Balaji Class 10 Maths Solutions Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations Ex 4.2 द्विघात समीकरण
निम्नलिखित समीकरणों को हल कीजिए
प्रश्न 1.
x4 – 8x2 – 9 = 0
हलः
दिया हुआ समीकरण
x4 – 8x2 – 9 = 0 …(1)
x2 = y समीकरण (1) में रखने पर
y2 – 8y – 9 = 0
⇒ y2 – 9y + y – 9 = 0
⇒ y(y – 9) + 1(y – 9) = 0
⇒ (y – 9)(y + 1) = 0
⇒ y = 9, – 1
अब y = 9 ⇒ x2 = 9
⇒ x = ±3
तथा y = – 1 = i2
⇒ x2 = i2
⇒ x = ±i
अतः समीकरण के (UPBoardSolutions.com) हल = (±3, ±i)
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
4x4 – 5x2 + 1 = 0
हलः
दिया गया समीकरण
4x4 – 5x2 + 1 = 0
4(x2)2 – 5x2 + 1 = 0 …(1)
x2 = y, समीकरण (1) में रखने पर
4y2 – 5y + 1 = 0
⇒ 4y2 – 4y – y + 1 = 0
⇒ 4y(y – 1) – 1(y – 1) = 0
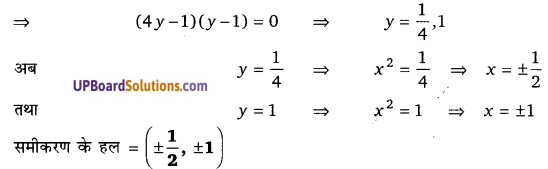
![]()
प्रश्न 3.
[latex]\left[\frac{\boldsymbol{x} – \boldsymbol{a}}{\boldsymbol{x} + \boldsymbol{a}}\right]^{2} – 5\left[\frac{\boldsymbol{x} – \boldsymbol{a}}{\boldsymbol{x} + \boldsymbol{a}}\right][/latex] + 6 = 0 (UPBoardSolutions.com)
हलः
दिया गया समीकरण
[latex]\left[\frac{\boldsymbol{x} – \boldsymbol{a}}{\boldsymbol{x} + \boldsymbol{a}}\right]^{2} – 5\left[\frac{\boldsymbol{x} – \boldsymbol{a}}{\boldsymbol{x} + \boldsymbol{a}}\right][/latex] + 6 = 0
समीकरण (1) में [latex]\frac{x – a}{x + a}[/latex] = y रखने पर
y2 – 5y + 6 = 0
⇒ y2 – 2y – 3y + 6 = 0
⇒ y(y – 2) – 3(y – 2) = 0
⇒ (y – 2) (y – 3) = 0
⇒ y = 2, 3
जब y = 2 ⇒ [latex]\frac{x – a}{x + a}[/latex] = 2
x – a = 2(x + a)
2x + 2a = x – a
2x – x = – a – 2a = – 3a
x = – 3a
जब y = 3 ⇒ [latex]\frac{x – a}{x + a}[/latex] = 3
x – a = 3(x + a)
3x + 3a = x – a
3x – x = – a – 3a
2x = – 4a
x = – 2a
अतः समीकरण के हल क्रमशः – 2a, – 3a हैं।
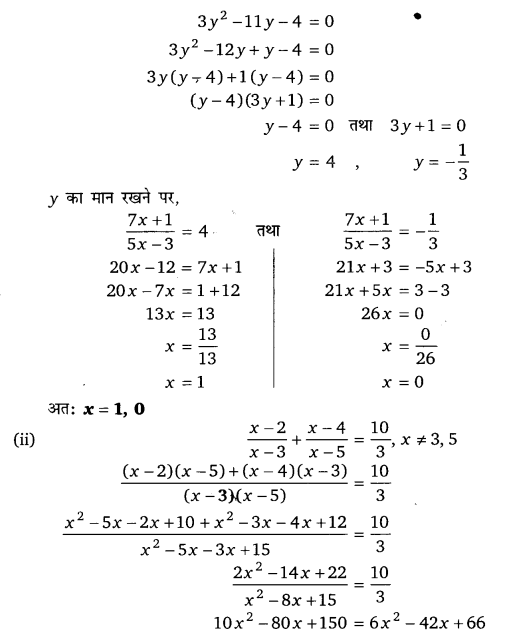
प्रश्न 4.
x – 2 – 12 = – x – 1
हलः
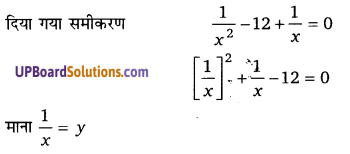
∴ दिया गया समीकरण y 2 + y – 12 = 0
y2 + 4y – 3y – 12 = 0
y(y + 4) – 3(y + 4) = 0
(y – 3)(y + 4) = 0
यदि y – 3 = 0, तब y = 3
और यदि y + 4 = 0, तब y = – 4
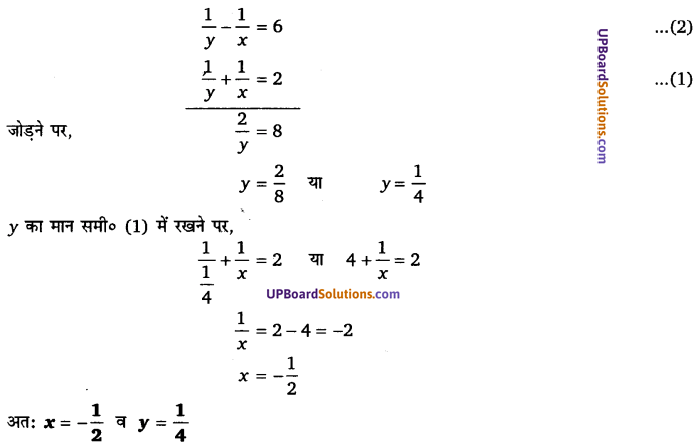
y = 3 लेने पर, [latex]\frac{1}{x}[/latex] = 3
x = [latex]\frac{1}{3}[/latex]
