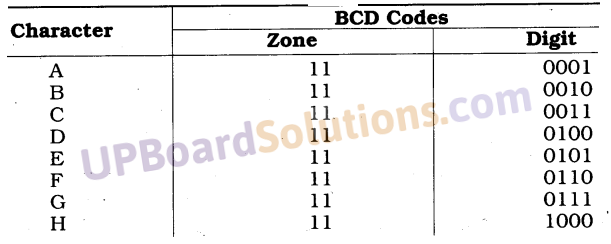
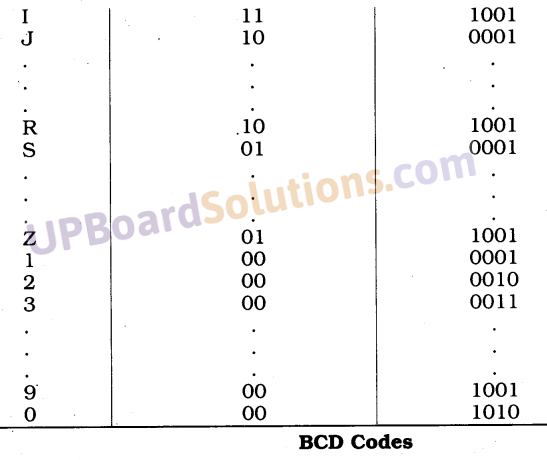
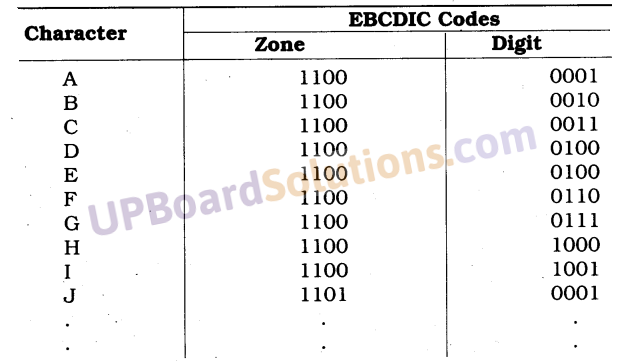
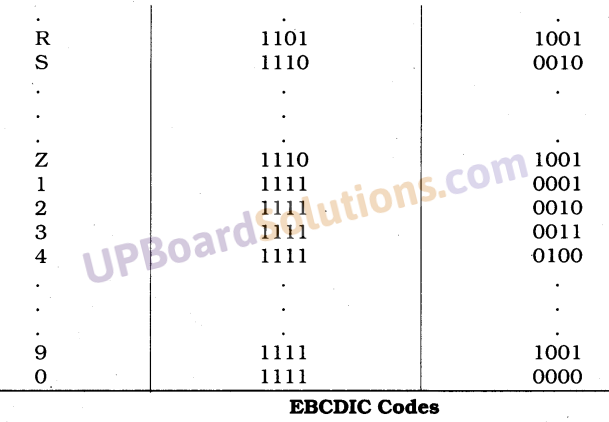
UP Board Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes (जैव-प्रक्रम)
These Solutions are part of UP Board Solutions for Class 10 Science. Here we have given UP Board Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes.
पाठगत हल प्रश्न
[NCERT IN-TEXT QUESTIONS SOLVED]
खंड 6.1 ( पृष्ठ संख्या 105)
प्रश्न 1.
हमारे जैसे बहुकोशिकीय जीवों में ऑक्सीजन की आवश्यकता पूरी करने में विसरण क्यों अपर्याप्त है?
उत्तर
हम जानते हैं कि बहुकोशिकीय जीवों में सभी कोशिकाएँ अपने आसपास के पर्यावरण के सीधे संपर्क में नहीं रह सकती हैं। अतः साधारण विसरण द्वारा सभी कोशिकाओं और ऊतकों तक ऑक्सीजन की पूर्ति नहीं हो पाती है, क्योंकि यह अत्यंत (UPBoardSolutions.com) धीमी प्रक्रिया है। इसलिए वहन तंत्र द्वारा शरीर के विभिन्न अंगों तक ऑक्सीजन पहुँचाई जाती है।
प्रश्न 2.
