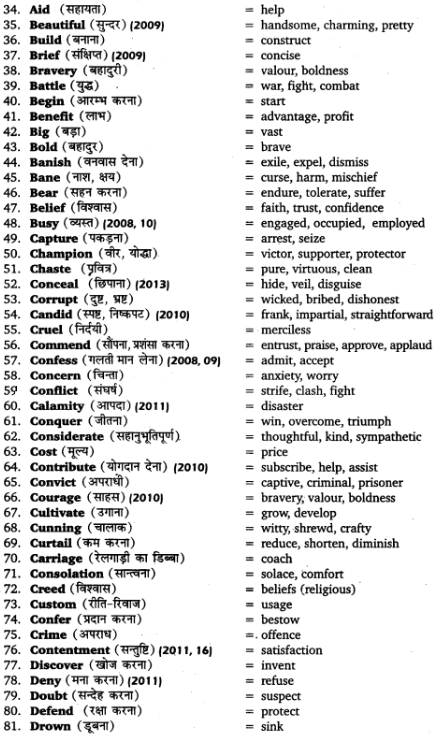
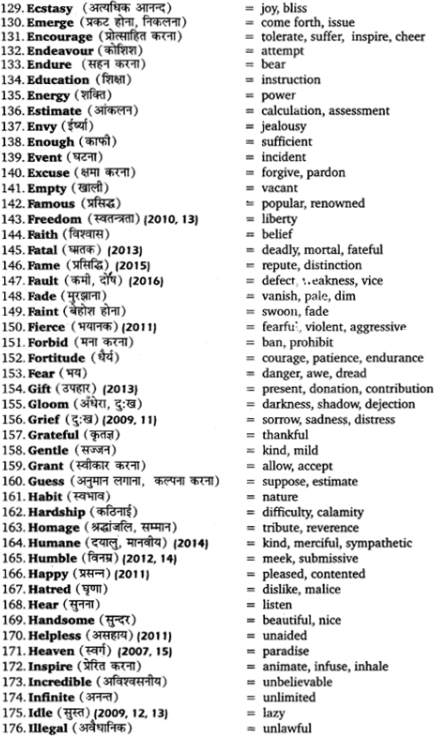
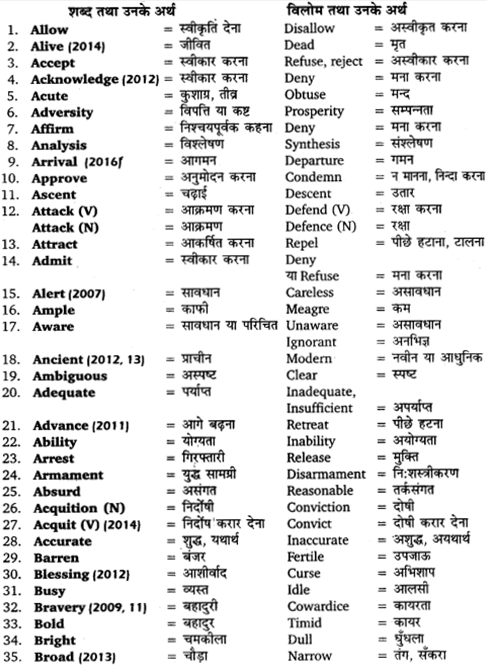
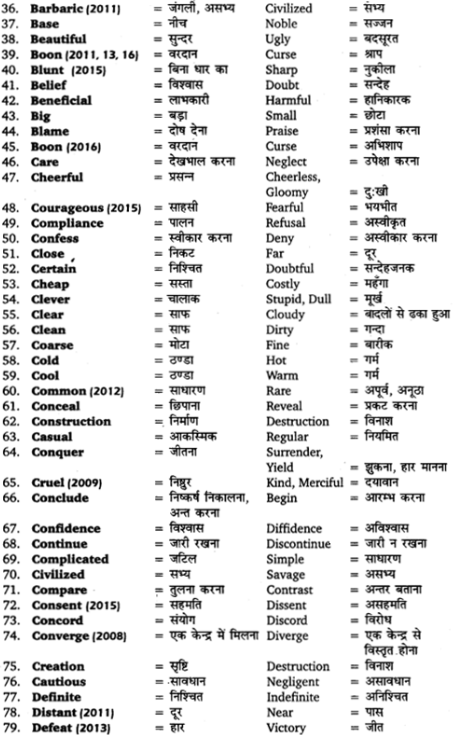
UP Board Solutions for Class 11 Sahityik Hindi प्रत्यय-प्रकरण are part of UP Board Solutions for Class 11 Sahityik Hindi . Here we have given UP Board Solutions for Class 11 Sahityik Hindi प्रत्यय-प्रकरण.
| Board | UP Board |
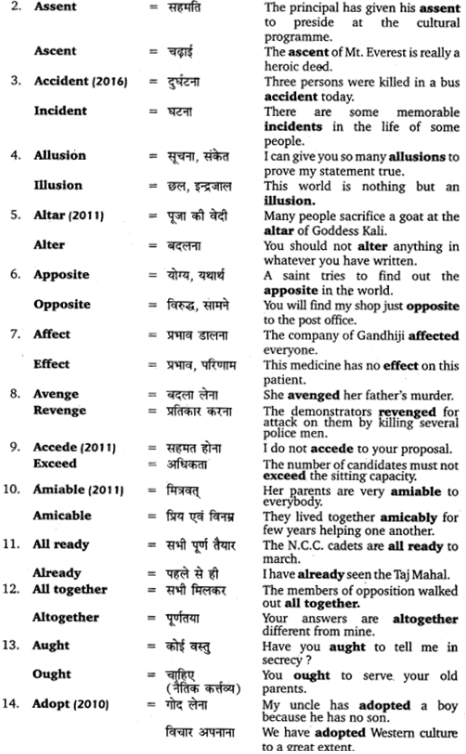
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 11 |
| Subject | Sahityik Hindi |
| Chapter | Chapter 3 |
| Chapter Name | प्रत्यय-प्रकरण |
| Category | UP Board Solutions |
UP Board Solutions for Class 11 Sahityik Hindi प्रत्यय-प्रकरण