y = – 4 लेने पर, [latex]\frac{1}{x}[/latex] = – 4
x = [latex] – \frac{1}{4}[/latex]
![]()
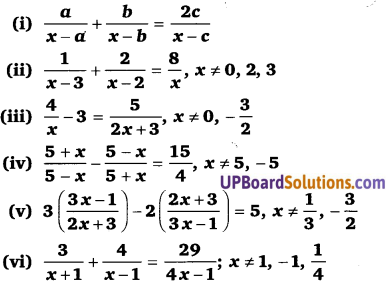
प्रश्न 5.
(x2 – 3x + 3)2 – (x – 1)(x – 2) = 7
हलः
दिया गया समीकरण (UPBoardSolutions.com)
(x2 – 3x + 3)2 – (x – 1)(x – 2) = 7
(x2 – 3x + 2 + 1)2 – (x2 – 3x + 2) – 7 = 0 …(1)
समीकरण (1) में x2 – 3x + 2 = y रखने पर
(y + 1)2 – y – 7 = 0
y2 + 1 + 2y – y – 7 = 0
y2 + y – 6 = 0
y2 + 3y – 2y – 6 = 0
y(y + 3) – 2(y + 3) = 0
(y – 2)(y + 3) = 0
y = 2, – 3
जब y = 2 ⇒ x2 – 3x + 2 = 2
x2 – 3x = 0
x(x – 3) = 0
x= 0, 3
जब y = – 3 ⇒ x2 – 3x + 2 = – 3
x2 – 3x + 2 + 3 = 0
x2 – 3x + 5 = 0
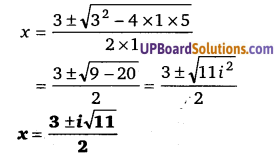
![]()
प्रश्न 6.
(x2 – 5x)2 – 30(x2 – 5x) – 216 = 0
हलः
दिया गया समीकरण
(x2 – 5x)2 – 30(x2 – 5x) – 216 = 0 …(1)
समीकरण (1) में x2 – 5x = y रखने पर
y2 – 30y – 216 = 0
y2 – 36y + 6y – 216 = 0
y(y – 36) + 6(y – 36) = 0
(y + 6)(y – 36) = 0
y = – 6, 36
जब y = – 6 ⇒ x2 – 5x = – 6
x2 – 5x + 6 = 0
x2 – 3x – 2x + 6 = 0
x(x – 3) – 2(x – 3) = 0
(x – 2)(x – 3) = 0
x = 2, 3
जब y = 36 ⇒ x2 – 5x = 36
x2 – 5x – 36 = 0
x2 – 9x + 4x – 36 = 0
x(x – 9) + 4(x – 9) = 0
(x + 4)(x – 9) = 0
x = – 4, 9
प्रश्न 7.
(x2 – 5x + 7)2 – (x – 2)(x – 3) = 1
हलः
दिया गया (UPBoardSolutions.com) समीकरण
(x2 – 5x + 7)2 – (x – 2)(x – 3) = 1
{(x2 – 5x + 6) + 1}2 – (x2 – 5x + 6) = 1 …(1)
समीकरण (1) में x2 – 5x + 6 = y रखने पर
(y + 1)2 – y = 1
y2 + 2y + 1 – y – 1 = 0
y2 + y = 0
y(y + 1) = 0
y = 0, – 1
जब y = 0 ⇒ x2 – 5x + 6 = 0
x2 – 2x – 3x + 6 = 0
x(x – 2) – 3(x – 2) = 0
x = 2, 3
जब y = – 1 ⇒ x2 – 5x + 6 = – 1
x2 – 5x + 7 = 0
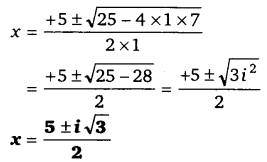
![]()
प्रश्न 8.
12x4 – 56x3 + 89x2 – 56x + 12 = 0
हलः
दिया गया समीकरण
12x4 – 56x3 + 89x2 – 56x + 12 = 0
दोनों पक्षों में x2 से भाग करने पर,
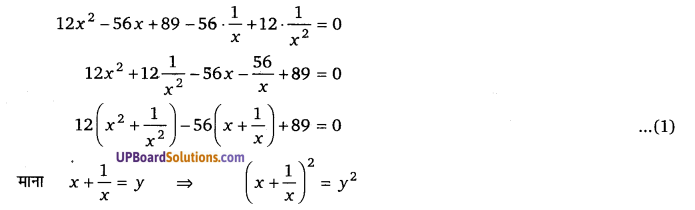
![]()
x2 + [latex]\frac{1}{x^{2}}[/latex] + 2 = y2
x2 + [latex]\frac{1}{x^{2}}[/latex] = y2 – 2
समीकरण (1) में x2 + (UPBoardSolutions.com) [latex]\frac{1}{x^{2}}[/latex] = y2 – 2 तथा x + [latex]\frac{1}{x}[/latex] = y
12(y2 – 2) – 56y + 89 = 0
12y2 – 24 – 56y + 89 = 0
12y2 – 56y + 65 = 0