कोई वस्तु सजीव है, इसका निर्धारण करने के लिए हम किस मापदंड का उपयोग करेंगे?
उत्तर
कोई वस्तु सजीव है इसका निर्धारण हम निम्न मापदंडों द्वारा कर सकते हैं|
- गति
- वृद्धि
- श्वसन
- उत्तेजनशीलता
- पोषण इत्यादि।
![]()
प्रश्न 3.
किसी जीव द्वारा किन कच्ची सामग्रियों का उपयोग किया जाता है?
उत्तर
किसी जीव द्वारा निम्न कच्ची सामग्रियों के उपयोग किए जाते हैं
- खाद्य पदार्थ (कार्बन आधारित)-यह जीवों के लिए ऊर्जा प्राप्त करने के लिए।
- ऑक्सीजन श्वसन तथा ATP के रूप में ऊर्जा प्राप्त करने के लिए।
- जल-भोजन के पाचन तथा शरीर के (UPBoardSolutions.com) अंदर अन्य कार्यों के लिए।
- कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड [CO,]-पौधों में प्रकाश संश्लेषण का एक आवश्यक घटक।।
प्रश्न 4.
जीवन के अनुरक्षण के लिए आप किन-किन प्रक्रमों को आवश्यक मानेंगे?
उत्तर
जीवन के अनुरक्षण के लिए सभी जैव क्रियाएँ आवश्यक होती हैं; जैसे-पोषण, श्वसन, परिवहन, उत्सर्जन, वृद्धि आदि।
खंड 6.2 ( पृष्ठ संख्या 111)
प्रश्न 1.
स्वयंपोषी पोषण तथा विषमपोषी पोषण में क्या अंतर है?
उत्तर

प्रश्न 2.
प्रकाश संश्लेषण के लिए आवश्यक कच्ची सामग्री पौधे कहाँ से प्राप्त करते हैं?
उत्तर
प्रकाश संश्लेषण के लिए आवश्यक कच्ची सामग्री तथा उनके स्रोत निम्न हैं:
- जल-पौधों की जड़े भूमि से जल प्राप्त करती हैं।
- कार्बन-डाइऑक्साइड (CO)-पौधे इसे वायुमंडल से रंध्रों (Stomata) द्वारा प्राप्त करते हैं।
- क्लोरोफिले-हरे पत्तों में क्लोरोप्लास्ट (UPBoardSolutions.com) होता है, जिसमें क्लोरोफिल मौजूद होते हैं।
- सूर्य का प्रकाश-सूर्य से प्राप्त करते हैं।
![]()
प्रश्न 3.
हमारे आमाशय में अम्ल की भूमिका क्या है?
उत्तर
हमारे आमाशय में अम्ल की निम्नलिखित भूमिका है
- आमाशय में HCl अम्ल की भूमिका आमाशय रस को अम्लीय बनाना है, क्योंकि एन्जाइम पेप्सिन केवल अम्लीय माध्यम में ही प्रभावशाली ढंग से प्रोटीनों का पाचन कर सकता है।
- अम्ल का एक अन्य कार्य यह भी है कि ये भोजन में मौजूद हानिकारक जीवाणुओं को मार देते हैं।
- यह अधपचे भोजन का किण्वन नहीं होने देता है।
प्रश्न 4.
पाचक एंजाइमों का क्या कार्य है?
उत्तर
पाचक एंजाइम अघुलनशील जटिल कार्बनिक अणुओं को सरल घुलनशील अणुओं में परिवर्तित कर देते हैं, ताकि क्षुद्रांत की भित्ति द्वारा सरलतापूर्वक अवशोषित कर लिए जाएँ।
प्रश्न 5.
