UP Board Solutions for Class 10 Commerce Chapter 6 Indexing
Indexing Objective Type Questions (1 Mark)
Question 1.
Card indexing was previously used only in:
(a) Libraries
(b) Hostel
(c) Canteen
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Libraries
Question 2.
In simple indexing, a special type of book is used bearing letters on the ……….. hand side.
(a) Left
(b) Right
(c) Either (a) or (b)
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Right

Question 3.
In vowel inducing each letter is sub-divided in ……….. sub-divisions.
(a) 8
(b) 4
(c) 5
(d) 10
Answer:
(c) 5
Question 4.
When for any reference name card is taken out ………… card in kept in its place.
(a) Index
(b) Absent
(c) Guide
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Absent
Question 5.
In the case of card indexing similar names can be clearly distinguished by using cards of …………. colours.
(a) Mix
(b) Different
(c) Black
(d) White
Answer:
(b) Different

Indexing Definite Answer Type Questions (1 Mark)
Question 1.
Write the name of the latest system of indexing?
Answer:
Card index.
Question 2.
What kind of indexing many cards can be seen of a time?
Answer:
Visible Index.
Question 3.
Write the name of the register in which details of outgoing letters arc written. (UP 2014)
Answer:
Despatch Register.
Indexing Very Short Answer Type Questions (2 Marks)
Question 1.
Give any two objects of indexing.
Answer:
Objects of indexing are as follows:
- The operation of filing will become (UPBoardSolutions.com) so complicated that it could be happened only by that person who has done filing.
- In the absence of indexing, the filing system will become unscientific and incomplete, because it would be a tedious job to find out any document for reference.

Question 2.
What do you mean by Absent cards?
Answer:
When for any reference, name card is taken out, an absent card is kept in its place. It contains all the information regarding the name card as to why is it taken out, who has taken it out and when is it taken out?
Question 3.
What is visible indexing?
Answer:
In visible indexing, cards are arranged in such a manner (UPBoardSolutions.com) that at a time many cards can be seen visible indexing occupies very little space. It can be fitted on the corner of a desk or on a wall.
Question 4.
Name various methods of indexing.
Answer:
Following methods of indexing are adopted by different business houses:
- Letter Book or Simple Index
- Vowel Index
- Card Index
- Visible Index.
Question 5.
Give any two advantages of card indexing.
Answer:
Advantages of card indexing are as follows:
1. Cleanliness: In card indexing, the index remains very clean because in this system there is no need to cut the names of those customers with whom the concern has stopped dealing. In this situation, in card indexing, the new card is kept at the appropriate place and the old card is taken out.
2. Time-Saving: This system saves a lot of time. The necessary card is taken immediately with the help of guide cards.

Question 6.
Point out four advantages of card indexing. (UP 2019)
Answer:
- Cleanliness
- Time-saving
- Easy in operation
- Elasticity.
Indexing Short Answer Type Questions (4 Marks)
Question 1.
What is Index? Describe its two importances. (UP 2012)
Answer:
Index: The object of filing is to preserve letters and documents in such a manner that they can be found out quickly, whenever they are required for future references. This object of filing can only be made possible (UPBoardSolutions.com) if letters are filed serially according to some particular method. Therefore, a technique is required which can indicate the exact location of a particular letter which is required for the reference and filed in a file. This particular technique is called index.
Importance of Index:
- In the absence of an index, it would not be possible to find out the name of the customers who have not placed any order since long.
- The employees cannot be held responsible for any delay and inefficiency. It will take a lot of time in finding out the references which will result in delays.

