससे घटनाओं का तारतम्यता के साथ वर्णन किया जाता है। घाटे के अनुसार, “इतिहास हमारे संपूर्ण भूतकाल का वैज्ञानिक अध्ययन तथा लेखा-जोखा अर्थात् ज्ञात प्रमाण है।”
इतिहास की परिभाषाओं से यह स्पष्ट हो जाता है कि इसमें मानव जाति के कार्यों का अध्ययन किया जाता है तथा इनका ठोस विवरण प्रस्तुत किया जाता है। इसमें भूतकाल घटनाओं का निरूपण किया जाता है। परंपरागत इतिहास केवल राजाओं और युद्ध की घटनाओं का वर्णन करने वाला विषय मात्र था, परंतु अब इतिहास के अध्ययन को ध्येय सभी प्रकार के आर्थिक, सामाजिक व राजीतिक परिवर्तनों का अध्ययन करना है। इतिहास में अतीतकालीन घटनाओं, सभ्यता एवं संस्कृति का अध्ययन किया जाता है जो कि समाजशास्त्री को समाज के विभिन्न पहलुओं का अध्ययन करने में विशेष रूप से सहायक है; अर्थात् समाजशास्त्र के अध्ययन में ऐतिहासिक पृष्ठभूमि को समझना परम आवश्यक है। पालवर्क के शब्दों में, “संस्कृति और संस्थाओं का इतिहास, समाजशास्त्र को समझने और सामग्री | जुटाने में सहायक होता हैं। जिस प्रकार समाजशास्त्र के अध्ययन में ऐतिहासिक पृष्ठभूमि की आवश्यकता पड़ती है, उसी प्रकार इतिहास के अध्ययन में भी सामाजिक पृष्ठभूमि को समझना आवश्यक होता है। प्रत्येक ऐतिहासिक घटना को अपना पृथक् सामाजिक मूल्य होता हैं, परंतु ऐतिहासिक घटनाओं का सामाजिक महत्त्व समझे बिना इतिहास का अध्ययन व्यर्थ हो जाता है। इस प्रकार समाजशास्त्र इतिहास के अध्ययन को उपयोगी और सरल बनाने में सहायक होता है। गिलिन तथा गिलिन ने ठीक लिखा है, “यदि समुचित रूप से विचार किया जाए तो इतिहासकार सामान्य रूप से उस सामाजिक अतीत का अध्ययन करता हैं, जिसे मानव द्वारा लिपिबद्ध कर लिया गया हो।” समाजशास्त्र और इतिहास के घनिष्ठ संबंधों के कारण ही जॉर्ज ई० होवार्ट ने लिखा है, “इतिहास भूतकालीन समाजशास्त्र है, जबकि समाजशास्त्र वर्तमान इतिहास है। आधुनिक युग में इतिहासकार समाजशास्त्रीय दृष्टिकोण रखकर ही अध्ययन करता है। समाजशास्त्री भी अतीत की सभ्यताओं के सामाजिकु पक्षों में प्रचलित ऐतिहासिक ज्ञान का प्रयोग करने लगे हैं। समाजशास्त्र और इतिहास के संबंधों पर प्रकाश डालते हुए राइट लिखते हैं, “किसी सीमा तक समाजशास्त्री और इतिहासवेत्ताओं के क्षेत्र समान है। इतिहासवेक्ता से इस प्रकार से प्राप्त किए ज्ञान को वर्तमान और भविष्य की समस्याओं के विश्लेषण से संबंधित करके समाजशास्त्री इस कार्य को आगे बढ़ाता है। समाजशास्त्री को इतिहासवेत्ता के परिणामों को उसी प्रकार ग्रहण करना चाहिए, जिस प्रकार वह एक वैज्ञानिक और मनोवैज्ञानिक के परिणामों को स्वीकार करता है तथा इसको समाज के अध्ययन से संबंधित करना चाहिए।”
समाजशास्त्र एवं इतिहास में मुख्य रूप से निम्नलिखित अंतर पाए जाते हैं-
- इतिहास में अधिकतर अतीतकालीन घटनाओं का ही अध्ययन किया जाता है, जबकि समाजशास्त्र समकालीन समय या कुछ पहले के अतीत की सामाजिक घटनाओं का अध्ययन करता है तथा उनके आधार पर भविष्यवाणी. भी करता है।
- समाजशास्त्र में घटनाओं के कारणों की खोज की जाती है और उसी के द्वारा वह अपनी विषय-वस्तु का निर्धारण करता है। इतिहास कारणों की खोज पर अधिक बल न देकर घटनाओं के यथासंभव वर्णन पर बल देता है।
- समाजशास्त्र एक विज्ञान है, परंतु इतिहास को विज्ञान की श्रेणी में नहीं रखा जा सकता। उल्फ समाजशास्त्र और इतिहास में भेद करते हुए लिखते हैं, “इतिहास विशेष राष्ट्रों, संस्थाओं, अनुसंधानों या अंवेषणों में रुचि लेता हैं, संस्थाओं और राष्ट्रों आदि से संबंधित नियमों में नहीं। ऐसे सामान्य नियम नृवंशशास्त्र (Ethnology), मानवशास्त्र, समाजशास्त्र तथा मनोविज्ञान में होते। हैं जो कि विज्ञान हैं, इतिहास नहीं।”
- ऐतिहासिक अध्ययन में किसी विशिष्ट समाज की क्रमबद्ध अध्ययन किया जाता है, जबकि समाजशास्त्र सर्वांगीण समाज का अध्ययन करता है।
- इतिहास मूर्त हैं, उसका संबंध स्थूल घटनाओं से है; परंतु समाजशास्त्र अमूर्त है, उसमें मुख्य रूप से सामाजिक संबंधों का अध्ययन किया जाता है जो कि अमूर्त हैं। पार्क के शब्दों में, “इसी अर्थ में इतिहास मूर्त तथा समाजशास्त्र मानवीय अनुभव एवं स्वभाव का अमूर्त विज्ञान है।”
- इतिहास में घटनाओं का यथातथ्य वर्णन किया जाता है, जबकि समाजशास्त्र इन समस्याओं का विश्लेषण करने के साथ-साथ उनको सुलझाने के साधन भी जुटाता है।
- इतिहास व्यक्ति के कार्यकलापों पर बल देता है, जबकि समाजशास्त्र के अध्ययन की इकाई मानव-समूह है।
- समाजशास्त्र वैज्ञानिक पद्धति का प्रयोग करता है, जबकि इतिहास मुख्यतया ऐतिहासिक पद्धति का।
- इतिहास एवं समाजशास्त्र में दृष्टिकोण का भी अंतर है। इतिहास मुख्य रूप से असाधारण घटनाओं का ही अध्ययन करता है, जबकि समाजशास्त्र मुख्य रूप से साधारण घटनाओं का अध्ययन करता है तथा अपवादों की अवहेलना करता है।

(स) समाजशास्त्र और मनोविज्ञान
समाजशास्त्र और मनोविज्ञान दोनों परस्पर संबंधित विज्ञान हैं। दोनों के संबंधों पर प्रकाश डालने से पूर्व यह आवश्यक है कि मनोविज्ञान को अर्थ समझा जाए। मनोविज्ञान को मुख्य रूप से व्यवहार के विज्ञान के रूप में परिभाषित किया जाता है तथा यह व्यक्ति से संबंधित है। मनोविज्ञान की प्रमुख परिभाषाएँ निम्न प्रकार हैं-
वुडवर्थ (Woodworth) के अनुसार-“मनोविज्ञान वातावरण के संबंध में व्यक्ति की क्रियाओं का अध्ययन करने वाला विज्ञान है।”
स्किनर (Skinner) के अनुसार-“मनोविज्ञान विविध परिस्थितियों के प्रति प्राणी की प्रतिक्रियाओं का अध्ययन करता है। प्रतिक्रियाओं अथवा व्यवहार से तात्पर्य प्राणी को सभी प्रकार की प्रतिक्रियाओं, समायोजन क्रियाओं तथा अनुभवों से हैं। इस प्रकार यह कहा जा सकता है कि मनोविज्ञान मानवे व्यवहार का एक विज्ञान है।
उपर्युक्त परिभाषाओं के विश्लेषण से स्पष्ट हो जाता है कि मनोविज्ञान मानव-व्यवहार का अध्ययन करने वाला एक प्रमुख विज्ञान है। मनोविज्ञान में मुख्यतया व्यक्ति की समायोजन संबंधी समस्याओं का अध्ययन किया जाता है, जिन्हें सुलझाने के लिए उसके सामाजिक परिवेश को समझना आवश्यक है। इस कार्य में समाजशास्त्र ही सहायता पहुँचा सकता है। इस प्रकार हम कह सकते हैं कि समाजशास्त्र मनोविज्ञान के अध्ययन में विशेष रूप से सहायक होता है।