पचे हुए भोजन को अवशोषित करने के लिए क्षुद्रांत्र को कैसे अभिकल्पित किया गया है?
उत्तर
क्षुद्रांत्र के आंतरिक आस्तर पर अनेक अँगुली जैसे प्रवर्ध होते हैं, जिन्हें दीर्घरोम कहते हैं, ये अवशोषण का सतही क्षेत्रफल बढ़ा देते हैं। दीर्घरोम में रुधिर वाहिकाओं की बहुतायत होती है, जो भोजन को अवशोषित करके शरीर की प्रत्येक (UPBoardSolutions.com) कोशिका तक पहुँचाती हैं।
![]()
खंड 6.3 (पृष्ठ संख्या 116)
प्रश्न 1.
श्वसन के लिए ऑक्सीजन प्राप्त करने की दिशा में एक जलीय जीव की अपेक्षा स्थलीय जीव किस प्रकार लाभप्रद है?
उत्तर
- जलीय जीव जल में विलेय ऑक्सीजन का उपयोग करते हैं। क्योंकि जल में विलेय ऑक्सीजन की मात्रा वायु में ऑक्सजीन की मात्रा की तुलना में बहुत कम है, इसलिए जलीय जीवों की श्वास दर स्थलीय जीवों की अपेक्षा द्रुत गति से होती है।
- स्थलीय जीवों में ऑक्सीजन भिन्न-भिन्न अंगों द्वारा अवशोषित की जाती है। इन सभी अंगों में एक रचना होती है, जो उस सतही क्षेत्रफल को बढ़ाती है जो ऑक्सीजन बाहुल्य वायुमंडल के संपर्क में रहता है।
प्रश्न 2.
ग्लूकोज़ के ऑक्सीकरण से भिन्न जीवों में ऊर्जा प्राप्त करने के विभिन्न पर्थ क्या हैं?
उत्तर
ग्लूकोज के ऑक्सीकरण से भिन्न जीवों में ऊर्जा प्राप्त करने के विभिन्न पथ इस प्रकार हैं:

![]()
प्रश्न 3.
मनुष्यों में ऑक्सीजन तथा कार्बन-डाइऑक्साइड का परिवहन कैसे होता है?
उत्तर
ऑक्सीजन का परिवहन-मानव शरीर के फुफ्फुस कूपिकाओं की रुधिर वाहिकाओं में RBC होते हैं, जिसमें मौजूद हीमोग्लोबिन ऑक्सीजन से संयुक्त होकर ऑक्सीहीमोग्लोबिन बनाता है तथा सभी ऊतकों एवं अंगों तक पहुँच जाता है। कार्बन-डाइऑक्साइड (co2) का परिवहन-ऑक्सीजन की अपेक्षा CO2 जल में अधिक विलेय है, इसलिए ऊतकों से फुफ्फुस तक परिवहन हमारे रुधिर (प्लाज्मा) में विलेय अवस्था में होता है।
प्रश्न 4.
गैसों के विनिमय के लिए मानव-फुफ्फुस में अधिकतम क्षेत्रफल को कैसे अभिकल्पित किया है?
उत्तर
फुफ्फुस के अंदर मार्ग छोटी और छोटी नलिकाओं में विभाजित हो जाता है, जो अंत में गुब्बारे जैसी रचना में अंतकृत हो जाता है, जिसे कूपिका कहते हैं। कूपिका एक सतह उपलब्ध कराती है। जिसमें गैसों का विनिमय हो सकता है। यदि (UPBoardSolutions.com) कूपिकाओं की सतह को फैला दिया जाए तो यह लगभग 80 से 100 वर्ग मीटर क्षेत्र ढक लेगी। इस तरह हमारे फुफ्फुस गैसों के विनिमय के लिए अधिकतम क्षेत्रफल बनाती है।
![]()
खंड 6.4 ( पृष्ठ संख्या 122)
प्रश्न 1.