Question 2.
What is a simple indexing? What are the points to be kept in mind in simple indexing?
Answer:
Simple Indexing: For simple indexing, a special type of book which contains thick letters in it is used. In this book, each sheet bears a letter of the alphabet on the right-hand side. Edges of the sheet are cut so that all the letters of the alphabet are seen together. In this, generally, the last page is allotted X, Y and Z, because the names beginning with these letters are generally very small in number.
Following points to be kept in mind in simple indexing:
- While writing the names in the book only first name should be considered. The words showing respect should be avoided. For example, name of ‘Thakur Pratap Singh’ should be written in ‘P’, not in T.
- Some business houses adopt the technique of writing names on the basis of surnames. They do not write the full name of the customers, but instead of that, they use initials. For example, the name of Shri S. K. Bhatia is written on the page bearing ‘B’.
Indexing Long Answer Type Questions (8 Marks)
Question 1.
What is Card Indexing? Describe its merits and demerits. (UP 2009, 13, 14)
Or
What is the index? What are the advantages of indexing? Describe briefly. (UP 2011)
Or
What is the index? Describe its two importances. (UP 2012)
Answer:
Card Indexing. Card indexing is the latest system in the field of maintaining the index. The system is given the name of “card indexing” for the fact that in it index is made on the card. Card indexing is mainly used in (UPBoardSolutions.com) connection with vertical filing.
The name card which is used in this indexing is made of thick paper which bears the name and address of the correspondent. These name cards are kept in an almirah having many drawers.
This system of card indexing also uses guide cards or index cards which are made of thick paper. These cards are used for the purpose of dividing the drawer into several compartments according to the vowel.
Merits of Card Indexing. Card indexing has several advantages of great value which increase its importance in a business house which are as follows :
1. Cleanliness: In card indexing, the index remains very clean because, in this system, there is no need to cut the names of those customers with whom the concern has stopped dealing. In this situation, in card indexing, the new card is kept at the appropriate place and the old card is taken out.
2. Easy in Operation: In this system, new cards are kept easily without disturbing the others. Whenever a new correspondent appears, his card can easily be inserted in the drawer without disturbing the present order.
3. Time-Saving: This system saves a lot of time. The necessary card is taken out immediately with the help of guide cards.
4. Easy in Finding Cards: The cards can be found out easily and quickly with the use of index or guide cards.
5. Only Current Cards Remain: If the correspondence with any customer is stopped, his card can easily be removed. Thus, only current cards are allowed to remain.
6. Economical and Cheap: This system is quite economical. In a big business house, this indexing is cheaper than ordinary indexing, since the expenses of having a bound book and its occasional renewal with additions to existing correspondents are saved or avoided.

Demerits of Card Indexing: The card indexing also suffers from certain disadvantages. These are as follows:
1. Occupies More Space: This system can be used by big business houses only because it requires more space than simple indexing.
2. Only One Card can be Seen at a Time: In this system, only one card can be seen at a time because each card is in front of another card. Several cards are to be handled for finding out a particular card. For this reason, (UPBoardSolutions.com) this method is known as ‘blind method’.
3. Difficulty in Finding Out Misplaced Cards: If any card is misplaced, it becomes difficult to locate it under this system.
4. Useful for Big Organization Only: The equipment of card indexing are costly, hence, it can only be used by big organizations.
5. Fear of being Lost or Altered: In this system, there is always a fear of the cards being lost or altered.
Question 2.
Describe Card Indexing and explain its utility. (UP 2009)
Answer:
Card Indexing: Card indexing is the latest system in the field of maintaining the index. The system is given the name of “card indexing” for the fact that in it index is made on the card.
This system of card indexing also uses guide cards or index cards which are made of thick paper. These cards are used for the purpose of dividing the drawer into several compartments according to the vowel.
The utility of Card Indexing. The utility of card indexing is as follows:
1. Keeping Files Vertically: Card indexing is particularly used for keeping the files vertically.
2. Address of the Customer: The address of the customer can be written along with the name on the card. This saves the cost of keeping an address book separately.
3. Page Number of the Customer’s Accounts: Sometimes reference of the ledger folio is mentioned in the card. If this is done, there remains no need for providing an index in the account books.
4. Customer’s Economic Condition: All the necessary information regarding the customer’s economic condition can also be written on the card.
5. Name of Customer’s Bank: Name of Customer’s bank can also be written on a card.
6. Pieces of information Regarding Instalments: Nowadays, generally costly goods are sold on instalments. In such cases, the details of the instalments can be written on name cards.

7. Helpful in Follow up System: Sometimes customers maintain silence after making enquiries of the goods and do not place orders. In this case, several letters are sent in order to secure orders. This is called a (UPBoardSolutions.com) Follow-up System of Correspondence. If this system is adopted, the card indexing is of great help. On receiving an enquiry from the customer, its reference may be written on his name card. The reference of the letters sent in reply can also be given on his name card.
8. Customer’s Business: On the name cards, nature of the business of the respective customers may be written, This helps in sending and securing goods from the customers. The important terms and conditions of business can also be written on name cards.
9. Preservation of Price-List etc: Price-lists and other information received from the customers can also be preserved on the name cards.
10. Informations Regarding Credit: When goods are sold on credit then it is convenient to maintain the reference regarding the period and maximum amount of credit allowed to the customers on the name card.

![]()
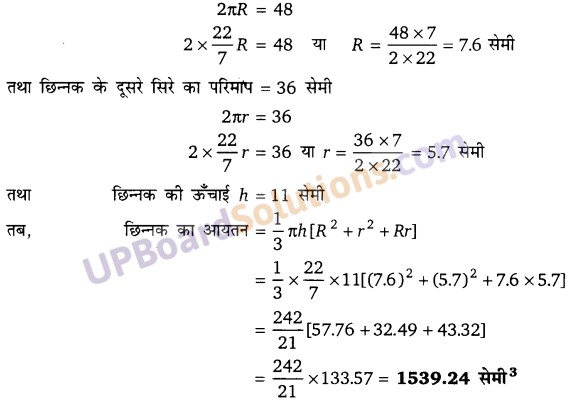
![]()

![]()


![]()