दूसरे; समाजशास्त्र एवं मनोविज्ञान दोनों ही मानसिक प्रक्रियाओं का अध्ययन करते हैं। दोनों विषयों का संबंध प्रत्यक्ष मस्तिष्क से होता है। दोनों का ही अध्ययन-क्षेत्र मानव-व्यवहार है। समाजशास्त्र में सामाजिक संबंधों को जानने के लिए व्यवहार का अवलोकन किया जाता है। उसका प्रमुख विषये पर्यावरण के संदर्भ में व्यक्ति के व्यवहार को समझना है, जिसके लिए मनोविज्ञान का सहारा लेना आवश्यक हो जाता है। वास्तव में, मनुष्य की प्रकृति की समस्याओं की व्याख्या के लिए दो विज्ञानों का सहयोग परम आवश्यक है। मैकाइवर तथा पेज इस विषय में लिखते हैं, “समाजशास्त्र विशेष रूप से मनोविज्ञान को सहायता देता है, जिस प्रकार मनोविज्ञान समाजशास्त्र को विशेष सहायता देता है।” समाजशास्त्र और मनोविज्ञान के संयोग से एक नवीन विज्ञान का जन्म हुआ जिसे सामाजिक मनोविज्ञान कहकर पुकारा जाता है। यह विषय समाजशास्त्र और मनोविज्ञान को परस्पर संबंधित करता हैं। इस कारण ही सामाजिक मनोविज्ञान को समाजशास्त्र और मनोविज्ञान दोनों की शाखा माना जाता है। मोटवानी ने लिखा है कि “सामाजिक मनोविज्ञान; मनोविज्ञान व समाजशास्त्र के बीच की कड़ी है।” सामाजिक मनोविज्ञान; समाजशास्त्र व मनोविज्ञान के संबंधों पर प्रकाश डालता है। क्रच एवं क्रचफील्ड के अनुसार, सामाजिक मनोविज्ञान समाज में व्यक्ति के व्यवहार का विज्ञान है। सामाजिक मनोविज्ञान की परिभाषा ही उसे समाजशास्त्र के निकट ले आती है, क्योंकि इस परिभाषा के अनुसार सामाजिक मनोविज्ञान व्यक्ति की समाज के साथ प्रतिक्रिया पर बल देता है। इस प्रकार समाजशास्त्र और सामाजिक मनोविज्ञान दोनों ही संमाज से संबधित हैं। समाजशास्त्र में मानव व्यवहार के उन सब रूपों का अध्ययन होता है, जो समूह के लिए समस्याएँ होते हैं। सामाजिक मनोविज्ञान में उस व्यक्तिगत व्यवहार का अध्ययन होता है जो कि समूह में दृष्टिगोचर होता है। इस प्रकार हम देखते हैं कि स्पष्ट रूप से सामाजिक मनोविज्ञान तथा समाजशास्त्र की पाठ्य-वस्तु में अलगाव नहीं है। लेपियर तथा फ्रांसवर्थ के अनुसार, “सामाजिक मनोविज्ञान; समाजशास्त्र तथा मनोविज्ञान के लिए उसी प्रकार है, जिस प्रकार शारीरिक रसायनशास्त्र; जीवशास्त्र तथा रसायनशास्त्र के लिए है।”
समाजशास्त्र एवं मनोविज्ञान में पाए जाने वाले मुख्य अंतर निम्नवर्णित हैं-
- मनोविज्ञान का दृष्टिकोण वैयक्तिक है, जबकि समाजशास्त्र का दृष्टिकोण सामूहिक है। भले ही दोनों विज्ञानों की सामग्री एक ही हैं, फिर भी अध्ययन के दृष्टिकोणों में अंतर के कारण इनमें पर्याप्त अंतर आ जाती है।
- समाजशास्त्र में मुख्य रूप से व्यक्ति के सामाजिक व्यवहार के बाह्य पक्ष का ही अध्ययन होता है जो कि सामाजिक संबंधों के रूप में प्रकट होता है, जबकि मनोविज्ञान व्यक्ति के केवल | मानसिक पक्ष का ही अध्ययन करता है।
- मनोविज्ञान की इकाई व्यक्ति है, जबकि समाजशास्त्र में समूह को इकाई माना जाता है।
- मनोविज्ञान और समाजशास्त्र की अध्ययन पद्धतियों में भी अंतर है। मनोविज्ञान में मुख्य रूप से प्रयोगात्मक और विकासात्मक पद्धतियों को अपनाया जाता है, जबकि समाजशास्त्र में अन्य पद्धतियों को अधिक अपनाया जाता है।
- समाजशास्त्र एवं मनोविज्ञान में क्षेत्र संबंधी अंतर भी है। समाजशास्त्र एक सामान्य विज्ञान है तथा | इसका क्षेत्र अत्यधिक विस्तृत है, जबकि मनोविज्ञान एक विशिष्ट विज्ञान है तथा इसका क्षेत्र सीमित है।
(द) समाजशास्त्र और राजनीतिशास्त्र
समाजशास्त्र और राजनीतिशास्त्र का परस्पर घनिष्ठ संबंध है। राजनीतिशास्त्र का संबंध मुख्यतया राज्य, राजनीतिक संस्थाओं व राजनीतिक व्यवहार से है तो समाजशास्त्र का सम्पूर्ण समाज, सामाजिर्क संस्थाओं तथा सामाजिक व्यवहार से। ऐसी दशा में दोनों में परस्पर घनिष्ठता का होना स्वभाविक ही है, परंतु इसका अर्थ यह नहीं है कि दोनों में अंतर नहीं है। समाजशास्त्र तथा राजनीतिशास्त्र के संबंधों पर प्रकाश डालने से पूर्व राजनीतिशास्त्र का अर्थ स्पष्ट कर लेना अनिवार्य है। प्रमुख विद्वानों ने राजनीतिशास्त्र को अग्रांकित रूप से परिभाषित किया है-
1. गैटिल (Gattle) के अनुसार-“राजनीतिशास्त्र राज्य का विज्ञान है। इसके अतंर्गत हम राजनीतिक समुदायों, शासन के संगठन, कानून की व्यवस्था तथा अन्य राज्य संबंधों का अध्ययन करते हैं। यह मानव के उन संबंधों का अध्ययन करता है, जिन पर राज्य का नियंत्रण होता है।”
2. पॉल जैनेट (Paul Jenett) के अनुसार–राजनीतिशास्त्र विज्ञान का वह भाग है, जिसमें राज्य के आधार तथा शासन के सिद्धांतों पर विचार किया जाता है।” राजनीतिशास्त्र की परिभाषाओं के आधार पर यह कहा जा सकता है कि राजनीतिशास्त्र एक विशेष प्रकार का सामाजिक विज्ञान है, जो व्यक्ति के उस राजनीतिक जीवन का अध्ययन करता है, जो संपूर्ण सामाजिक जीवन का अंग है। यह विषय समाज की एक विशेष संगठित राजनीतिक इकाई में रुचि रखता है, जिसे राज्य कहा जाता है। राज्य का मानव-जीवन से अप्रत्यक्ष संबंध होता है; अतः राजनीतिशास्त्र मनुष्य का राजनीतिक प्राणी के रूप में अध्ययन करता है। यदि राजनीतिशास्त्र मनुष्य का राजनीतिक प्राणी के रूप में अध्ययन करता है तो समाजशास्त्र बताता है कि मनुष्य क्यों और कैसे राजनीतिक प्राणी बना। इस प्रकार दोनों विज्ञानों के अध्ययन के विषय मानव-जीवन के क्रियाकलाप हैं; अत: दोनों के मध्य आदान-प्रदान चलता रहता है। समस्त राजनीतिक संस्थाएँ सामाजिक व्यवस्थाओं से प्रभावित होती हैं तथा प्रत्येक राज्य कानूनों का निर्माण करते समय सामाजिक संस्थाओं का सदा ध्यान रखता है। वास्तव में राजनीतिशास्त्र को ठीक प्रकार से समझने के लिए समाजशास्त्र का अध्ययन आवश्यक हो जाता है। गिडिंग्स का यह कहना पूर्णतया सत्य है कि समाजशास्त्र के प्रारंभिक सिद्धांतों से अनभिज्ञ लोगों को राज्य के सिद्धांतों को पढ़ाना वैसे ही व्यर्थ है, जैसे न्यूटन द्वारा बताए गए गति-नियमों को न जानने वाले व्यक्ति को खगोलशास्त्र अथवा ऊष्मा विज्ञान पढ़ाना।”
यदि एक ओर राजनीतिशास्त्र को समझने के लिए समाजशास्त्र सहायक होता है, तो दूसरी ओर समाजशास्त्र भी राजनीतिशास्त्र से सहायता प्राप्त करता है। राजनीतिशास्त्र समाजशास्त्र को समाज के सामान्य सामाजिक संगठन के अंग के रूप में राज्य के संगठन और कार्यों से संबंधित तथ्यों को प्रदान करता है। समाजशास्त्र को राजनीतिशास्त्र से उन सिद्धान्तों का ज्ञान प्राप्त होता है, जिनकी संगठित संबंधों से उत्पत्ति होती है। समाजशास्त्र राजनीतिशास्त्र को न केवल अध्ययन-पद्धति उपलब्ध कराता है, अपितु राजनीतिशास्त्र की शब्दावली को तीक्ष्ण बनाने में सहायता प्रदान करता है। इस प्रकार हम देखते हैं कि राजनीतिशास्त्र और समाजशास्त्र एक-दूसरे से घनिष्ठ रूप से संबंधित हैं। इस विषय पर एफ० जी० विल्सन लिखते हैं, “वास्तव में यह मान लिया जाना चाहिए कि अक्सर यह निश्चित करना बहुत कठिन होता है कि कोई विशेष लेखक समाजशास्त्री माना जाए या राजनीतिशास्त्री या दार्शनिक?’