मानव में वहन तंत्र के घटक कौन से हैं? इन घटकों के क्या कार्य हैं?
उत्तर
मानव में वहन तंत्र के घटक हैं-हृदय, रुधिर वाहिकाएँ और रुधिर। उनके कार्य इस प्रकार हैं :
1. हृदय (Heart)–यह एक पंप की तरह कार्य करता है।
2. रुधिर वाहिकाएँ (Blood Vessels):
- धमनियाँ (Arteries)-हृदय से शरीर के सभी अंगों तक ऑक्सीजन युक्त रक्त (Oxygenated blood) | ले जाती हैं।
- शिराएँ (Veins)-विभिन्न अंगों से हृदय तक वापस डीऑक्सीजनेटेड (De-Oxygenated) रक्त शुद्धिकरण के लिए लाती हैं।
- कोशिकाएँ (capillaries)-धमनी छोटी-छोटी वाहिकाओं में विभाजित हो जाती है, जिसे कोशिकाएँ कहते हैं। रुधिर एवं आसपास की कोशिकाओं के मध्य पदार्थों का विनिमय होता है।
3. रुधिर या रक्त (Blood)-यह परिवहन का माध्यम है जो निम्नलिखित से बने हैं:
- प्लाज्मा (Plasma)-भोजन के अणुओं, CO2नाइट्रोजनी वर्त्य (nitrogenous wastes), लवण, हार्मोन, प्रोटीन आदि का विलीन रूप में वहन करता है।
- RBC-इसमें हीमोग्लोबीन होता है, जो ऑक्सीजन को ले जाती है।
- WBC-संक्रमण से लड़ने में सहायता करता है। यह शरीर में आए रोगाणुओं को मारकर शरीर को स्वस्थ बनाए रखता है।
- प्लेटलेट्स (Plateletes)-रक्तस्राव के स्थान पर रुधिर का थक्का बनाकर मार्ग अवरुद्ध कर देती है।
प्रश्न 2.
स्तनधारी तथा पक्षियों में ऑक्सीजनित तथा विऑक्सीजनित रुधिर को अलग करना क्यों आवश्यक है?
उत्तर
हृदय का दायाँ व बायाँ बँटवारा ऑक्सीजनित तथा विऑक्सीजनित रुधिर को मिलने से रोकता है तथा शरीर को उच्च दक्षतापूर्ण ऑक्सीजन की पूर्ति करता है, क्योंकि पक्षी और स्तनधारी जंतुओं को अपने शरीर का तापक्रम बनाए रखने के (UPBoardSolutions.com) लिए निरंतर उच्च ऊर्जा की आवश्यकता होती है, जिसके लिए यह बहुत लाभदायक होता है।
![]()
प्रश्न 3.
उच्च संगठित पादप में वहन तंत्र के घटक क्या हैं?
उत्तर
उच्च संगठित पादप में निम्नलिखित वहन तंत्र होते हैं :
- जाइलम ऊतक (Xylem tissue)-जाइलम ऊतक पादप के जड़ से खनिज लवण तथा जल इसके सभी अंगों तक पहुँचाता है। जाइलम ऊतक में जड़ों, तनों और पत्तियों की वाहिनिकाएँ तथा वाहिकाएँ आपस में जुड़कर जल संवहन वाहिकाओं का एक जाल बनाती हैं, जो पादप के सभी भागों से संबद्ध होता है।
- फ्लोएम ऊतक (Phloem tissue)-भोजन तथा अन्य पदार्थों का संवहन (Translocation) पत्तियों से अन्य सभी अंगों तक फ्लोएम ऊतक द्वारा होता है।
प्रश्न 4.
पादप में जल और खनिज लवण का वहन कैसे होता है?