2(x2 + 1) = 5x
2x2 – 5x + 2 = 0
2x2 – x – 4x + 2 = 0
x(2x – 1) – 2(2x – 1) = 0
(x – 2)(2x – 1) = 0

6(x2 + 1) = 13x
6x2 – 13x + 6 = 0
6x2 – 9x – 4x + (UPBoardSolutions.com) 6 = 0
3x(2x – 3) – 2(2x – 3) = 0
(3x – 2)(2x – 3) = 0
x = [latex]\frac{2}{3}, \frac{3}{2}[/latex]
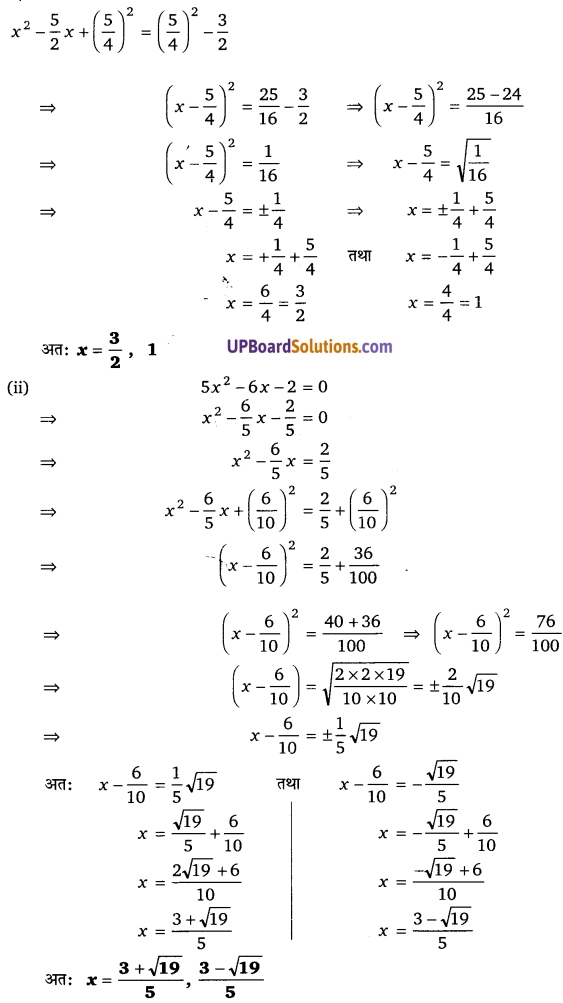
प्रश्न 9.