बार्स के अनुसार, “समाजशास्त्र और आधुनिक राजनीतिक सिद्धांत के विषय में सबसे अधिक मइत्त्वपूर्ण बात यह है कि राज्य सिद्धांत के पिछले तीस वर्षों में जो परिवर्तन हुए हैं, उनमें से अधिकतर समाजशास्त्र द्वारा सुझाए हुए और बतलाए गए मार्ग पर ही हुए हैं।”
राजनीतिक समाजशास्त्र एक ऐसा विषय है, जो दोनों विषयों को परस्पर निकट लाता है। राजनीतिक समाजशास्त्र में राज्य अथवी राजीनीतिक संस्थाओं तथा समाज अथवा सामाजिक संस्थाओं के परस्पर प्रभाव को अध्ययन किया जाता है; अर्थात् इसमें राजनीतिक तथा सामाजिक दृष्टिकोणों को एक समान महत्त्व दिया जाता है।
समाजशास्त्र तथा राजनीतिशास्त्र में निम्नलिखित प्रमुख अंतर पाए जाते हैं-
- समाजशास्त्र अपने विस्तृत अर्थ में समाज के समस्त स्वरूपों एवं पहलुओं का अध्ययन करता है। जबकि राजनीतिशास्त्र में केवल राज्य और सरकार तथा राजनीतिक स्वरूपों का अध्ययन किया जाता है। गिलक्राइस्ट के शब्दों में, “समाजशास्त्र समाज का विज्ञान है, राजनीतिशास्त्र राज्य अथवा राजनीतिक समाज का विज्ञान है। समाजशास्त्र मानव का एक सामाजिक प्राणी के रूप में अध्ययन करता है। चूंकि राजनीतिक संगठनका एक विशेष तरह का सामाजिक संगठन है, इसलिए राजनीतिशास्त्र समाजशास्त्र की अपेक्षा अधिक विशिष्ट है।”
- राजनीतिशास्त्र में केवल उन नियंत्रणों का अध्ययन किया जाता है, जिन्हें राज्य द्वारा स्वीकार किया जाता है, जबकि समाजशास्त्र में सामाजिक नियंत्रणों के समस्त साधनों (जैसे रूढ़ियों, प्रथाओं, परंपराओं, आदर्शों इत्यादि) का भी अध्ययन किया जाता है। दूसरे शब्दों में यह कहा जा सकता है कि राजनीतिशास्त्र में संस्थागत व्यवहार का ही अध्ययन किया जाता है। इन तथ्यों के आधार पर कहा जा सकता है कि राजनीतिशास्त्र तथा समाजशास्त्र में दृष्टिकोण संबंधी अंतर भी है। समाजशास्त्र का दृष्टिकोण राजनीतिशास्त्र की तुलना में अधिक व्यापक है।।
- समाजशास्त्र संगठित तथा असंगठित दोनों प्रकार के समुदायों का अध्ययन करता है, परंतु राजनीतिशास्त्र का संबंध केवल संगठित समुदायों और समाजों का अध्ययन करना ही है। अराजनीतिक समुदाय से उसका कोई संबंध नहीं है।
- समाजशास्त्र में समाज का अध्ययन मुख्यतया सामाजिक दृष्टिकोण को ध्यान में रखकर किया | जाता है, जबकि राजनीतिशास्त्र में राजनीतिक अथवा शासकीय दृष्टिकोण को अपनाया जाता है।
- समाजशास्त्र व्यक्ति के चेतन और अचेतनं दोनों प्रकार के व्यवहार से संबंधित है, परंतु राजनीतिशास्त्र केवल चेतन व्यवहार से संबंधित है।

(य) समाजशास्त्र एवं सामाजिक मानव विज्ञान
विश्व के विभिन्न देशों में मानवविज्ञान में पुरातत्व विज्ञान, भौतिक मानवविज्ञान, सांस्कृतिक इतिहास, भाषा की विभिन्न शाखाएँ और सामान्य समाजों में जीवन के सभी पक्षों का अध्ययन सम्मिलित किया जाता है। यहाँ सामाजिक मानवविज्ञान और सांस्कृतिक मानवविज्ञान से समाजशास्त्र के संबंधों की बात है क्योंकि यह समाजशास्त्र के अध्ययन से संबंध है। समाजशास्त्र को आधुनिक जटिल समाजों का अध्ययन माना गया है जबकि सामाजिक मानवविज्ञान को सरल समाजों का अध्ययन माना गया है। प्रत्येक विषय का अपना अलग इतिहास या विकास यात्रा होती है। सामाजिक मानवविज्ञान का विकास पश्चिम में उन दिनों हुआ जब यह माना जाता था कि पश्चिमी शिक्षित सामाजिक मानवविज्ञानियों ने गैर-यूरोपियन समाजों का अध्ययन किया जिनको प्रायः विजातीय, अशिष्ट और असभ्य समझा जाता था। जिनका अध्ययन किया गया और जिनका अध्ययन नहीं किया गया था, उनके मध्य असमान संबंध पर अधिक प्रकाश नहीं डाला गया। लेकिन अब समय बदल गया है और अब वे मूल निवासी विद्यमान हैं, चाहे वे भारतीय हैं या सूडानी, नागा हैं या संथाल, जो अब अपने समाजों के बारे में बोलते हैं और लिखते हैं। अतीत के मानवविज्ञानियों ने सरल समाजों का विवरण तटस्थ वैज्ञानिक तरीके से लिखा था। प्रत्यक्ष व्यवहार में वे निरंतर उन समाजों की तुलना आधुनिक पश्चिमी समाजों से करते रहे थे, जिसे वे एक मानदंड के रूप में देखते थे।
अन्य परिवर्तनों ने भी समाजशास्त्र और सामाजिक मानवविज्ञान की प्रकृति को पुन: परिभाषित किया आधुमिकता ने एक ऐसी प्रक्रिया की शुरुआत की जिसमें छोटे से छोटा गाँव भी भूमण्डलीय प्रक्रियाओं से प्रभावित हुआ। इसका प्रत्यक्ष उदाहरण है-उपनिवेशवाद। ब्रिटिश उपनिवेशवाद काल में भारत के अत्यधिक दूरस्थ गाँवों ने भी अपने प्रशासन और भूमि कानूनों में परिवर्तन, अपने राजस्व उगाही में परिवर्तन और अपने उत्पादक उद्योग को समाप्त होते हुए देखा था। समकालीन भूमण्डलीय प्रक्रियाओं ने ‘विश्व के इस प्रकार सिकुड़ने’ को और अधिक बल प्रदान किया है। एक सरल समाज का अध्ययन करते समय यह मान्यता थी कि यह एक सीमित समाज है किंतु आज ऐसा नहीं है।
सामाजिक मानवविज्ञान द्वारा सरल व निरक्षर समाजों पर किए गए परंपरागत अध्ययन का प्रभाव मानवविज्ञान की विषवस्तु और विषय सामग्री पर भी पड़ा। सामाजिक मानवविज्ञान की प्रवृत्ति समाज (सरल समाज) के सभी पक्षों का एक समग्र में अध्ययन करने की होती थी। अभी तक जो विशेषज्ञता प्राप्त हुई है वह क्षेत्र पर आधारित थी। उदाहरण के लिए अंडमान द्वीप समूह, नूअर अथवा मेलैनेसिया समाजशास्त्री जटिल समाजों का अध्ययन करते हैं, अत: समाज के भागों जैसे नौकरशाही अथवा धर्म या जाति अथवा एक प्रक्रिया जैसे सामाजिक गतिशीलता पर अपना ध्यान केंद्रित करते हैं। सामाजिक मानवविज्ञान की विशेषताएँ थीं, लंबी क्षेत्रीय कार्य, परंपरा, समुदाय जिसका अध्ययन किया उसमें रहना और अनुसंधान की नृजाति पद्धतियों का उपयोग। समाजशास्त्री प्रायः सांख्यिकी एवं प्रश्नावली विधि का प्रयोग करते हुए सर्वेक्षण पद्धति एवं संख्यात्मक आँकड़ों पर निर्भर करते हैं। आज एक सरल और जटिल समाज में अंतर को स्वयं एक बड़े पुनर्विचार की आवश्यकता है। भारत स्वयं परंपरा और आधुनिकता का, गाँव और शहर, जाति और जनजाति का, वर्ग एवं समुदाय का एक जटिल मिश्रण है। गाँव राजधानी दिल्ली के बीचों-बीच निवास करते हैं। कॉल सेंटर देश के विभिन्न कस्बों से यूरोपीय और अमेरिकी ग्राहकों की सेवा करते हैं।
भारतीय समाजशास्त्र दोनों परंपराओं से भार ग्रहण करने में अत्यधिक उदार रहा है। भारतीय समाजशास्त्री अक्सर भारतीय समाजों के अध्ययन में केवल अपनी संस्कृति का नहीं बल्कि उनका भी अध्ययन करते हैं जो उनकी संस्कृति का अंग नहीं है। यह शहरी आधुनिक भारत के जटिल अंतर करने वाले समाजों के साथ-साथ जनजातियों का भी एक समग्र रूप में अध्ययन कर सकता है। इस बात का डर बना रहता था कि सरल समाजों के समाप्त होने से सामाजिक मानवविज्ञान अपनी विशिष्टता खो देगा और समाजशास्त्र में मिल जाएगा। हालाँकि दोनों विषयों में लाभदायक अन्त:परिवर्तन हुए हैं और वर्तमान पद्धतियों एवं तकनीकों को दोनों विषयों से लिया जाता है। राज्य और वैश्वीकरण के मानवविज्ञानी अध्ययन किए गए हैं जोकि सामाजिक मानवविज्ञान की परंपरागत विषय-वस्तु से एकदम अलग हैं। दूसरी ओर समाजशास्त्र भी आधुनिक समाजों की जटिलताओं के अध्ययन के लिए संख्यात्मक एवं गुणात्मक तकनीकों, समष्टि और व्यष्टि उपागमों का उपयोग करता है क्योंकि भारत में समाजशास्त्र और सामाजिक मानवविज्ञान में अति निकट का संबंध रहा है।
प्रश्न 4.