उत्तर
पापों में जल और खनिज लवण का वहन जाइलम ऊतक द्वारा होता है।
जड़ों की कोशिकाएँ मृदा के संपर्क में हैं तथा वे सक्रिय रूप से आयन प्राप्त करती हैं। यह जड़ और मृदा के मध्य आयन सांद्रण में एक अंतर उत्पन्न करता है। इस अंतर को समाप्त करने के लिए जल अनवरत गति से जड़ के जाइलम में जाता है और जल के स्तंभ का निर्माण करता है, जो लगातार ऊपर की ओर धकेला जाता है। यह दाब जल को ऊँचाई तक पहुँचाने में पर्याप्त नहीं होता है। पत्तियों के द्वारा वाष्पोत्सर्जन क्रिया द्वारा (UPBoardSolutions.com) रंध्र से जल की हानि होती है, जो एक चूषण उत्पन्न करता है, जो जल को जड़ों में उपस्थित जाइलम कोशिकाओं द्वारा खींचता है। अतः वाष्पोत्सर्जन कर्षण जल की गति के लिए एक मुख्य प्रेरक बल होता है।
![]()
प्रश्न 5.
पादप में भोजन का स्थानांतरण कैसे होता है?
उत्तर
पादप में भोजन का स्थानांतरण फ्लोएम ऊतक द्वारा होता है। प्रकाश संश्लेषण के उत्पादों के अलावा फ्लोएम अमीनो अम्ल तथा अन्य पदार्थों का परिवहन भी करता है। ये पदार्थ विशेष रूप से जड़ के भंडारण अंगों, फलों, बीजों तथा वृद्धि वाले अंगों में ले जाए जाते हैं। भोजन तथा अन्य पदार्थों का स्थानांतरण संलग्न साथी कोशिका की सहायता से चालनी नलिका में उपरिमुखी तथा अधोमुखी दोनों दिशाओं में होता है। सुक्रोज सरीखे पदार्थ फ्लोएम ऊतक में ए०टी०पी० से प्राप्त ऊर्जा से ही स्थानांतरित होते हैं।
खंड 6.5 ( पृष्ठ संख्या 124)
प्रश्न 1.
वृक्काणु (नेफ्रॉन) की रचना तथा क्रियाविधि का वर्णन कीजिए।
उत्तर
संरचना (Structure)-मानव शरीर में दो वृक्क होते हैं। प्रत्येक वृक्क नेफ्रॉन की अनेक इकाइयों से बना होता है। वृक्काणु (नेफॉन) वृक्क की क्रियात्मक इकाई होती है। नेफॉन में कप के आकार का बोमन संपुट (Bowman’s Capsule) होता है, जिसमें कोशिका गुच्छ (Glomerulus) होते हैं। यह रुधिर कोशिकाओं का एक गुच्छ होता है जो एफेरेन्ट कोशिकाओं द्वारा बने होते हैं। एफेरेन्ट धमनियाँ अशुद्ध रक्त नेफ्रॉन तक लाते हैं। कप के आकार का बोमन संपुट वृक्काणु के निलिकाकार भाग (Tubular part of rephron) का निर्माण करती है। जो संग्राहक वाहिनी (collecting duct) से जुड़ा होता है।
क्रियाविधि (Working)–वृक्क धमनी (Renal artery) ऑक्सीजनित रुधिर लाती है, जिसमें नाइट्रोजनी वर्त्य होते हैं। मूत्र बोमन संपुट में स्थित कोशिका गुच्छ (ग्लामेरूलस) में फिल्टर होकर कुंडली के आकार में नेफ्रॉन के नलिकाकार भाग में पहुँचता है। मूत्र में कुछ उपयोगी पदार्थ; जैसे-ग्लूकोज, अमीनों अम्ल, लवण तथा जले रह जाते हैं जो पुनः इस नलिकाकार भाग में अवशोषित कर लिए जाते हैं। इसके बाद मूत्र (UPBoardSolutions.com) संग्राहक वाहिनी में एकत्र हो जाती है तथा मूत्रवाहिनी; में प्रवेश करता है जहाँ से मूत्राशय में चली जाती है। अतः प्रत्येक वृक्क में बनने वाला मूत्र एक लंबी नलिका, मूत्रवाहिनी में प्रवेश करता है, जो वृक्क को मूत्राशय से जोड़ती है।
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
उत्सर्जी उत्पाद से छुटकारा पाने के लिए पादप किन विधियों का उपयोग करते हैं?