प्रत्यय-प्रकरण
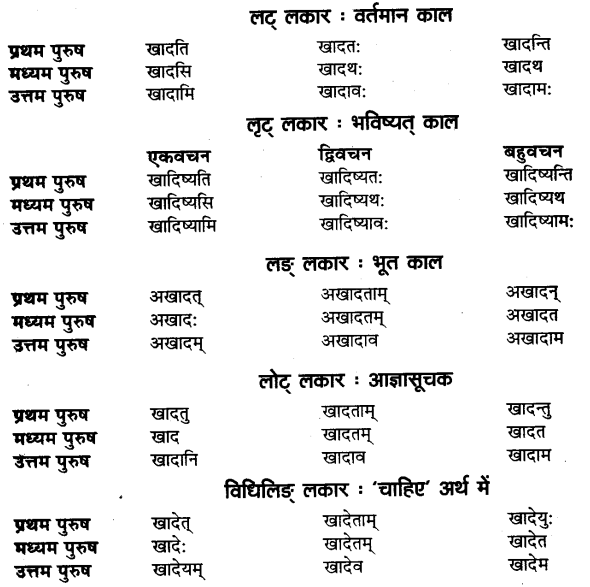
संस्कृत में धातु या शब्दों के बाद प्रत्यय जोड़कर नये शब्दों का निर्माण होता है। प्रत्यय मुख्यतः दो प्रकार के होते हैं
(अ) कृत् प्रत्यय तथा
(ब) तद्धित प्रत्यय।
(अ) कृत् प्रत्यय
जिस प्रत्यय को धातु से जोड़कर संज्ञा, विशेषण अथवा अव्यय बनाया जाता है, उसको कृत् प्रत्यय कहते हैं। कृत् प्रत्यय के योग से बनने वाले शब्दों को कृदन्त (अर्थात् जिनके अन्त में कृत् प्रत्यय है) कहते हैं; जैसे – ‘कृ’ धातु में तृच् प्रत्यय जोड़ने से ‘कर्तृ’ शब्द बनता है, यह कृदन्त है। यह संज्ञा शब्द है और इसके रूप अन्य संज्ञाओं की तरह विभिन्न विभक्तियों में चलेंगे (जैसे – प्रथमा विभक्ति में कर्ता, कर्तारौ, कर्तारः आदि)। यहाँ यह द्रष्टव्य है