समाजशास्त्र के विषय-क्षेत्र के संबंध में स्वरूपात्मक एवं समन्वयात्मक संप्रदाय संबंधी विचारों को समझाइए।
या
समाजशास्त्र की परिभाषा दीजिए तथा इसके अध्ययन-क्षेत्र की विवेचना कीजिए।
या
समाजशास्त्र की परिभाषा दीजिए। इसके विषय-क्षेत्र के किसी एक संप्रदाय की व्याख्या कीजिए।
या
‘समाजशास्त्र सामाजिक संबंधों का अध्ययन है।’ इस कथन के परिप्रेक्ष्य में समाजशास्त्र के अध्ययन-क्षेत्र की विवेचना कीजिए।
उत्तर
प्रत्येक विषय का अपना-अपना विषय-क्षेत्र होता है। इस विषय-क्षेत्र के आधार पर ही प्रत्येक विषय दूसरे विषयों से अलग हो जाता है। अन्य विषयों के समान ही समाजशास्त्र का भी अपना क्षेत्र है, परंतु एक आधुनिक एवं विस्तृत विज्ञान होने के कारण इसका विषय-क्षेत्र निर्धारित करना कठिन हैं। * यह कठिनाई विद्वानों के विचारों में मतभेद के कारण और अधिक बढ़ जाती है। कुछ विद्वान इसे समस्त सामाजिक विज्ञानों का मूल आधार मानते हैं तो कुछ इसे अनेक विषयों का भंडार या स्वामी बनाने की भूल करते हैं। कालबर्टन (Calberton) ने इस संदर्भ में उचित ही लिखा है, “समाजशास्त्र एक लचीला विज्ञान है, इसकी सीमाओं का आदि और अंत निर्धारित करना कठिन है। कहीं समाजशास्त्र सामाजिक मनोविज्ञान बन जाता है और कहीं आर्थिक सिद्धांत समाजशास्त्रीय विचारधारा बन जाता है। या प्राणिशास्त्रीय विचारधारा बन जाता है; अतः इसकी सीमा निश्चित करना असंभव है।” [संकेत-समाजशास्त्र की परिभाषा हेतु विस्तृत उत्तरीय प्रश्न 1 का उत्तर देखें।]
समाजशास्त्र का विषय-क्षेत्र
मतभेदों के बावजूद, समाजशास्त्र के विषय-क्षेत्र को दो प्रमुख संप्रदायों द्वारा स्पष्ट करने का प्रयास किया गया है जो कि इस प्रकार हैं–
(अ) विशेषात्मक संप्रदाय तथा
(ब) समन्वयात्मक संप्रदाय।
इन दोनों संप्रदायों को विस्तारपूर्वक समझकर, समाजशास्त्र के विषय-क्षेत्र का अनुमान लगाया जा सकता है।
(अ) विशेषात्मक या विशिष्टवादी या यथारूपेण संप्रदाय
विशेषात्मक विचारधारा के प्रमुख समर्थक सिमेल (Simmel), रिचार्ड (!Richard), टॉनीज (Tonnies), स्टेमलर (Stemmler), रॉस (Rose), वेबर (Weber), वीरकांत (Vierkant), पार्क (Park), बर्गेस (Burgess) तथा वॉन वीज (Von wiese) हैं। ये विद्वान समाजशास्त्र को विशेष विज्ञान के रूप में मानते हैं। इस संप्रदाय के समर्थक समाजशास्त्र का विषय-क्षेत्र वैसा ही निश्चित तथा परिसीमित कर देना चाहते हैं जैसा कि प्राकृतिक विज्ञान तथा अन्य सामाजिक विज्ञानों का है। इस संप्रदाय की प्रमुख विशेषताएँ निम्नलिखित हैं-
- इस संप्रदाय के समर्थकों के अनुसार समाजशास्त्र का क्षेत्र सामाजिक संबंधों के स्वरूपों का अध्ययन करना होना चाहिए।
- समाज के विभिन्न पक्षों का अध्ययन विभिन्न सामाजिक विज्ञान (जैसे-राजनीतिशास्त्र, इतिहास, अर्थशास्त्र आदि) करते हैं; अतः समाजशास्त्र में इनके अध्ययन की आवश्यकता नहीं है।
- समाजशास्त्र का एक विशिष्ट एवं निश्चित क्षेत्र होना चाहिए।
- समाजशास्त्र एक स्वतंत्र विज्ञान है।
- समाजशास्त्र एक विश्लेषणात्मक विज्ञान है।
इस संप्रदाय के विचारकों के दृष्टिकोण को ठीक प्रकार से समझने के लिए निम्नलिखित प्रमुख समाजशास्त्रियों के विचारों पर प्रकाश डालना आवश्यक है-
1. सिमेल (Simmel) के विचार-जॉर्ज सिमेल के अनुसार समाजशास्त्र में प्रत्यक्ष और वास्तविक व्यवहारों के स्थान पर स्वरूपकीय व्यवहारों का अध्ययन करना चाहिए। उनके अनुसार समाजशास्त्र का अन्य विज्ञानों से वहीं संबंध है जो भौतिक विज्ञानों से रेखागणित का है। जिस प्रकार रेखागणित में भौतिक वस्तुओं की अंतर्वस्तु (Content) का नहीं वरन उसके। स्थान संबंधी स्वरूपों का अध्ययन किया जाता है, उसी प्रकार समाजशास्त्र का क्षेत्र भी। सामाजिक संबंधों और क्रियाओं का नहीं वरन् उनके स्वरूपों का अध्ययन है। सिमेल के अनुसार, सामाजिक संबंध के दो रूप होते हैं-(i) सूक्ष्म तथा (ii) स्थूल। इसके अनुसार समाजशास्त्र में सूक्ष्म संबंधों की विवेचना की जाती है। विभिन्न विज्ञानों में समाजशास्त्र के जो सूक्ष्म सिद्धांत काम कर रहे हैं, उन सिद्धांतों को उन विज्ञानों से अलग करके उनका स्वतंत्र रूप में अध्ययन करना ही समाजशास्त्र का प्रमुख अधिकार-क्षेत्र है। इस प्रकार हम देखते हैं कि विभिन्न सामाजिक विज्ञानों में तो सामाजिक संबंधों का अंतर्वस्तु का अध्ययन करते हैं, परंतु समाजशास्त्र में स्वरूप (Form) का अध्ययन किया जाता है। उदाहरण के लिए–आर्थिक क्रियाओं में उत्पादक, श्रमिक, विक्रेता, क्रेता, अर्थ मंत्री, मिल मालिक आदि सभी का योग रहता है; इन सबकी आर्थिक क्रियाएँ और उनके नियम वह अंतर्वस्तु हैं जिनका कि अध्ययन अर्थशास्त्र में किया जाता है, परंतु इन आर्थिक क्रियाओं में भाग लेने वाले व्यक्तियों में जो परस्पर संबंध है उसके स्वरूप का अध्ययन समाजशास्त्र में किया जाता है।
2. वीरकांत (Vierkant) के विचार-जर्मन समाजशास्त्री वीरकांत के अनुसार समाजशास्त्र का कार्य समाज के उन तत्त्वों का अंवेषण करना है जिनकी उत्पत्ति सामाजिक संबंधों के कारण होती है; उदाहरण के लिए–प्रेम, द्वेष, लज्जा, सहकारिता आदि। ये वे तत्त्व हैं जिनसे सामाजिक एकता उत्पन्न होती है। अन्य शब्दों में, ये संबंध व्यक्तियों को एक-दूसरे से बाँधते । हैं। समाजशास्त्र में इन मूल तत्त्वों या संबंधों का ही अध्ययन किया जाता है। वीरकांत ने समाजशास्त्र के विषय-क्षेत्र को इन शब्दों में स्पष्ट किया है, “समाजशास्त्र उन मानसिक संबंधों के अन्तिम स्वरूपों का अध्ययन है जो कि मनुष्य को एक-दूसरे से बाँधते हैं।”