उत्तर
उत्सर्जी उत्पाद से छुटकारा पाने के लिए पादप निम्न विधियों को उपयोग करते हैं
- प्रकाश संश्लेषण में O2 उत्पाद के रूप में तथा CO2 श्वसन क्रिया में रंध्रों द्वारा निष्कासित किए जाते हैं।
- पौधे अतिरिक्त जल से वाष्पोत्सर्जन क्रिया द्वारा छुटकारा पा सकते हैं।
- पौधों में निष्क्रिय पत्तियाँ समय-समय पर अलग होती रहती हैं, जिनमें अपशिष्ट उत्पाद संचित रहते हैं।
- पादपों में अन्य अपशिष्ट उत्पाद रेजिन तथा गोंद के रूप में विशेष रूप से पुराने जाइलम में संचित रहते हैं।
- पादप कुछ अपशिष्ट पदार्थों को अपने आसपास की मृदा में उत्सर्जित करते हैं।
- बहुत से पादप अपशिष्ट उत्पाद कोशकीय रिक्तिका में संचित रहते हैं।
प्रश्न 3.
मूत्र’ बनने की मात्रा का नियमन किस प्रकार होता है?
उत्तर
- जल की मात्रा पुनरवशोषण (Reabsorption) शरीर में उपलब्ध अतिरिक्त जल की मात्रा पर तथा कितना जल की मात्रा पर तथा कितना विलेय वयं उत्सर्जित करना है, पर निर्भर करती है।
- जैसे गर्मी के दिनों में शरीर से अत्यधिक पसीने के द्वारा जल एवं लवण निष्कासित होते हैं। इसलिए वृक्क के द्वारा छने (filterate) हुए मूत्र में विद्यमान जल एवं लवण की अधिकांश मात्रा पुनः अवशोषित कर ली जाती है। अतः मूत्र (UPBoardSolutions.com) कम मात्रा में उत्सर्जित होते हैं इसके विपरीत सर्दियों में कम पसीना आता है, इसलिए मूत्र अधिक बनता है। जल एवं लवण पुनरवशोषण हार्मोन के द्वारा नियंत्रित होते हैं।
- अत: मूत्र निर्माण पर नियंत्रण रक्त के ऑसमोटिक (osmotic) संतुलन को भी बनाए रखता है।
पाठ्यपुस्तक से हल प्रश्न
[NCERT TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS SOLVED]
प्रश्न 1.
मनुष्य में वृक्क एक तंत्र का भाग है, जो संबंधित है
(a) पोषण
(b) श्वसन
(C) उत्सर्जन
(d) परिवहन
उत्तर
(c) उत्सर्जन।।
प्रश्न 2.
पादप में जाइलम उत्तरदायी है
(a) जल का वहन
(b) भोजन का वहन
(C) अमीनो अम्ल का वहन
(d) ऑक्सीजन का वहन
उत्तर
(a) जल का वहन।।
![]()
प्रश्न 3.
स्वपोषी पोषण के लिए आवश्यक है
(a) कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड तथा जल
(b) क्लोरोफिल
(C) सूर्य का प्रकाश
(d) उपरोक्त सभी
उत्तर
(d) उपरोक्त सभी
प्रश्न 4.