कि जो कृदन्त शब्द संज्ञा या विशेषण होते हैं, उनके रूप तो चलते हैं, पर अव्यय सदा एक रूप रहते हैं (उनके रूप नहीं चलते)।
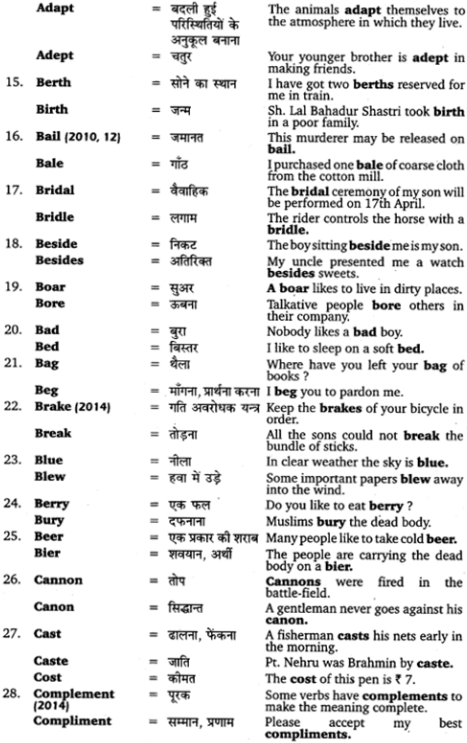
(क) क्त (तु) – भूतकालिक क्रिया और विशेषण शब्द बनाने के लिए ‘क्त’ प्रत्यय का प्रयोग किया जाता है। ‘क्त’ प्रत्यय का प्रयोग कर्मवाच्य एवं भाववाच्य में किया जाता है। इसका प्रयोग करते समय कर्ता में तृतीया विभक्ति तथा कर्म में प्रथमा विभक्ति रखी जाती है। ‘क्त’ प्रत्ययान्त शब्दों का प्रयोग कर्म के लिङ्ग, विभक्ति और वचनों के अनुसार होता है। कर्ता के लिङ्ग और वचन का इस पर कोई प्रभाव नहीं पड़ता; जैसे
- रामेण पुस्तकं पठितम्।
- सीतया ग्रन्थः पठितः।
- मया पुस्तिका पठिता।
‘क्त’ प्रत्यय से बने क्रिया-रूपों के कुछ उदाहरण ।