3. वेबर (Weber) के विचार-मैक्स वेबर के अनुसार समाजशास्त्र सामाजिक क्रिया को समझने और व्याख्या करने में सहायक होता है। उनके अनुसार, सामाजिक व्यवहार दो व्यक्तियों के मध्य तब होता है जबकि वे एक-दूसरे के संपर्क में आते हैं और परस्पर कोई व्यवहार करते हैं। इस पर भी यह आवश्यक नहीं है कि प्रत्येक सामाजिक संबंध सामाजिक व्यवहार ही हो। उदाहरण के लिए दो व्यक्ति साइकिल से टकरा जाते हैं। इस प्रकार का टकराना एक प्राकृतिक घटना है, परंतु उन व्यक्तियों में से एक का दूसरे की चोट पर हाथ फेरना और क्षमा माँगना एक सामाजिक क्रिया है। इस प्रकार, वेबर के अनुसार, समाजशास्त्र का कार्य सामाजिक क्रिया की व्याख्या करना है।
4. टॉनीज (Tonnies) के विचार–टॉनीज भी समाजशास्त्र को एक विशिष्ट विज्ञान की श्रेणी में रखने के पक्षपाती थे। उनका कहना था कि समाजशास्त्र को विशिष्ट विज्ञान बनाने के लिए आवश्यक है कि इसके अंतर्गत सामाजिक संबंधों के केवल विशेष स्वरूपों का ही अध्ययन किया जाए। टॉनीज समाजशास्त्र को एक विशुद्ध विज्ञान बनाने के पक्ष में थे।
5. वॉन वीज (Von wiese) के विचार-वॉन वीज भी स्पष्ट रूप से सामाजिक संबंधों के स्वरूपों के अध्ययन को ही समाजशास्त्र का विषय-क्षेत्र मानते हैं। उन्होंने समाजशास्त्र के विषय-क्षेत्र को स्पष्ट करने के लिए सामाजिक संबंधों को 650 प्रकारों में वर्गीकृत किया है।
विशेषात्मक संप्रदाय की आलोचना-विशेषात्मक संप्रदाय की आलोचना प्रमुख रूप से फ्रांसीसी तथा अंग्रेज समाजशास्त्रियों ने निम्नलिखित प्रकार से की हैं-
1. समाजशास्त्र सामाजिक संबंधों के सूक्ष्म तथा अमूर्त स्वरूपों के अध्ययन तक ही सीमित नहीं है-इस संप्रदाय के प्रतिपादक समाजशास्त्र को सामाजिक संबंधों के सूक्ष्म तथा अमूर्त रूपों के अध्ययन तक सीमित कर देते हैं, परंतु किसी भी घटना का अध्ययन हम तब तक नहीं कर सकते जब तक कि उसके वास्तविक स्वरूपों का अध्ययन न कर लें। इस प्रकार, सिमेल का मत अपूर्ण है। समाजशास्त्र के छात्र का मुख्य उद्देश्य तो सामाजिक घटनाओं के सजीव रूप तथा उसकी वास्तविक परिस्थितियों दोनों को ही अध्ययन करना है।
2. स्वरूप (Form) और अंतर्वस्तु (Content) दो पृथक् वस्तुएँ नहीं हैं—इस संप्रदाय के समर्थकों के अनुसार स्वरूप’ और ‘अंतर्वस्तु’ एक-दूसरे से अलग हैं, परंतु यथार्थ में सामाजिक संबंधों में स्वरूप और अंतर्वस्तु को अलग नहीं किया जा सकता। वे एक-दूसरे पर आश्रित है और एक-दूसरे से घनिष्ठ रूप से संबंधित हैं। जब सामाजिक संबंधों की अंतर्वस्तु में कोई परिवर्तन आता है तो उनके स्वरूपों में भी परिवर्तन आ जाता है। इस तथ्य को ध्यान में रखते हुए सोरोकिन (Sorokin) ने इन शब्दों में आलोचना की है, “हम एक गिलास को | उसके स्वरूप को बदले बिना शराब, पानी या शक्कर से भर सकते हैं, परंतु मैं एक ऐसी सामाजिक संस्था की कल्पना भी नहीं कर सकता जिसका स्वरूप सदस्यों के बदलने पर भी न बदले।”
3. स्वरूपों का अध्ययन अन्य विज्ञानों में भी होता है-इस संप्रदाय के समर्थकों का यह कहना सत्य नहीं है कि केवल समाजशास्त्र में ही सामाजिक संबंधों के स्वरूपों का अध्ययन किया जाता है। समाजशास्त्र के अतिरिक्त और भी ऐसे विज्ञान हैं जिनमें सामाजिक संबंधों के अनेक स्वरूपों का अध्ययन किया जाता है। उदाहरण के लिए राजनीतिशास्त्र में युद्ध, शांति, संघर्ष, समझौता आदि सामाजिक संबंधों के अनेक स्वरूपों का अध्ययन किया जाता है। इसी प्रकार विधिशास्त्र में शक्ति दासता, आज्ञापालन, अधिकार आदि सामाजिक संबंधों के स्वरूपों का अध्ययन सदा होता आया है।
4. शुद्ध समाजशास्त्र की धारणा अव्यावहारिक हैं—विशेषात्मक संप्रदाय के समाजशास्त्रियों की शुद्ध समाजशास्त्र की धारणा अव्यावहारिक है क्योंकि प्रत्येक विज्ञान दूसरे विज्ञान से संबंधित हैं, अतः किसी भी विज्ञान को अन्य विज्ञानों से पूर्णतया अलग करके अध्ययन नहीं किया जा सकता। सामाजिक घटनाओं की तो प्रकृति ही ऐसी हैं कि इसे समझने के लिए विभिन्न दृष्टिकोणों द्वारा इसका अध्ययन करना अनिवार्य है।
5. समाज के सदस्यों को कम महत्त्व देना उचित नहीं है—विशेषात्मक संप्रदाय समाज के सदस्यों को कम महत्त्व देता है, परंतु यथार्थ में सभी सदस्य सामाजिक संबंधों की अंतर्वस्तु हैं।
6. समाजशास्त्र के क्षेत्र को अत्यधिक संकुचित कर दिया है-इस संप्रदाय ने समाजशास्त्र के क्षेत्र को अत्यधिक संकुचित कर दिया है। कोई भी विज्ञान वास्तविकता के बिना उचित प्रकार से विकसित नहीं होता। इसके लिए आवश्यक है कि समस्या के प्रत्येक पहलू का अध्ययन किया जाए, परंतु विशेषात्मक विचारधारा समाजशास्त्र को एक पक्ष विशेष तक ही सीमित कर देती है।
7. सूक्ष्म और अमूर्त स्वरूपों का अध्ययन लाभदायक नहीं इस विषय में राइट (Wright) का कथन है कि “विशुद्ध स्वरूपों के अध्ययन के परिणामस्वरूप हम ऐसे अमूर्त सिद्धांतों । का निर्माण कर लेते हैं, जो सामान्य होते हैं और हमारे मन में ये विचार उत्पन्न होते हैं कि इन सिद्धांत का ज्ञाने तो हम अपनी सामान्य बुद्धि से भी कर सकते हैं। इन्हें जानने के लिए इतने लंबे विचार, तर्क-शक्ति और विभिन्न परिभाषाओं के शब्दाडम्बरों की कोई आवश्यकता नहीं है। अनेक बार ये सिद्धांत इतने अस्पष्ट और धुंधले होते हैं कि पाठक झुंझला जाता है। और सोचने लगता है कि इनका कोई अर्थ है या नहीं। अतः राइट ने ठीक ही कहा है कि यदि सामाजिक संबंधों का सूक्ष्म और अमूर्त रूप से अध्ययन किया जाएगा तो वह समाजशास्त्र के लिए लाभदायक नहीं होगा।’