पायरुवेट के विखण्डन से यह कार्बन-डाइऑक्साइड, जल तथा ऊर्जा देता है और यह क्रिया होती है
(a) कोशिका द्रव्य
(b) माइटोकॉन्ड्रिया
(C) हरित लवक
(d) केन्द्रक
उत्तर
(b) माइटोकॉन्ड्रिया।
प्रश्न 5.
हमारे शरीर में वसा का पाचन कैसे होता है? यह प्रक्रम कहाँ होता है?
उत्तर
- वसा का पाचन छोटी आँत में होता है।
- क्षुद्रांत में वसा बड़ी गोलिकाओं के रूप में होता है, जिससे उस पर एंजाइम का कार्य करना मुश्किल हो जाता है।
- लीवर द्वारा स्रावित पित्त लवण उन्हें छोटी (UPBoardSolutions.com) गोलिकाओं में खंडित कर देता है, जिससे एंजाइम की क्रियाशीलता बढ़ जाती है। यह इमल्सीकृत क्रिया कहलाती है।
- पित्त रस अम्लीय माध्यम को क्षारीय बनाता है, ताकि अग्न्याशय से स्रावित लाइपेज एंजाइम क्रियाशील हो सके।
- लाइपेज एंजाइम वसा को वसा अम्ल तथा ग्लिसरॉल में परिवर्तित कर देता है।
- पाचित वसा अंत में आंत्र की भित्रि अवशोषित कर लेती है।
![]()
प्रश्न 6.
भोजन के पाचन में लार की क्या भूमिका है?
उत्तर
भोजन के पाचन में लार की भूमिका निम्नलिखित है
- लार भोजन को गीला करता है जिससे निगलने में आसानी होती है।
- लार में एमिलेस (amylase) एंजाइम होता है, जो मंड (स्टार्च) के जटिल अणु को शर्करा में खंडित करता | है। (जटिल कार्बोहाइड्रेट को सरल कार्बोहाइड्रेड में बदलना)
- इसमें मौजूद लाइसोजाइम हानिकारक जीवाणुओं को नष्ट कर देता है।
प्रश्न 7.
स्वपोषी पोषण के लिए आवश्यक परिस्थितियाँ कौन-सी हैं और उसके उपोत्पाद क्या हैं?
उत्तर
हरे पौधे स्वपोषी कहलाते हैं, क्योंकि प्रकाश संश्लेषण क्रिया द्वारा वे अपना भोजन स्वयं बनाते हैं। प्रकाश संश्लेषण के लिए आवश्यक परिस्थितियाँ निम्नलिखित हैं
-
- क्लोरोफिल-पौधों के हरे भाग में क्लोरोफिल होते हैं, जो प्रकाश ऊर्जा को अवशोषित करता है।
- सूर्य का प्रकाश-सूर्य के (UPBoardSolutions.com) प्रकाश से
- कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड-वायुमंडल से
- जल-पौधे जड़ों द्वारा भूमि से प्रकाश संश्लेषण की क्रिया को निम्न रासायनिक समीकरण द्वारा बनाया जाता है।

अत: कार्बोहाइड्रेट (ग्लूकोज़), ऑक्सीजन तथा जल उपोत्पाद के रूप में प्राप्त होते हैं।
![]()
प्रश्न 8.
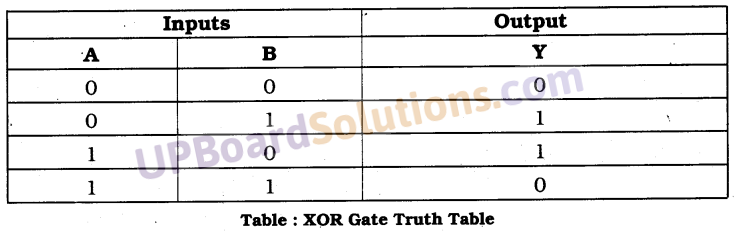
वायवीय श्वसन तथा अवायवीय श्वसन में क्या अंतर है? कुछ जीवों के नाम लिखिए जिनमें अवायवीय श्वसन होता है।
उत्तर

प्रश्न 9.