हलः

2(y2 + 1) = 5y
2y2 – 5y + 2 = 0
2y2 – 4y – y + (UPBoardSolutions.com) 2 = 0
2y(y – 2) – 1(y – 2) = 0
(y – 2)(2y – 1) = 0
जब y – 2 = 0 तब जब y = 2
जब 2y – 1 = 0 तब y = [latex]\frac{1}{2}[/latex]
y = 2 लेने पर, [latex]\frac{3 x+1}{x+1}[/latex] = 2
3x + 1 = 2(x + 1)
3x + 1 = 2x + 2
3x – 2x = 2 – 1
x = 1
y = [latex]\frac{1}{2}[/latex] लेने पर, [latex]\frac{3 x+1}{x+1}=\frac{1}{2}[/latex]
2(3x + 1) = x + 1
6x + 2 = x + 1
6x – x = 1 – 2
5x = -1
x = [latex]-\frac{1}{5}[/latex]
![]()
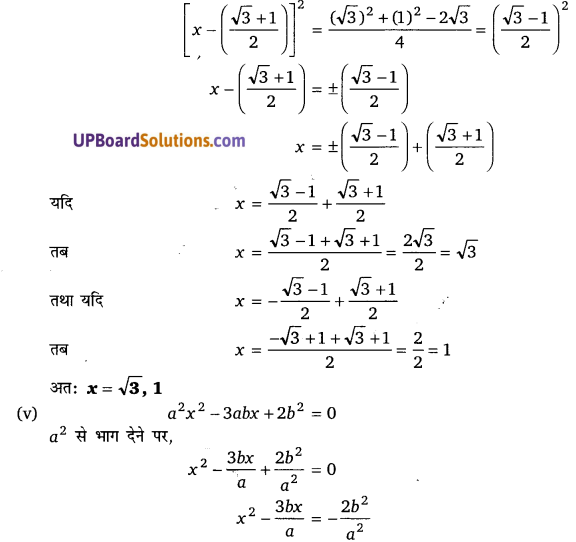
प्रश्न 10.
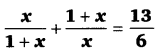
हलः
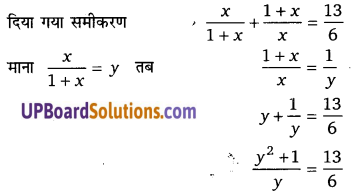
6(y2 + 1) = 13y
6y2 – 13y + 6 = 0
6y2 – 4y – 9y + 6 = 0
2y(3y – 2) – 3(3y – 2) (UPBoardSolutions.com) = 0
(2y – 3)(3y – 2) = 0
जब 2y – 3 = 0 तब y = [latex]\frac{3}{2}[/latex]
जब 3y – 2 = 0 तब y = [latex]\frac{2}{3}[/latex]
y = [latex]\frac{3}{2}[/latex] लेने पर, [latex]\frac{x}{1+x}=\frac{3}{2}[/latex]
3(1 + x) = 2x
3 + 3x = 2x
3x – 2x = -3
x = – 3
y = [latex]\frac{2}{3}[/latex] लेने पर, [latex]\frac{x}{1+x}=\frac{2}{3}[/latex]
3x = 2(1 + x)
3x = 2 + 2x
3x – 2x = 2
x = 2
![]()
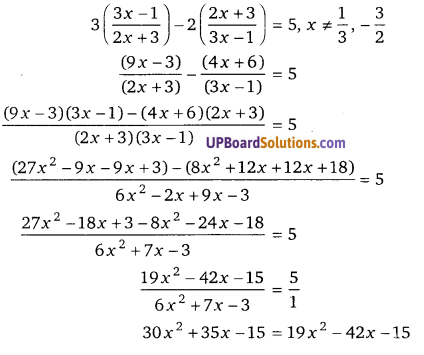
प्रश्न 11.
[latex]\frac{4 x-1}{4 x+1}+\frac{4 x+1}{4 x-1}=\frac{10}{3}[/latex]
हलः