(ख) क्त्वा (त्वा) – जब किसी क्रिया के हो जाने पर दूसरी क्रिया आरम्भ होती है, तब सम्पन्न हुई क्रिया को , ‘पूर्वकालिक क्रिया कहते हैं। हिन्दी में इसका बोध करके’ लगाकर होता है। पूर्वकालिक क्रिया का बोध कराने के . लिए संस्कृत में धातु के आगे क्त्वा (त्वा) प्रत्यय जोड़ा जाता है। क्त्वा (त्वा) प्रत्ययान्त धातुओं के रूप नहीं चलते।
‘क्त्वा’ (त्वा) प्रत्यय लगाकर धातुओं के रूप

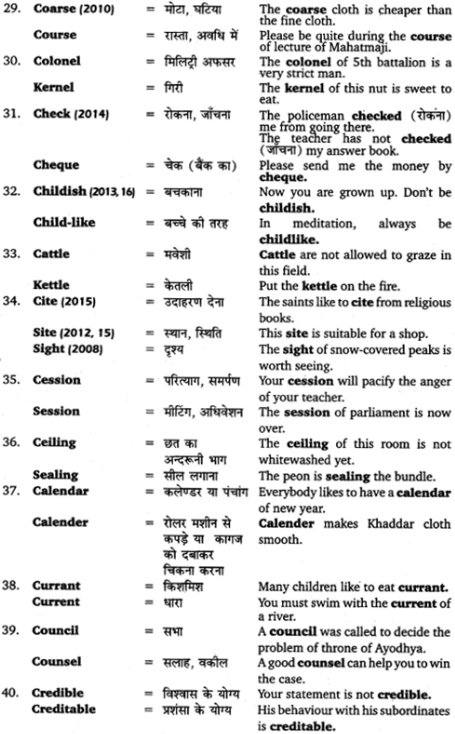
(ग) तव्यत् (तव्य), अनीयर् (अनीय) – सामान्यत: क्रिया में विधिलिङ् लकार चाहिए’ के अर्थ में तव्यत् और अनीयर् प्रत्ययों का प्रयोग होता है। इन शब्दों का प्रयोग सकर्मक धातुओं के कर्मवाच्य में तथा अकर्मक धातुओं के भाववाच्य में होता है। कर्तृवाच्य में इनका प्रयोग नहीं होता। ये शब्द योग्य के अर्थ में भी प्रयुक्त होते हैं; जैसे
पठ् + तव्यत् (तव्य) = पठितव्य (पढ़नी चाहिए)।
पठ् + अनीयर् (अनीय) = पठनीय (पढ़नी चाहिए या पढ़ने योग्य)।
मया पुस्तकं पठितव्यम् (पठनीयम्) = मेरे द्वारा पुस्तक पढ़ी जानी चाहिए (या, मुझे पुस्तक पढ़नी चाहिए)। इन प्रत्ययों से बने शब्दों का प्रयोग लिंग, वचन और विभक्ति के अनुसार किया जाता है। इनके रूप पुंल्लिङ्ग में ‘बालक’, नपुंसकलिङ्ग में ‘फल और स्त्रीलिङ्ग में ‘बाला’ के समान बनेंगे।
तव्यत् और अनीयर् प्रत्यय से निर्मित उदाहरण