गैसों के अधिकतम विनिमय के लिए कूपिकाएँ किस प्रकार अभिकल्पित हैं?
उत्तर
कूपिका एक सतह उपलब्ध कराती है, जिससे गैसों का विनिमय हो सके। कूपिकाओं की भित्ति में रुधिर वाहिकाओं का विस्तीर्ण जाल होता है, जो वायु से ऑक्सीजन लेकर हमारे शरीर की सभी कोशिकाओं तक पहुँचाता है तथा रुधिर में विलेय Co2 को कूपिकाओं में छोड़ने के लिए लाता है ताकि CO2 हमारे शरीर से बाहर निकल जाए।
प्रश्न 10.
हमारे शरीर में हीमोग्लोबिन की कमी के क्या परिणाम हो सकते हैं?
उत्तर
हम जानते हैं कि मानव में श्वसन वर्णक हीमोग्लोबिन है, जो ऑक्सीजन के लिए उच्च बंधुता रखता है। इसकी कमी के कारण हमारे शरीर के विभिन्न अंगों में ऑक्सीजन की कमी हो जाएगी, जिससे ऊर्जा कम मात्रा में निर्मित होगी (UPBoardSolutions.com) और हम थकान का अनुभव करेंगे। हमारी श्वास गति भी बढ़ जाएगी। अतः हीमोग्लोबिन की कमी से एनीमिया
(anaeamia) होता है।
![]()
प्रश्न 11.
मनुष्य में दोहरा परिसंचरण की व्याख्या कीजिए। यह क्यों आवश्यक है?
उत्तर
मनुष्य के परिसंचरण तंत्र को दोहरा परिसंचरण इसलिए कहते हैं, क्योंकि प्रत्येक चक्र में रुधिर दो बार हृदय में जाती है। हृदय का दायाँ और बायाँ बँटवारा ऑक्सीजनित तथा विऑक्सीजनित रुधिर को मिलने से रोकता है। चूंकि हमारे । शरीर में उच्च ऊर्जा की आवश्यकता होती है, जिसके लिए उच्च दक्षतापूर्ण ऑक्सीजन जरूरी होता है। अतः शरीर का तापक्रम बनाए रखने तथा निरंतर ऊर्जा की पूर्ति के लिए यह (UPBoardSolutions.com) परिसंचरण लाभदायक होता है।
प्रश्न 12.
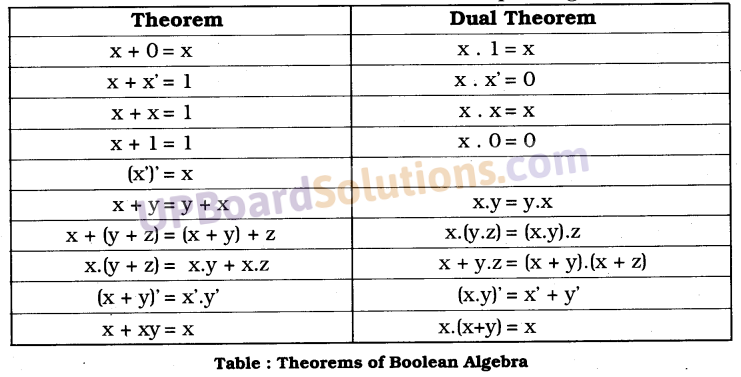
जाइलम तथा फ्लोएम में पदार्थों के वहन में क्या अंतर है?
उत्तर

![]()
प्रश्न 13.
फुफ्फुस में कूपिकाओं तथा वृक्क में वृक्काणु (नेफ्रॉन) की रचना तथा क्रियाविधि की तुलना कीजिए।
उत्तर

Hope given UP Board Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 are helpful to complete your homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. UP Board Solutions try to provide online tutoring for you.