3(y2 + 1) = 10y
3y2 – 10y + 3 = 0
3y2 – 9y – y + 3 = 0
3y(y – 3) – 1(y – 3) = 0
(y – 3)(3y – 1) = 0
जब y – 3 = 0, तब y = 3
जब 3y – 1 = 0, तब y = 1/3 (UPBoardSolutions.com)
y = 3 लेने पर, [latex]\frac{4 x-1}{4 x+1}=\frac{3}{1}[/latex]
3(4x + 1)= 4x – 1
12x + 3 = 4x – 1
12x – 4x = – 1 – 3
8x = – 4
x = [latex]-\frac{4}{8}=-\frac{1}{2}[/latex]
y = [latex]\frac{1}{3}[/latex] लेने पर, [latex]\frac{4 x-1}{4 x+1}=\frac{1}{3}[/latex]
⇒ 3(4x – 1) = 4x + 1
12x – 3 = 4x + 1
12x – 4x = 1 + 3
8x = 4
⇒ x = [latex]\frac{4}{8}=\frac{1}{2}[/latex]
अतः x = [latex]\pm \frac{1}{2}[/latex]
प्रश्न 12.
51+x + 51-x = 26
हलः
दिया गया समीकरण 5·5x + 5·5-x = 26
5(5x + 5-x) = 26
5x + 5-x = [latex]\frac{26}{5}[/latex]
माना 5x = y तब 5-x = [latex]\frac{1}{y}[/latex]
∴ दिया गया समीकरण y + [latex]\frac{1}{y}[/latex] = [latex]\frac{26}{5}[/latex]
[latex]\frac{y^{2}+1}{y}=\frac{26}{5}[/latex]
5(y2 + 1) = 26y
5y2 + 5 – 26y = 0
5y2 – 26y + 5 = 0
5y2 – 25y – y + 5 = 0
5y(y – 5) – 1(y – 5) = 0
(y – 5)(5y – 1) = 0
जब y – 5 = 0 तब y = 5
तथा जब 5y – 1 = 0 तब y = [latex]\frac{1}{5}[/latex]
y = 5 लेने पर, 5x = 5 = 51
x = 1
y = [latex]\frac{1}{5}[/latex] लेने पर, 5x = 5-1
x = -1
![]()
प्रश्न 13.
5x+1 + 52-x = 53 + 1
हलः
दिया गया समीकरण
5x+1 + 52-x = 53 + 1
5x ·5 + [latex]\frac{5^{2}}{5^{x}}[/latex] = 53 + 1
5·5x · 5x + 52 = 53 · 5x + 5x
माना 5x = y 5y · y + 52 = 125y + y
5y2 – 126y + 52 = 0 (UPBoardSolutions.com)
5y2 – 126y + 25 = 0
5y2 – 1y – 125y + 25 = 0
y(5y – 1) – 25(5y – 1) = 0
(y – 25)(5y – 1) = 0
y = 25 या y = [latex]\frac{1}{5}[/latex]
यदि y = 25, तब 5x = y = 25
5x = 52
तब x = 2 (घातों की तुलना करने पर)
तथा यदि y = [latex]\frac{1}{5}[/latex] = 5-1
तब 5x = y
5x = 5-1
x = – 1 (घातों की तुलना करने पर)
अतः x = – 1, 2
प्रश्न 14.
3x + 3-x – 2 = 0
हलः

y2 + 1 – 2y = 0
(y – 1)2 = 0
y = 1, 1
y = 1 लेने पर, 3x = 1
3x = 30
x = 0
प्रश्न 15.
22x+8 – 8·2x+2 + 1 = 0
हलः
दिया गया (UPBoardSolutions.com) समीकरण
22x+4-4 – 8·2x+2+1 = 0
22x+4 · 24 – 8·2x+2 + 1 = 0
16·22(x+2) – 8·2x+2 + 1 = 0
माना 2x+2 = y
∴ दिया गया समीकरण
16yx – 8y + 1 = 0
16yx – 4y – 4y + 1 = 0
4y(4y – 1) – 1(4y – 1) = 0
(4y – 1)(4y – 1) = 0

दोनों पक्षों में घातों की तुलना करने पर
x + 2 = – 2
x = – 2 – 2
x = – 4
![]()
प्रश्न 16.