(घ) क्तवतु (तवत्) – ‘क्त’ प्रत्ययान्त शब्दों के परिवर्तनों के अनुसार ही ‘क्तवतु’ प्रत्ययान्त शब्दों के रूपों में भी परिवर्तन होते हैं। केवल उनके अन्त में ‘वत्’ और जोड़ दिया जाता है, क्योंकि इस प्रत्यय का प्रारम्भिक अक्षर भी ‘क्त ही है। ‘क्तवतु’ प्रत्यय का भी उन्हीं धातुओं के साथ प्रयोग होता है, जिनके साथ ‘क्त का प्रयोग होता है। इस प्रत्यय से निर्मित शब्दों का प्रयोग भूतकालिक क्रिया की भाँति ‘कर्तृवाच्य में होता है। इस प्रत्यय से निर्मित शब्दों के रूप पुंल्लिग में ‘श्रीमत् के समान, स्त्रीलिंग में नदी के समान तथा नपुंसकलिंग में जगत् के समान होते हैं।
“क्तवतु’ प्रत्यय से बने क्रिया-रूपों के कुछ उदाहरण

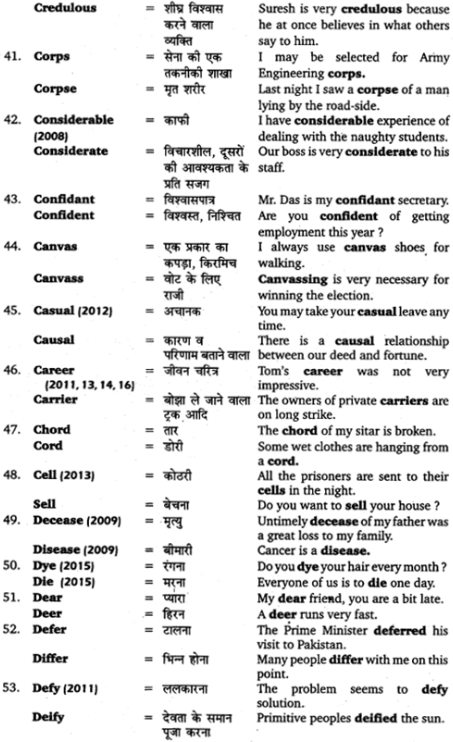
(ब) तद्धित प्रत्यय
तद्धित प्रत्यय सदा किसी सिद्ध (अर्थात् बनाये हुए) संज्ञा, विशेषण, अव्यय या क्रिया के अनन्तर जोड़कर उससे अन्य संज्ञा, विशेषण, अव्यय, क्रिया आदि बनाने में प्रयुक्त होता है। यह ध्यान रखना चाहिए कि कृत् प्रत्यय सदा धातु में ही जोड़े जाते हैं, किसी सिद्ध शब्द में नहीं।
(क) मतुप् , वतुप् – संज्ञा से ‘वाला’, ‘वाली’ (गाड़ी वाला, बुद्धि वाली आदि) अर्थ प्रकट करने के लिए ‘मतुप्’ (मत्) तथा वतुप् (वत्) प्रत्यय का प्रयोग किया जाता है। जिन शब्दों के अन्त में ‘अ’ या ‘आ’ होता है, उनमें ‘वत्’ तथा जिन शब्दों के अन्त में ह्रस्व अथवा दीर्घ ‘ई’, ‘उ’, ‘ऋ’ होता है, उनमें ‘मत्’ जुड़ता है। किन्तु यदि अन्त में आने वाले ‘इ’, उ’ व्यंजन ‘म’ में लगे हों तो ‘वत्’ ही जुड़ता है। ‘मतुप्’ या ‘वतुप्’ प्रत्ययान्त शब्दों के रूप पुंल्लिङ्ग में ‘भवत्’ के समान, स्त्रीलिङ्ग में नदी के समान और नपुंसकलिङ्ग में ‘जगत् के समान होते हैं; जैसे


ये शब्द विशेषण होते हैं, इसलिए ये अपने विशेष्य के अनुसार ही लिङ्ग, वचन और विभक्ति ग्रहण करते हैं। उदाहरणार्थ, ‘श्रीमत् के पुंल्लिङ्ग में प्रथमा विभक्ति के तीनों वचनों के रूप इस प्रकार होंगे
श्रीमान् श्रीमन्तौ श्रीमन्तः।
(ख) त्व, तल् प्रत्यय – संज्ञा और विशेषण शब्दों से भाववाचक संज्ञा बनाने के लिए त्व’ और ‘तलु’ प्रत्ययों का प्रयोग होता है। ‘त्व’ प्रत्ययान्त शब्द नपुंसकलिङ्ग तथा ‘तल्’ प्रत्ययान्त शब्द स्त्रीलिङ्ग होते हैं। इनके रूप भी क्रमशः ‘फलम्’ और ‘बाला’ के समान चलते हैं।

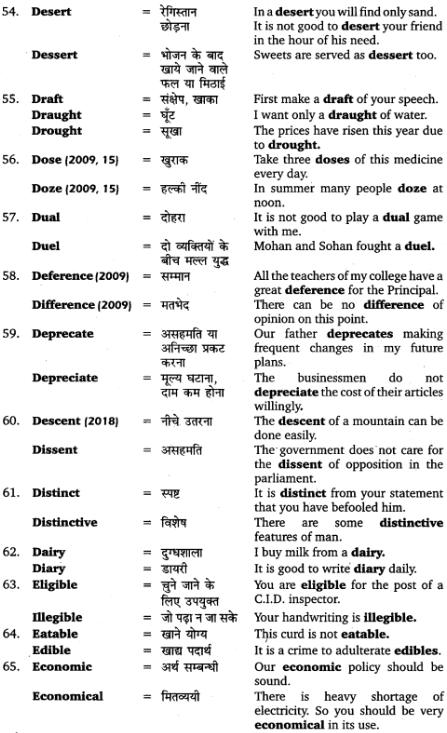
प्रथम – दिये गये पदों में से किन्हीं दो के सम्बन्ध में स्पष्ट कीजिए कि वे किस धातु अथवा शब्द में किस प्रत्यय के योग से बने हैं – गतः, पठनीयम्, बुद्धिमान्।
उत्तर:

द्वितीय – दिये गये पदों में से किन्हीं दो धातु में ‘क्त’ या ‘क्तवतु’ प्रत्यय लगाकर उसके प्रथमा पुंल्लिङ्ग एकवचन और द्विवचन के रूप लिखिए-पठ्, गम्, दा, प्रेष्।
उत्तर:

तृतीय – दिये गये शब्दों में से किसी एक शब्द में उसके सामने लिखा प्रत्यय जोड़कर शब्द का यथानिर्दिष्ट रूप लिखिए-धन + मतुप् (पुंल्लिङ्ग रूप), पठ् + अनीयर् (नपुंसकलिङ्ग रूप)
उत्तर:

पाठ्य-पुस्तक ‘संस्कृत दिग्दर्शिका’ में आये प्रत्यययुक्त शब्द
पाठ 2:

पाठ 3:

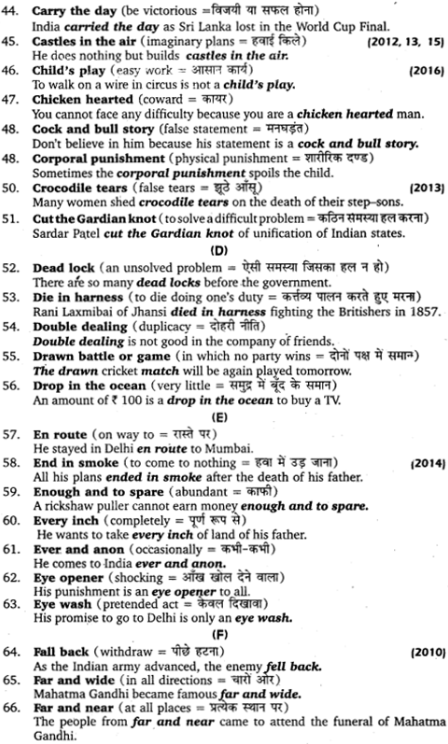
पाठ 4:

पाठ 6:
![]()

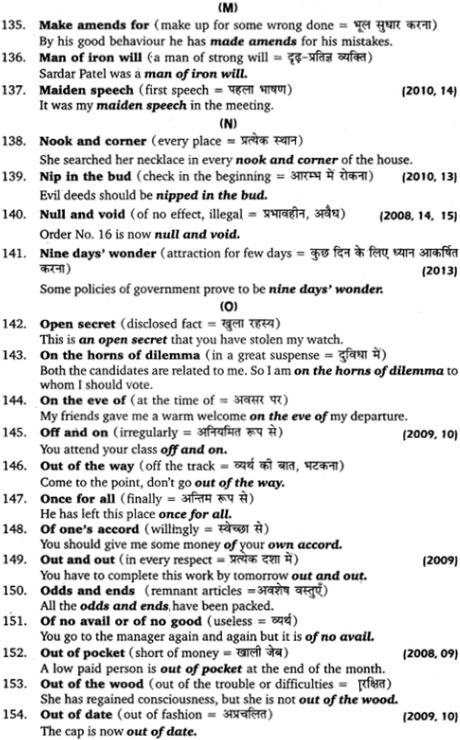
पाठ 7:
![]()
पाठ 9:

पाठ 10:

We hope the UP Board Solutions for Class 11 Sahityik Hindi प्रत्यय-प्रकरण help you. If you have any query regarding UP Board Solutions for Class 11 Sahityik Hindi प्रत्यय-प्रकरण, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.