8. समाजशास्त्र की मौलिक प्रकृति के विरुद्ध विशेषात्मक विचारधारी समाजशास्त्र की प्रकृति के पूर्णतया प्रतिकूल है, जैसा कि गिडिंग्स (Giddings) लिखते हैं कि “समाजशास्त्र का मुख्य विषय सामाजिक संबंधों का अध्ययन है। संबंध सामाजिक जीवन में ही पाए जाते हैं। सामाजिक जीवन की प्रकृति इस प्रकार की है कि इसके समस्त भागों को एक-दूसरे के साथ गहरा संबंध है। ये सब एक-दूसरे पर प्रभाव डालते हैं और एक-दूसरे से प्रभावित होते हैं। ये भाग मिलकर कार्य करते हैं; अतः यदि इनको पृथक् करके इनका सूक्ष्म अध्ययन करें तो हम सामाजिक संबंधों के पारस्परिक प्रभावों का कोई ज्ञान प्राप्त न कर सकेंगे, हमारा ज्ञान बिल्कुल अपूर्ण
रहेगा।”
(ब) समन्वयात्मक संप्रदाय
समन्वयात्मक संप्रदाय के अनुसार समाजशास्त्र एक सामान्य विज्ञान है तथा यह अन्य विशिष्ट साम्राजिक विज्ञानों का समन्वय मात्र है। इस संप्रदाय के प्रमुख समर्थक फ्रांसीसी और अंग्रेज समाजशास्त्री हैं। इनके अनुसार समाजशास्त्र को अपना क्षेत्र सीमित तथा संकुचित न बनाकर विस्तृत और व्यापक बनाना होगा। समाजशास्त्र के क्षेत्र को कुछ विषयों तक सीमित न करके उसे अन्य सभी विज्ञानों में भी समन्वित करना चाहिए। अन्य विज्ञानों से पृथक् रखने पर समाजशास्त्र एक जड़ विषय हो
जाएगा। दुर्वीम, हॉबहाइस, सोरोकिन, जिंसबर्ग तथा मोटवानी आदि इसी मत के समर्थक हैं। इन विद्वानों के मत में समाजशास्त्र एक विज्ञानों का विज्ञान’ है। सभी विज्ञान उसके क्षेत्र में आते हैं और वह सभी को अपने में समन्वित करता है। सामाजिक जीवन के समस्त भाग परस्पर संबंधित हैं। इस कारण किसी एक पक्ष का अध्ययन करने से हम संपूर्ण सामाजिक जीवन को नहीं समझ सकते। ऐसी दशा में आवश्यक है कि हम समाजशास्त्र में संपूर्ण सामाजिक जीवन का व्यवस्थित अध्ययन करें, केवल सूक्ष्म सिद्धांतों का अध्ययन करने से काम नहीं चलेगा। मोटवानी'(Motwani) के अनुसार, इस प्रकार, समाजशास्त्र जीवन को पूरी तरह और एक समग्र रूप में देखने का प्रयास करता है। इस प्रकार, समाजशास्त्र के क्षेत्र के अंतर्गत समाज के सामाजिक संबंधों को सामान्य अध्ययन होना चाहिए। इस संप्रदाय के प्रमुख समर्थकों के विचार निम्नांकित हैं-
दुर्वीम के विचार-दुर्वीम के अनुसार, प्रत्येक समाज में कुछ विचार, धारणाएँ एवं भावनाएँ होती हैं, जिनका पालन संबंधित समाज के अधिकांश सदस्य करते हैं। ये विचार एवं धारणाएँ संबंधित समाज के सामाजिक जीवन का सामूहिक प्रतिनिधित्व करते हैं। दुर्णीम के अनुसार, समाजशास्त्र का कार्य इसी सामूहिक प्रतिनिधित्व का अध्ययन करना है। इस स्थिति में स्पष्ट हैं कि समाजशास्त्र को एक सामान्य विज्ञान होना चाहिए।
हॉबहाउस के विचार-हॉबहाउस ने भी समाजशास्त्र को एक सामान्य विज्ञान माना है। इनके अनुसार समाजशास्त्र अन्य विज्ञानों द्वारा प्राप्त विभिन्न सिद्धांतों का अध्ययन करता है तथा कुछ सामान्य तत्त्वों को ज्ञात करता है। इन सामान्य तत्त्वों द्वारा समाज पर पड़ने वाले प्रभावों का अध्ययन भी समाजशास्त्र के अंतर्गत किया जाता है।
सोरोकिन के विचार–सोरोकिन ने भी समाजशास्त्र को एक सामान्य विज्ञान माना है तथा अपने मत की पुष्टि इन शब्दों में की हैं, “मान लीजिए, यदि सामाजिक घटनाओं को वर्गों में वर्गीकृत कर दिया जाए और प्रत्येक वर्ग का अध्ययन एक विशेष सामाजिक विज्ञान करें तो इन विशेष सामाजिक विज्ञानों के अतिरिक्त एक ऐसे विज्ञान की आवश्यकता होगी जो सामान्य हो एवं विभिन्न विज्ञानों के संबंधों का अध्ययन करें।”
वार्ड के विचार-वार्ड ने समाजशास्त्र को ज्ञान की विभिन्न शाखाओं का समन्वय मात्र माना हैं। समाज का निर्माण करने वाले समूह एवं संस्थाएँ आदि परस्पर एक-दूसरे से जुड़े हुए हैं, जिसके कारण एक में हुआ परिवर्तन दूसरों पर प्रभाव डालता है। इस प्रकार समाजशास्त्र का आधार अन्य सामाजिक विज्ञानों के परिणाम हैं और इसलिए समाजशास्त्र को विभिन्न सामाजिक विज्ञानों से प्राप्त केंद्रीय विचारों का समन्वय और अध्ययन करना चाहिए।
समन्वयात्मक संप्रदाय की आलोचना–जर्मन समाजशास्त्री समन्वयात्मक संप्रदाय की निम्नांकित बिदुओं के आधार पर आलोचना करते हैं-
- इन विद्वानों के अनुसार, समाजशास्त्र के समन्वयात्मक दृष्टिकोण से किए गए अध्ययन या सामान्य अध्ययन में, समाज में पाए जाने वाले प्रत्येक प्रकार के सामाजिक संबंधों का ज्ञान प्राप्त करना पड़ेगा; परंतु ये संबंध इतने अधिक हैं कि उनका संपूर्ण अध्ययन करना प्रायः संभव नहीं है।
- दूसरा दोष यह है कि यदि हम समन्वयात्मक अध्ययन को समाजशास्त्र का लक्ष्य बना लेते हैं तो समाजशास्त्र में भी प्रायः उन विषयों का अध्ययन करना पड़ेगा। जिनका कि अध्ययन अन्य सामाजिक विज्ञान करते हैं। इस प्रकार समाजशास्त्र और अन्य सामाजिक विज्ञानों की अध्ययन-वस्तु में कोई अंतर नहीं रह जाएगा।
- दि समाजशास्त्र सभी प्रकार के तथ्यों एवं सामाजिक घटनाओं का अध्ययन करना शुरू कर देगा तो यह विशुद्ध शास्त्र न रहकर एक मिश्रित शास्त्र बन जाएगा।
निष्कर्ष–उपर्युक्त विवेवचन से स्पष्ट हो जाता है कि समाजशास्त्र की विषय-वस्तु के समुचित अध्ययन के लिए प्रस्तुत समन्वयात्मक तथा विशेषात्मक दोनों दृष्टिकोण एकपक्षीय हैं तथा दोनों दृष्टिकोणों में समन्वय की आवश्यकता है। केवल एक ही दृष्टिकोण अपनाने से हमारी समस्याओं का समाधान नहीं हो पाएगा। अन्य शब्दों में, समाजशास्त्र के पूर्ण अध्ययन के लिए विशिष्ट व सामान्य दोनों विचारधाराएँ आवश्यक हैं। यदि हम ऐसा नहीं करेंगे तो समाजशास्त्र को एक जटिल विज्ञान के रूप में परिणत कर देंगे। यथार्थ में विशेषात्मक और समन्वयात्मक विचारधाराएँ एक-दूसरे की विरोधी नहीं हैं वरन् एक-दूसरे की पूरक हैं। हॉबहाउस ने ठीक ही कहा है, “सामान्य समाजशास्त्र में जब तक विशिष्टता उत्पन्न नहीं होती, तब तक यह न तो स्वतंत्र तथा पूर्ण शास्त्र है और न यह अन्य सामाजिक संबंधों का समन्वय ही है, जो उनके द्वारा खोजे हुए सिद्धांतों में शाब्दिक संवर्द्धन करता है।”

प्रश्न 5.