हलः

y2 + 4 = 5y
y2 – 5y + 4 = 0
y2 – y – 4y + 4 = 0
y(y – 1) – 4(y – 1) = 0
(y – 1)(y – 4) = 0
जब y – 1 = 0 तब y = 1
जब y – 4 = 0 तब y = 4
y = 1 लेने पर, [latex]\sqrt{3 x^{2}+1}[/latex] = 1
3x2 + 1 = 1
3x2 = 0
x2 = 0 ⇒ x = 0, 0
y = 4 लेने पर, [latex]\sqrt{3 x^{2}+1}[/latex] = 4 ⇒ 3x2 + 1 = 16
3x2 = 16 – 1 = 15
⇒ 3x2 = 15
⇒ x2 = ±[latex] \sqrt{{5}} [/latex]
⇒ x = + 15
![]()
प्रश्न 17.
2x = 42x-1
हलः
दिया गया समीकरण (UPBoardSolutions.com) 22 = 42x-1
2x = [latex]\frac{4^{2 x}}{4}[/latex]
4·22 = 42x
4·2x = (22)2x
4·2x = (22x)2
4·2x = 22x22x = (2x)2(2x)2
माना 2x = y तब, 4y = yx·yx
4y = y4
(4y – y4) = 0
y(4 – y3) = 0
y = 0 या 4 – y3 = 0
4 = y3
∴ y3 = 4
y = 41/3 = (22)1/3
यदि y = 0 तब 2x = 0, x = 0 (अमान्य)
y = 41/3 तब 2x = 41/3
2x = 22/3
दोनों ओर घातों की तुलना करने पर
x = [latex]\frac{2}{3}[/latex]
प्रश्न 18.
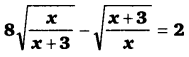
हलः
दिया गया समीकरण

8y2 – 1 = 2y
8y2 – 2y – 1 = 0
8y2 – 4y + 2y – 1 = 0
4y(2y – 1) + 1(2y – 1) = 0
(2y – 1)(4y + 1) = 0
जब 2y – 1 = 0 तब y = [latex]\frac{1}{2}[/latex]
जब 4y + 1 = 0 तब y = [latex]-\frac{1}{4}[/latex]

4x = x + 3
4x – x = 3
3x = 3
x = 1

16x = x + 3
16x – x = 3
15x = 3 ⇒ x = [latex]\frac{3}{15}=\frac{1}{5}[/latex]
परन x= [latex]\frac{1}{5}[/latex] समीकरण को सन्तुष्ट नहीं करती है अतः x = 1