क्या समाजशास्त्र एक विज्ञान है? सविस्तार लिखिए।
या
समाजशास्त्र की वैज्ञानिक प्रकृति का वर्णन कीजिए।
या
समाजशास्त्र की परिभाषा दीजिए। समाजशास्त्र की प्रकृति का निर्धारण कीजिए।
या
समाजशास्त्र की प्रकृति एवं अध्ययन-क्षेत्र की विवेचना कीजिए।
उत्तर
सामान्य धारणा के अनुसार भौतिकशास्त्र, रसायनशास्त्र तथा प्राणिविज्ञान जैसे विषयों को ही विज्ञान माना जाता है, परंतु यह धारणा भ्रामक है। वास्तव में किसी भी विषय को उसकी विषय-वस्तु के आधार पर विज्ञान अथवा कला की श्रेणी में नहीं रखा जा सकता। यदि ऐसा होता तो भौतिकशास्त्र तथा रसायनशास्त्र दोनों को एक ही नाम ‘विज्ञान’ कैसे दिया जा सकता था। अब प्रश्न उठता है कि विज्ञान किसे कहते हैं? एक विशिष्ट पद्धति द्वारा किया गया प्रत्येक अध्ययन विज्ञान कहलाता है तथा इस पद्धति को वैज्ञानिक पद्धति (Scientific Method) कहा जाता है। अब प्रश्न उठता है कि क्या समाजशास्त्र एक विज्ञान है? समाजशास्त्र की प्रकृति के मूल्यांकन के लिए सर्वप्रथम विज्ञान के अर्थ एवं विशेषताओं का निर्धारण किया जाएगा तथा फिर उसी कसौटी पर समाजशास्त्र की प्रकृति का मूल्यांकन किया जाएगा।
[संकेत–समाजशास्त्र के अर्थ एवं परिभाषा के लिए इसी अध्याय के विस्तृत उत्तरीय प्रश्न 1 तथा समाजशास्त्र के अध्ययन-क्षेत्र हेतु प्रश्न 5 का उत्तर देखें।]
विज्ञान का अर्थ एवं परिभाषाएँ
किसी भी विषय के क्रमबद्ध ज्ञान को विज्ञान कहा जाता है। यह अध्ययन की एक विशिष्ट पद्धति है, जिसके निश्चित चरण हैं। प्रमुख विद्वानों ने विज्ञान को निम्न प्रकार से परिभाषित किया है-
गिलिन एवं गिलिन (Gillin and Gillin) के अनुसार-“विज्ञान का वास्तविक प्रतीक उस क्षेत्र, जिस पर हम अनुसंधान करना चाहते हैं, के प्रति एक निश्चित प्रकार को दृष्टिकोण है।”
बीसंज एवं बीसंज (Biesanz and Biesanz) के अनुसार-“यह पद्धति है, न कि अंतर्वस्तु, जो विज्ञान की कसौटी है।”
कार्ल पियर्सन (Karl Pearson) के अनुसार-“समस्त विज्ञान की एकता उसकी प्रणाली में है, न कि उसकी विषय-वस्तु में।”
जूलियन हक्सले (Julian Huxley) के अनुसार-“विज्ञान वह कार्यकलाप है, जिसके द्वारा हम आज प्रकृति के तथ्यों के विषय में ज्ञान तथा उन पर नियंत्रण का अधिकांश भाग प्राप्त करते हैं।” उपर्युक्त विवरण द्वारा विज्ञान का अर्थ स्पष्ट हो जाता है। वास्तव में, विज्ञान की कसौटी एक विशिष्ट पद्धति है। इस पद्धति को वैज्ञानिक पद्धति कहा जाता है। वैज्ञानिक पद्धति द्वारा किया गया प्रत्येक अध्ययन ‘वैज्ञानिक अध्ययन’ कहलाता है तथा इस प्रकार से प्राप्त ज्ञान को वैज्ञानिक ज्ञान कहा जाता है। विज्ञान या वैज्ञानिक पद्धति के विषय में कार्ल पियर्सन ने इस प्रकार कहा है, “तथ्यों का वर्गीकरण उनके अनुक्रम और सापेक्षिक महत्त्व को जानना ही विज्ञान का कार्य है।”
विज्ञान के प्रमुख तत्त्व
किसी भी विज्ञान में निम्नलिखित तत्त्व पाएँ जाते हैं-
- कोई भी विषय विज्ञान तभी कहा जा सकता है जबकि उसकी पद्धति वैज्ञानिक हो।
- विज्ञान वास्तविकता से संबंधित है। उसका संबंध आदर्शों से न होकर तथ्यों से होता है।
- विज्ञान के सिद्धांत सार्वभौमिक (Universal) होते हैं जो कि समस्त विश्व में प्रत्येक युग में खरे उतरते हैं।
- विज्ञान का स्वरूप तार्किक (Logical) है।
- विज्ञान विषय-वस्तु को क्रमबद्ध रूप में प्रस्तुत करता है।
- वैज्ञानिक सिद्धांत प्रामाणिक होते हैं। अनेक बार जाँच किए जाने पर भी वे सत्य सिद्ध होते हैं।
- विज्ञान सदा कार्य-कारण संबंधों की खोज करता है।
- विभिन्न प्रकार के कार्य-कारण संबंधों के आधार पर विज्ञान भविष्यवाणी भी करता है।
समाजशास्त्र एक विज्ञान है”
यद्यपि समाजशास्त्र की प्रकृति के बारे में विद्वानों में मतभेद हैं, तथापि अधिकांश विद्वान इसे विज्ञान ही मानते हैं। समाजशास्त्र के जनक ऑगस्त कॉम्टे ने इसे ‘विज्ञानों की रानी’ (Queen of Sciences) के रूप में प्रतिपादित करने का प्रयास किया। विज्ञान के उपर्युक्त तत्त्वों के आधार पर यदि समाजशास्त्र का मूल्यांकन किया जाए तो हम देखेंगे कि वह एक विज्ञान सिद्ध होता है। इसे निम्नांकित आधारों पर विज्ञान कहा जा सकता है–
- समाजशास्त्र में वैज्ञानिक पद्धति का प्रयोग होता है–समाजशास्त्र में वैज्ञानिक पद्धति द्वारी ज्ञान का संकलन किया जाता है। समाजशास्त्र सामाजिक घटनाओं और सामाजिक प्रक्रियाओं को विज्ञान है; अतः वह इनके अध्ययन के लिए एक निश्चित तथा वैज्ञानिक पद्धति का विकास करता है जिसके आधार पर वह अपने तथ्यों का अध्ययन करता है। समाजशास्त्रीय अध्ययन में अपनाई जाने वाली विशिष्ट पद्धतियाँ या विधियाँ भी हैं। इनमें मुख्य गुणात्मक विधि, सांख्यिकीय विधि, ऐतिहासिक विधि, तुलनात्मक विधि तथा प्रयोगात्मक विधि हैं। इन सब अध्ययन विधियों में भी वैज्ञानिक पद्धति के अनिवार्य तत्त्वों को ध्यान में रखा जाता है।
- समाजशास्त्र यथार्थवादी है–समाजशास्त्र का स्वरूप यथार्थवादी है। उसमें सामाजिक घटनाओं, संबंधों और प्रक्रियाओं का यथार्थ तथ्यों के आधार पर अध्ययन किया जाता है। समाजशास्त्र के तथ्यात्मक स्वरूप के कारण कॉम्टे ने उसे ‘सामाजिक भौतिकशास्त्र’ (Social Physics) भी कहकर पुकारा है।
- समाजशास्त्र के सिद्धांत सार्वभौमिक हैं-समाजशास्त्र द्वारा प्रतिपादित सिद्धांत सभी देश-काल में सही सिद्ध हुए हैं। यदि सिद्धांत आनुभविक आँकड़ों के आधार पर निर्मित किए। गए हैं तो एक समान परिस्थितियाँ रहने पर उनके गलत होने का प्रश्न ही नहीं उठता।।
- समाजशास्त्र का स्वरूप तार्किक है–समाजशास्त्र का स्वरूप तार्किक है। उसमें किसी भी बात को आँख मींचकर या भगवान की देन मानकर स्वीकार नहीं किया जाता अपितु इसकी | विवेचना तार्किक आधार पर की जाती है।
- समाजशास्त्र में अवलोकन द्वारा तथ्यों का संकलन किया जाता है-अवलोकन विज्ञान का ही एक महत्त्वपूर्ण चरण है। समाजशास्त्र में अवलोकन करके ही तथ्यों का संकलन किया जाता। | है और अवलोकन के पश्चात् तथ्यों का वर्गीकरण तथा विश्लेषण किया जाता है।
- समाजशास्त्र के सिद्धांत प्रामाणिक हैं—समाजशास्त्र के सिद्धांत पूर्ण रूप से प्रामाणिक होते हैं। उन्हें कभी भी और कितनी भी बार प्रामाणित किया जा सकता है अथवा उनकी प्रामाणिकता की कभी भी परीक्षा की जा सकती है।
- समाजशास्त्र कार्य-कारण संबंधों की स्थापना करता है–समाजशास्त्र में सामाजिक घटना की वास्तविकता को ज्ञात करने के पश्चात् इस बात का पता लगाया जाता है कि किस कारण से यह घटना घटी। इस प्रकार समाजशास्त्र ‘क्या’ के साथ कैसे’ का उत्तर भी देता है।
- समाजशास्त्र भविष्यवाणी करता है—कार्य-कारण संबंधों के आधार पर समाजशास्त्री अनुमान लगा सकते हैं कि उसका सामाजिक संबंधों पर क्या प्रभाव पड़ेगा। अन्य शब्दों में, कार्य-कारण संबंधों के आधार पर कुछ सिद्धांत का निर्माण किया जाता है और उन सिद्धांतों के आधार पर भविष्यवाणी भी की जा सकती हैं। यद्यपि इस दिशा में अभी तक कोई अधिक प्रयास नहीं हुए हैं, तथापि सामान्यीकरणों एवं पूर्वानुमानों में पर्याप्त सफलता मिली है।