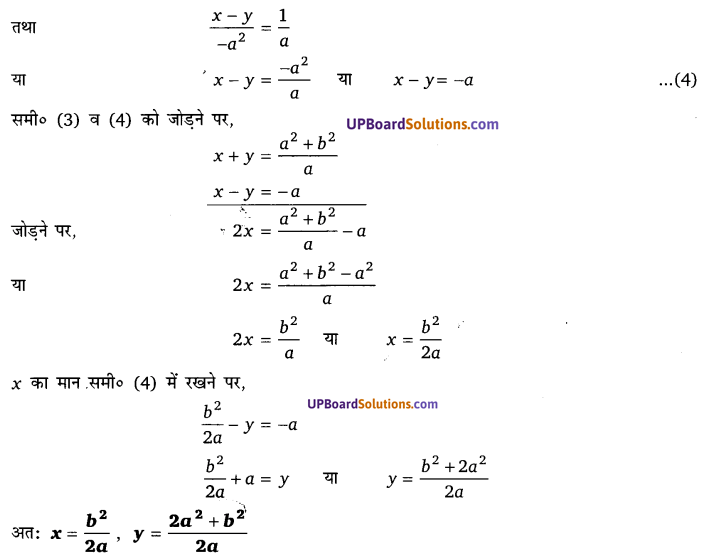

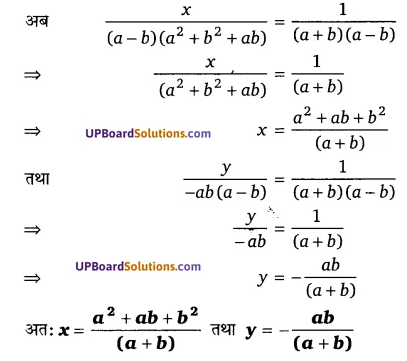

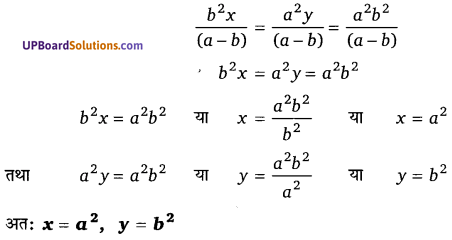

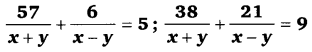
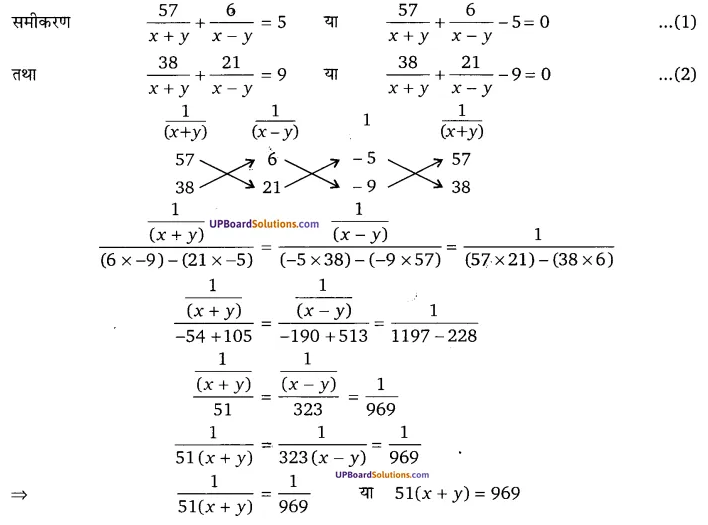