उपर्युक्त तथ्यों के आधार पर हम यह कह सकते हैं कि समाजशास्त्र में विज्ञान,की अधिकांश विशेषताएँ पाई जाती हैं अत: यह एक विज्ञान है।
समाजशास्त्र को विज्ञान स्वीकार करने में आपत्तियाँ
समाजशास्त्र एक नव-विकसित सामाजिक विज्ञान हैं। कुछ विद्वान समाजशास्त्र को विज्ञान के रूप में स्वीकार नहीं करते। इन विद्वानों का कथन है कि समाजशास्त्र में शुद्ध वैज्ञानिक तत्वों का अभाव पाया जाता हैं। इन विद्वानों ने समाजशास्त्र के वैज्ञानिक स्वरूप पर विभिन्न आक्षेप लगाए हैं। अधिकांश आक्षेपों का आधार सामाजिक घटना की विलक्षण प्रकृति को बनाया गया है। समाजशास्त्र के वैज्ञानिक स्वरूप के विरुद्ध मुख्य रूप से निम्नलिखित आपत्तियाँ उठाई गई हैं-
- प्रयोगशाला का अभाव-समाजशास्त्र के वैज्ञानिक स्वरूप पर सबसे बड़ी आपत्ति यह उठाई जाती है कि समाजशास्त्र की अपनी कोई प्रयोगशाला नहीं है। प्रत्येक भौतिक विज्ञान के पास अपनी प्रयोगशाला होती है, जिसमें प्रयोग द्वारा निष्कर्षों पर पहुँचा जाता है, परंतु समाजशास्त्र के लिए यह संभव नहीं है; समाजशास्त्र में अध्ययन प्रयोगशाला में नहीं किए जाते हैं।
- सामाजिक घटनाओं की जटिलता एवं परिवर्तनशीलता-सामाजिक संबंध जटिल और विविध प्रकार के होते हैं। सामाजिक संबंधों का जाल बड़ा उलझा हुआ होता हैं। संसार में जितने परिवार होंगे, उतनी ही उनके सामाजिक संबंधों में भिन्नता होगी। साथ-ही-साथ संबंधों में परिवर्तन भी होता रहता है। ऐसी दशा में सामाजिक संबंधों का वैज्ञानिक अध्ययन सरलता से नहीं किया जा सकता।
- तटस्थ दृष्टिकोण का अभाव-समाजशास्त्र को विज्ञान न मानने का एक अन्य कारण यह है। कि कोई भी समाजशास्त्री कभी तटस्थ नहीं रह सकता। प्रत्येक समाजशास्त्री का परिवार, धर्म, वर्ग तथा जाति आदि के बारे में अपना स्वयं का निजी दृष्टिकोण होता है और वह इनकी पृष्टभूमि में ही अध्ययन करता है। ऐसी दशा में उसका दृष्टिकोण तटस्थ नहीं हो सकता। चार्ल्स बियर्ड लिखते हैं कि “समाजशास्त्र अपने सामाजिक संसार में कभी भी तटस्थ नहीं रह सकता। समाजशास्त्री जिस समाज का अध्ययन करता है उसका वह अंश होता है; अतः ऐसी दशा में उसका तटस्थ रहना संभव ही नहीं है।”
- मापन की कठिनाइयाँ-समाजशास्त्रं अपनी विषय-वस्तु की ठीक प्रकार से माप-तोल नहीं कर सकता। इसके विपरीत, भौतिकशास्त्र में यंत्रों की सहायता से विषय-वस्तु की भली प्रकार से माप-तोल हो सकती है। दूरियों की नाप हो सकती है, वृत्त तथा त्रिभुजों की माप हो सकती है, ताप एवं ऊष्मा का मापन किया जा सकता है, परंतु सामाजिक व्यवहार की घटनाओं को नहीं मापा जा सकता। सामाजिक घटनाएँ अमूर्त होती हैं; अतः उनके मापन का तो प्रश्न ही नहीं उठता।
- सार्वभौमिकता की कमी-भौतिक संसार में प्रत्येक काल तथा स्थान पर एक-सी स्थिति पाई जाती हैं, किंतु समाज में ऐसा नहीं होता। यह आवश्यक नहीं कि कोई घटना यदि एक समाज एवं स्थान पर घटित हुई है तो वैसी घटना अन्य देशकाल में भी घटित होगी। अन्य शब्दों में, सामाजिक घटनाओं में सार्वभौमिकता की कमी पाई जाती है।
- यथार्थता का अभाव-समाजशास्त्र के सिद्धांत सर्वथा सत्य नहीं निकलते; अतः उन्हें हम * विज्ञान की श्रेणी में नहीं रख सकते हैं। अधिकतर अध्ययन अनुसंधानकर्ता की मनोवृत्तियों द्वारा प्रभावित होते हैं, जिसके कारण वे यथार्थ नहीं होते हैं।
- भविष्यवाणी करने में असमर्थ-कुछ आलोचकों ने समाजशास्त्र के वैज्ञानिक स्वरूप पर आक्षेप करते हुए कहा है कि समाजशास्त्र या तो कोई भविष्यवाणी कर ही नहीं सकता अथवा उसके द्वारा की गई भविष्यवाणी केवल सीमित क्षेत्र में ही सत्य हुआ करती है। समाजशास्त्र द्वारा की गई भविष्यवाणी सार्वभौमिक नहीं होती है।
समाजशास्त्र की वास्तविक प्रकृति
समाजशास्त्र कैसा विज्ञान है; अर्थात् विज्ञान के रूप में समाजशास्त्र की वास्तविक प्रकृति क्या है? रॉबर्ट बीरस्टीड (Robert Bierstedt) द्वारा प्रस्तुत अग्रलिखित विवरण द्वारा समाजशास्त्र की । वस्तिविक प्रकृति स्पष्ट हो जाएगी-
-
- समाजशास्त्र एक सामाजिक विज्ञान है, न कि प्राकृतिक विज्ञान–बीरस्टीड का कहना है कि समाजशास्त्र निश्चित रूप से एक सामाजिक विज्ञान है। उनका अभिप्राय यह नहीं है कि समाजशास्त्र और सामाजिक विज्ञान एक ही है, अपितु समाजशास्त्र सामाजिक विज्ञानों में से एक विज्ञान है, क्योंकि इसका संबंध भौतिक तथा प्राकृतिक घटनाओं से न होकर सामाजिक घटनाओं, समाज तथा सामाजिक संबंधों से हैं क्योंकि इसका भौतिक घटनाओं से कोई अंबंध नहीं है इसलिए समाजशास्त्र को प्राकृतिक विज्ञानों की श्रेणी में नहीं रखा जा सकता।
- समाजशास्त्र तथ्यात्मक विज्ञान है, आदर्शात्मक विज्ञान नहीं समाजशास्त्र सामाजिक संबंधों का तथ्यात्मक अध्ययन करता है। यह शास्त्र ‘क्या है’ का अध्ययन करता है, क्या होना चाहिए’ का अध्ययन नहीं करता। इसीलिए समाजशास्त्र को तथ्यात्मक सामाजिक विज्ञान माना जाता है, न कि आदर्शात्मक विज्ञान।।
- समाजशास्त्र एक अमूर्त विज्ञान है, न कि मूर्त विज्ञान–समाजशास्त्र अन्य सामाजिक विज्ञानों की तरह अमूर्त है, क्योंकि इसकी विषय-वस्तु सामाजिक संबंध हैं तथा सामाजिक संबंधों को मूर्त रूप में नहीं देखा जा सकता। सामाज़िक संबंध क्योंकि अमूर्त होते हैं अत: समाजशास्त्र भी एक अमूर्त विज्ञान है।
- समाजशास्त्र एक विशुद्ध विज्ञान है, न कि व्यावहारिक विज्ञान–समाजशास्त्र एक विशुद्ध विज्ञान है, क्योंकि अन्य विशुद्ध विज्ञानों की तरह यह भी क्रमबद्ध ज्ञान प्राप्त करता है तथा अपनी ओर से किसी प्रकार के व्यावहारिक सुझाव नहीं देता है।
- समाजशास्त्र एक सामान्य विज्ञान है, न कि विशिष्ट विज्ञान–समाजशास्त्र एक सामान्य विज्ञान है क्योंकि इसका संबंध समाज तथा सामाजिक घटनाओं से है, जो सब में समान हैं; अतः यह एक सामान्य विज्ञान है।
- समाजशास्त्र तार्किक तथा अनुभवाश्रित दोनों प्रकार का विज्ञान है—समाजशास्त्र एक तार्किक विज्ञान है, क्योंकि इसमें प्रत्येक घटना की तार्किक व्याख्या देने का प्रयास किया जाता है। यह एक अनुभवाश्रित (आनुभविक) विज्ञान भी हैं, क्योंकि इसका अध्ययन पुस्तकालय में नहीं अपितु अनुसंधान क्षेत्र में जाकर किया जाता है।
संक्षेप में, बीरस्टीड के विवरण को निम्नांकित प्रकार से प्रस्तुत किया जा सकता हैसमाजशास्त्र क्या है?-
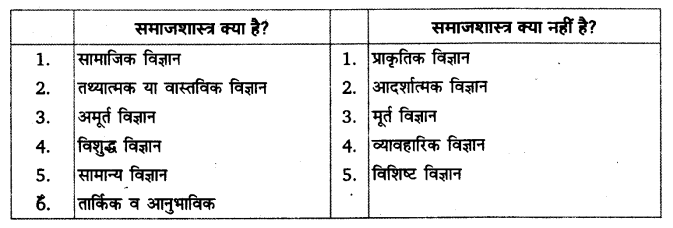
We hope the UP Board Solutions for Class 11 Sociology Introducing Sociology Chapter 1 Sociology and Society (समाजशास्त्र एवं समाज) help you. If you have any query regarding UP Board Solutions for Class 11 Sociology Introducing Sociology Chapter 1 Sociology and Society (समाजशास्त्र एवं समाज), drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.