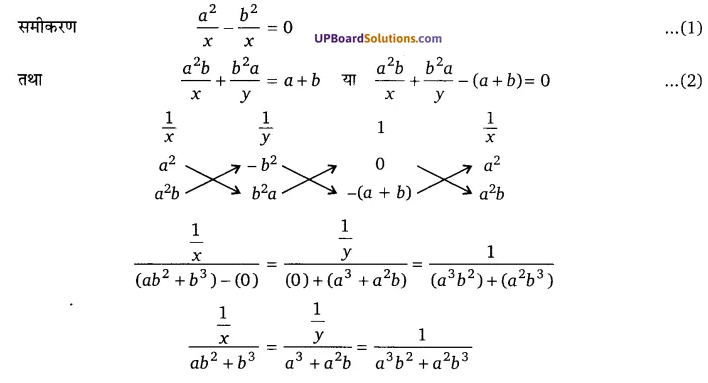

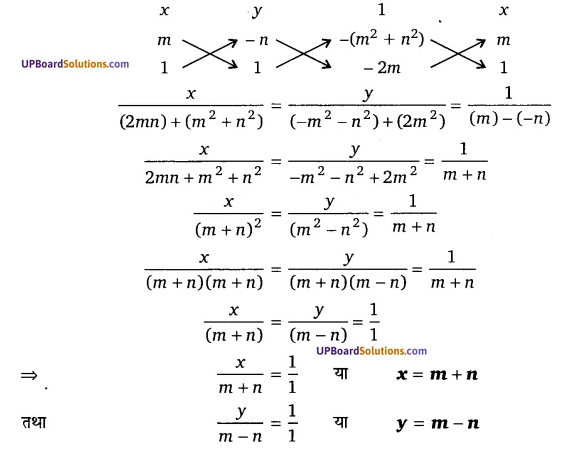


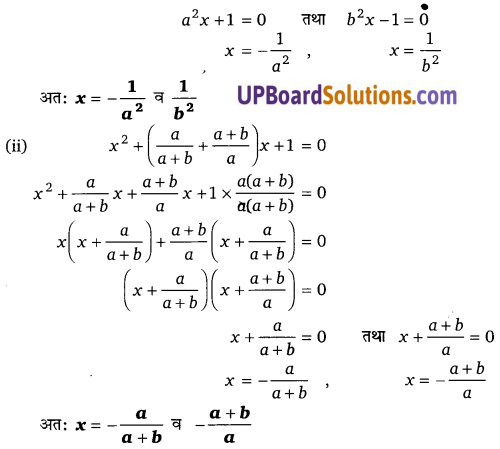




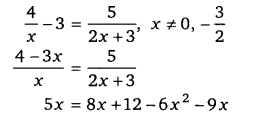


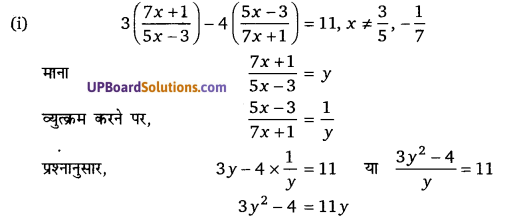






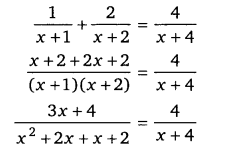



















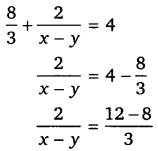


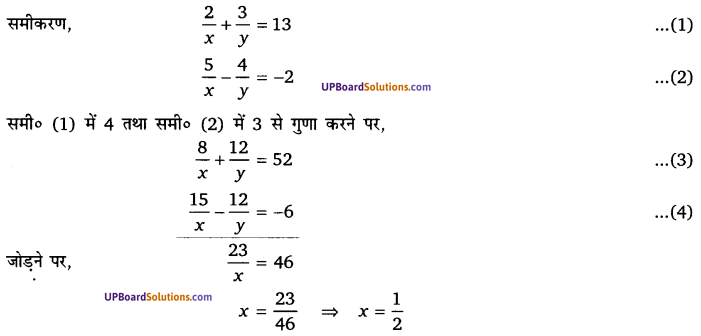
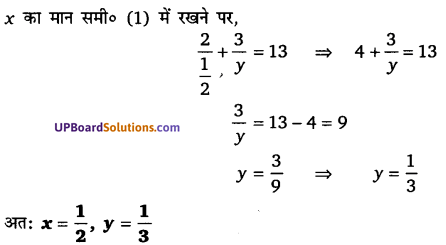


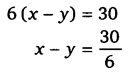







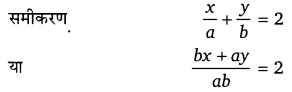


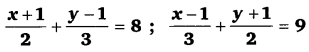



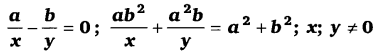
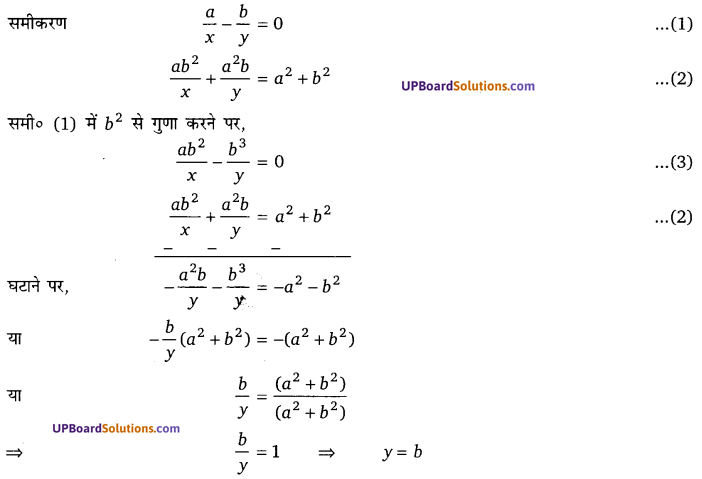






































 घण्टे
घण्टे








